Tags
Ample Reserves, CBO, Fed Balance Sheet, Federal Debt, Federal Funds Rate Target, Federal Reserve, FOMC, Inflation Target, Jackson Hole, Jerome Powell, Long and Variable Lags, Milton Friedman, Monetize Debt, Quantitative Tightening
The late, great Milton Friedman said monetary policy has “long and variable lags” in its effect on the economy. Easy money might not spark an inflation in goods prices for two years or more, though the typical lag is thought to be more like 15-20 months. Tight money seems to have similar lags in its effects. Debates surround the division and timing of these effects between inflation and real GDP, and too many remain convinced that a reliable tradeoff exists between inflation and unemployment.
With that preface, where do we stand today? The Fed executed a veritable helicopter drop of cash during the pandemic, in concert with support payments by the Treasury, with predictable inflationary results. It was also, in part, an accommodation to supply-side pressures. Then the tightening of policy began in the spring of 2022. How will the timing and strength of these shifting policies ultimately play out, as well as the impact of expectations regarding future policy moves?
Help On the Way?
Federal Reserve Chairman Jerome Powell and the Fed’s Open Market Committee (FOMC) are now poised to ease policy after three-plus years of a tighter policy stance. The FOMC is widely expected to cut its short-term interest rate target by a quarter point at the next FOMC on September 17-18. There is an outside chance that the Fed will cut the target by a half point, depending on the strength of new data to be released over the next couple of weeks. In particular, this Friday’s employment report looms large.
What sometimes goes unacknowledged is that the Fed will be following market rates downward, not leading them. The chart below shows the steep drop in the one-year Treasury yield over the past couple of months. Other rates have declined as well. Granted, longer rates are determined in large part by expectations of future short-term rates over which the Fed has more control.
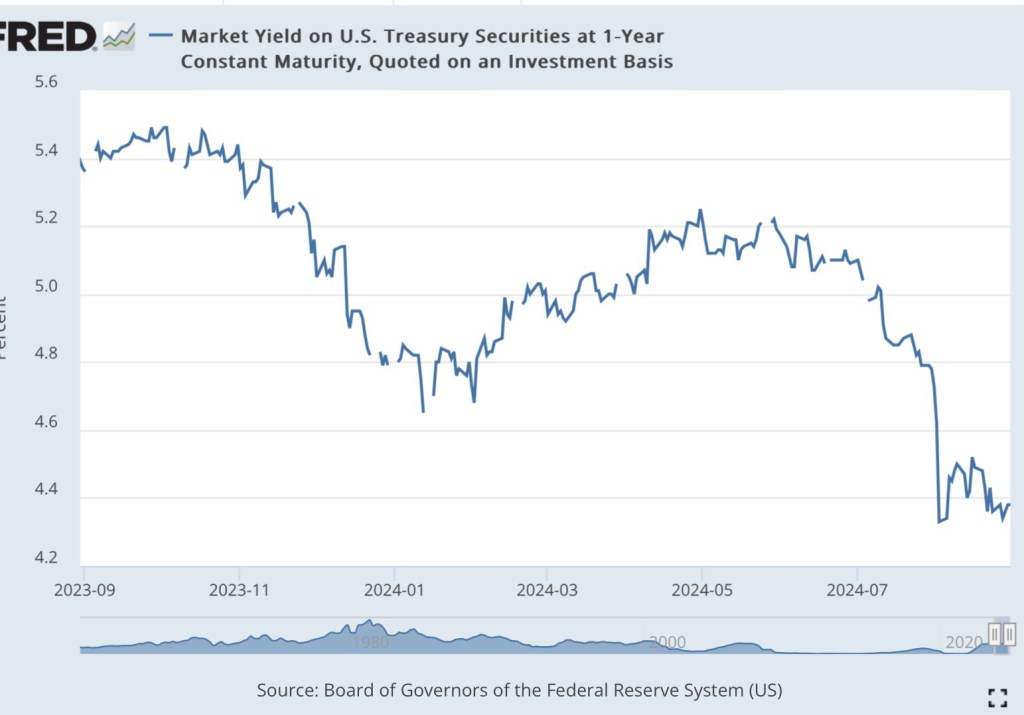
And yet the softening of market rates may well be a signal of weaker economic activity. There is certainly concern among investors that a failure by the Fed to ease policy might jeopardize the much hoped-for “soft landing”. The lagged effects of the Fed’s tighter policy stance may drag on, with damage to the real economy and the labor market. Indeed, some assert that a recession remains a strong possibility (and see here), and the manufacturing sector has been in a state of contraction for five months.
On the other hand, the Fed has fallen short of its 2% inflation goal. The core PCE deflator, the Fed’s preferred inflation gauge, was up 2.6% for the year ending in July. Some observers fear that easing policy prematurely will lead to a new acceleration of inflation.
Powell Gives the Nod
Nevertheless, markets were relieved when Jerome Powell, in his recent speech in Jackson Hole, Wyoming, indicated his determination that a shift in policy was appropriate. From Bloomberg:
“Federal Reserve Chair Jerome Powell said ‘the time has come’ for the central bank to start cutting interest rates.
“Powell’s comments cemented expectations for a rate cut at the central bank’s next gathering in September. The Fed chief said the cooling of the labor market is ‘unmistakable,’ adding, ‘We do not seek or welcome further cooling in labor market conditions.’ Powell also said his confidence has grown that inflation is on a ‘sustainable path’ back to the Fed’s goal of 2%.“
The “sustainable path back to … 2%” might imply a view inside Fed that policy will remain somewhat restrictive even after a quarter or half-point rate cut in September. Or perhaps the “sustainable path” has to do with the aforementioned lags, which might continue to be operative regardless of any immediate change in policy. The feasibility of a “soft landing” depends on whether policy is indeed still restrictive or on how benign those lagged effects turn out to be. But if we take the lags seriously, an easing of policy wouldn’t have real economic force for perhaps 15 months. Still, the market puts great hope in the salutary effects of a move by the Fed to ease policy.
Big Balance Sheet
It can be argued that the Fed already took a step toward easing policy in May when it reduced the rate at which it was allowing runoff in its portfolio of Treasury and mortgage-backed securities. Prior to that, it had been redeeming $95 billion of maturing securities a month. The new runoff amount is $60 billion per month. Unless neutralized in other ways, the runoff has a contractionary effect on bank reserves and the money supply. It is known as “quantitative tightening” (QT). but then the May announcement was a de facto easing in the degree of QT.
Thus far, the total reduction in the Fed’s portfolio has amounted to only $1.7 trillion from the original high-water mark of $8.9 trillion. Here is a chart showing the recent evolution in the size of the Fed’s securities holdings.
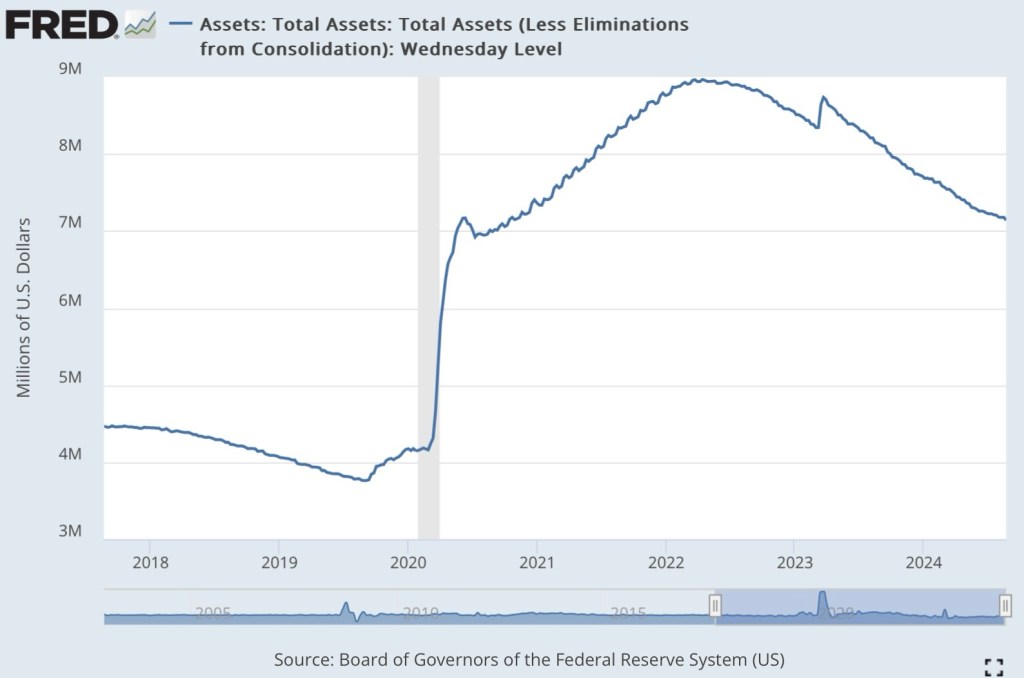
The Fed’s current balance sheet of $7.2 trillion is gigantic by historical standards. It’s reasonable to ask why the Fed considers what we have now to be a more “normalized” portfolio, and whether its size (and correspondingly, the money supply) represents potential “dry tinder” for future inflation. It remains to be seen whether the Fed will further pare the rate of portfolio runoff in the months ahead.
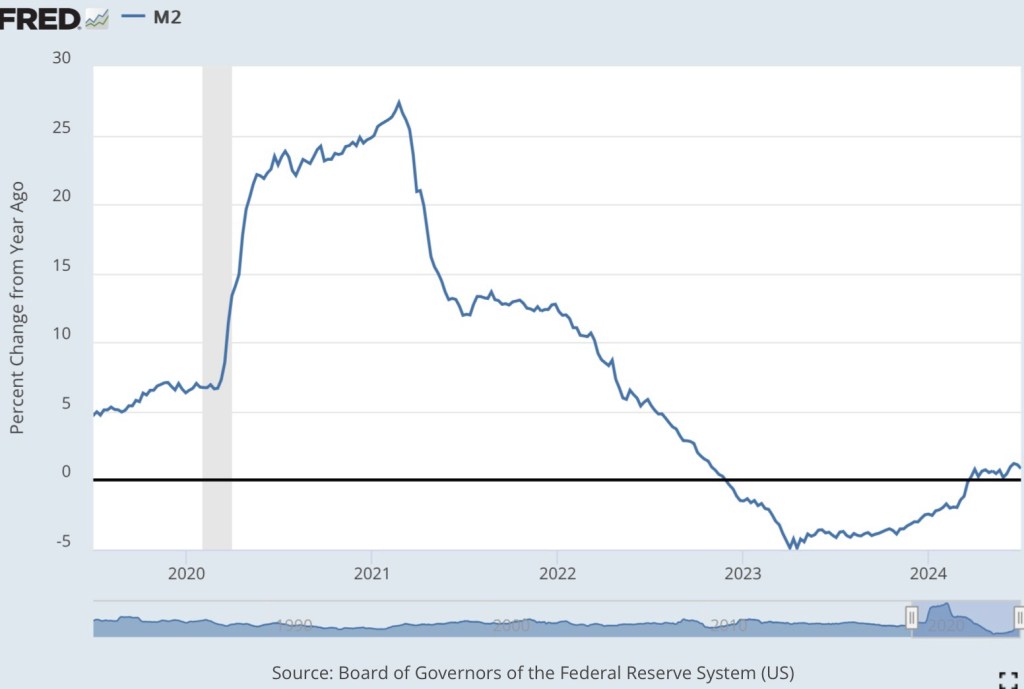
Money growth had been running negative for roughly a year and a half, but it edged closer to zero in late 2023 before accelerating to a slow, positive rate a few months into 2024. The timing didn’t exactly correspond to the Fed’s slowing of portfolio runoff. Nevertheless, the Fed’s strong preference is to supply the banking system with “ample reserves”, and reserves drive money growth. Thus, the Fed’s reaction to conditions in the market for reserves was a factor allowing money growth to accelerate.
A Cut Too Soon?
A rate cut later this month will make reserves still more ample and support additional money growth. And again, this will be an effort to mediate the negative impact of earlier policy tightness, but the effect of this move on the economy will be subject to similar lags.
A danger is that the Fed might be easing too soon, so that inflation will fail to taper to the 2% goal and possibly accelerate again. And perhaps policy was not quite as tight as it needed to be to achieve the 2% goal. Now, new supply bottlenecks are cropping up, including a near shutdown of shipping through the Suez Canal and a potential strike by east coast dockworkers.
Fiscal Incontinence
An even greater threat now, and in the years ahead, is the massive pressure placed on the economy and the Fed by excessive federal spending and Treasury borrowing. The growth of federal debt over the 12 months ending in July was almost 10%. Total federal debt stands at about $35 trillion. According to the Congressional Budget Office (CBO) projections, federal debt held by the public will be almost $28 trillion by the end of 2024 (the rest the public debt is held by the Fed or federal agencies). The CBO also projects that the federal budget deficit will average almost $1.7 trillion annually through 2027 before rising to $2.6 trillion by 2034. That would bring federal debt held by the public to more than $48 trillion.
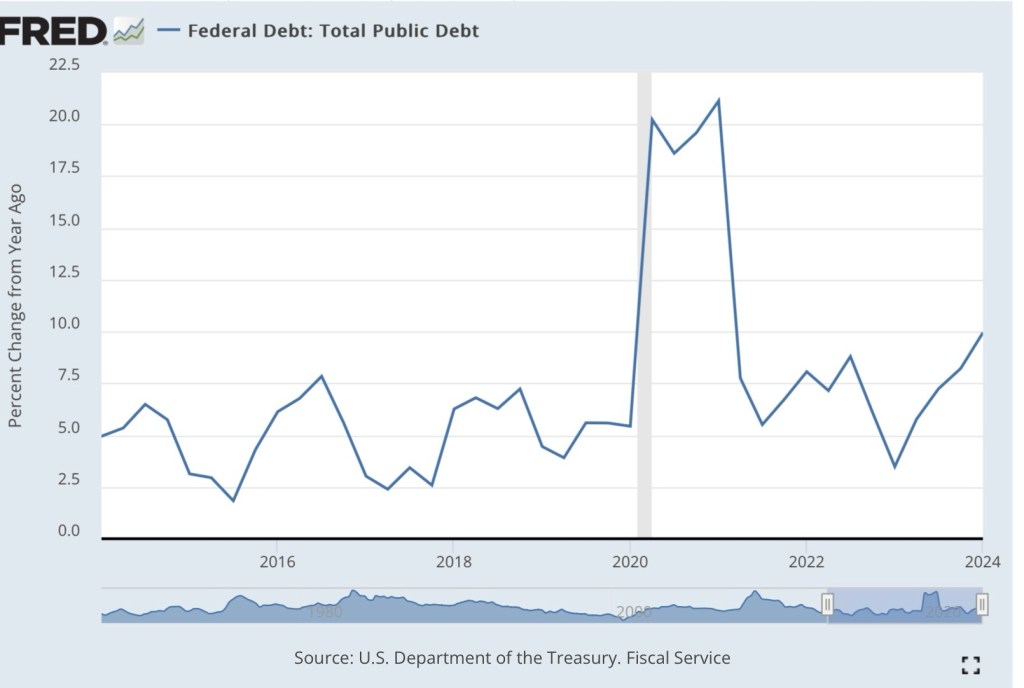
Inflation is receding ever so slowly for now, but it’s unclear that investors will remain comfortable that growth in the public debt can be paid down by future surpluses. If not, the only way its real value can be reduced is through higher prices. Most observers believe such an inflation requires that the Fed monetize federal debt (buy it from the public with printed money). Tighter credit markets will increase pressure on the Fed to do so, but the growing debt burden is likely to exert upward pressure on the prices of goods with or without accommodation by the Fed.
Hard, Soft, Or Aborted Landing?
Some economists are convinced that the Fed has successfully engineered a “soft landing”. I might have to eat some crow…. I felt that a “hard landing” was inevitable from the start of this tightening phase. Even now I would not discount the possibility of a recession late this year or in early 2025. And perhaps we’ll get no “landing” at all. The Fed’s expected policy shift together with the fiscal outlook could presage not just a failure to get inflation down to the Fed’s 2% target, but a subsequent resurgence in price inflation.
