Tags
Balance of Payments, Capital Account, Capital Deepening, Capital Surplus, central planning, Cronyism, Current Account, Donald Trump, Federal Budget Deficit, John Cochrane, Reciprocal Tariffs, Scott Lincicome, Trade Barriers, Trade Deficit
I’m nowhere near eating crow over the skepticism I’ve directed at Donald Trump’s trade offensive. The uncertainty created by his erratic policy changes is very likely to drag the U.S. into recession. However, there were signs last week of movement in a more promising direction, as he placed a 90-day pause on the targeted “reciprocal” tariffs announced in early April. However, a “baseline” universal tariff of 10% still applies to all imported goods. So do tariffs targeted at China, which have ratcheted up through a few rounds of retaliation. Now, he’s announced exemptions for some key electronics products, many of which come from China, and there are signs that he’s ready to exempt imports of auto parts. Needless to say, the tariffs and their exemptions represent an ill-advised escapade in central planning, replete with ample opportunities for politically-motivated favoritism and prejudice.
Why the Pause?
The pause in reciprocal tariffs was ostensibly intended to allow time to negotiate lower trade barriers with “more than 75 countries” that came forward to engage with Trump rather than retaliate. Now, there are said to be as many as 90 countries that wish to negotiate. This more or less aligns with an evolution of the strategy I described in my last post: game theory suggests that a dominant trading partner may be able to threaten or impose higher tariffs and ultimately achieve agreement on a regime with lower trade barriers on both sides. In Trump’s case, that would involve reaching many different bilateral agreements within a very short time, an imposing challenge given the history of trade negotiations. So far we have no deals, though Trump claims some are close. If only we didn’t have to reach formal agreements not to interfere with mutually beneficial trade!
A debate ensued almost immediately over whether Trump’s pause showed that he “caved” to the negative market reaction to his tariffs, but perhaps he acted primarily because a number of nations approached with hats in hand. Trump knew he had the leverage to force other nations to make concessions on trade barriers. They obviously responded.
The timing of the pause was surely a combination of those overtures, market reaction, advisor opinion, and Trump’s own instincts. This view is buttressed by the unaltered universal 10% tariffs, the remaining special tariffs on specific nations and product categories, and the punative tariffs on China. Furthermore, Trump knows he can reimpose a targeted tariff on any country that refuses a deal satisfactory to him. Let’s hope he’s reasonable and doesn’t allow his love affair with tariffs to color his position in these talks.
My hope is that the Trump Administration can negotiate a large number of new agreements with trading partners to reduce or eliminate tariffs and other barriers to trade. Obviously the pause is no guarantee of success, and severe challenges remain with more belligerent trading partners, especially China.
Disclaimer!
None of the foregoing is intended as a dispensation for the many apparent misconceptions Trump has about trade. In the MAGA cult clamor to defend all-things Trump, there have been a number of absurd claims about tariffs and trade, such as: tariffs are not a tax; tariffs don’t raise the price of imports; trade deficits are a deduction from GDP; tariffs can replace the income tax; trade deficits will bankrupt the country; high tariffs produced rapid growth in the late 19th century; “reciprocal” tariffs will eliminate our bilateral trade deficits; U.S. manufacturing is in crisis; value added taxes are trade barriers; it’s better to export goods than services; and trade deficits reduce investment. Every one a laugher, but I’ll leave most of them aside for now.
In the remainder of this post, I’ll focus on Trump’s aims for coaxing firms, via tariff avoidance, to make capital investment in the U.S., and the implications of that effort for the trade balance. An influx of capital might be construed as a strength of Trump’s policy agenda, though his effort to “cut deals” in this manner is a form of economic meddling as well as a vehicle for cronyism. Moreover, he doesn’t understand the nexus between foreign investment, the federal deficit, and the balance of payments. He’ll be disappointed to learn that his notion that trade deficits are ruinous conflicts with his vision of encouraging foreign accumulations of productive U.S. assets.
Oh No! A Capital Surplus!
It isn’t a widely understood equivalence, but each year we have a surplus in foreign purchases of U.S. assets (the capital account surplus) that is roughly matched by a deficit in trade for foreign goods and services (the current account deficit). This is why the balance of payments (BoP) balances! Here is the near mirror image of these two sides of the BoP, from Scott Lincicome’s “Things Everyone Should Know about Trade Deficits”:
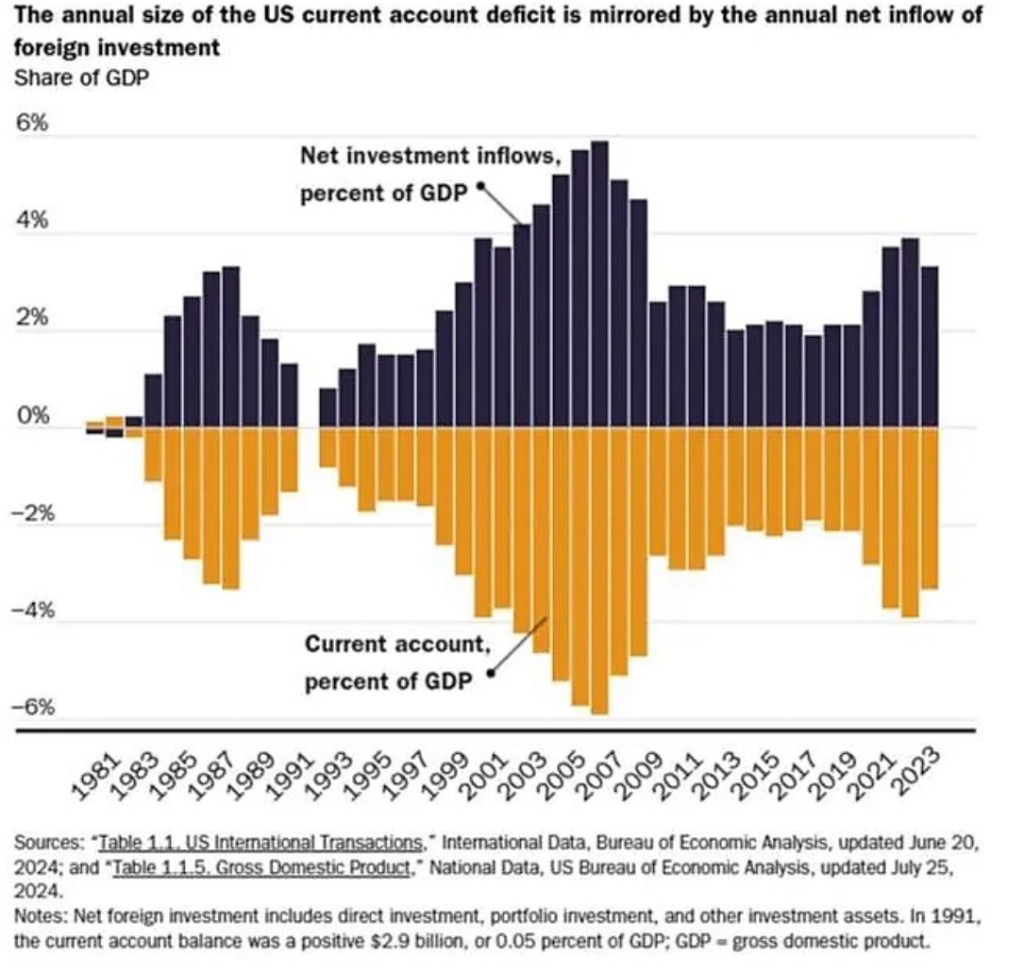
The two sides of the BoP are very much codetermined. One does not exclusively drive the other.
It’s wonderful to be in a position to avail ourselves of foreign savings to invest in our economy. Unfortunately, a large portion of this foreign investment finances our huge government budget deficit, and that is a real problem. Otherwise, the investment would make a greater contribution to U.S. growth.
Funding the Federal Deficit
As John Cochrane explains, transfer payments account for a large share of government spending and borrowing. In turn, these transfers are spent by recipients on consumer goods, some of which come from overseas. Cochrane emphasizes that we are borrowing from abroad, as shown by our capital surplus, to finance this consumption, rather than investing foreign capital in productive assets. While one might conclude that our capital surplus and our trade deficit are creating a long-term vulnerability, the root of the problem is the federal government’s largess.
There is a sense in which different prongs of Trump’s policy agenda could act to address this problem. These are his efforts to reduce government waste, deregulate, and encourage direct investment in new plant and equipment. Reducing the federal budget deficit is paramount, but huge doubts remain over his determination to control spending or undertake real entitlement reforms. Tariffs will generate some revenue, but part of that will be required to offset other tax breaks Trump is contemplating.
Deepening the Capital Base
Trump harps on the need for firms, both foreign and domestic, to produce goods here in the U.S. Currently he’s taking credit for $5 trillion of new investment in the U.S., though we really don’t know whether all of these are “new deals” or had already been planned. Deregulation can improve incentives to invest in physical capital and increase the speed with which it comes online. To the extent that investment in productive capital replaces government borrowing, the debt we accumulate (held by foreign and domestic lenders) will be more sustainable.
However, Trump seems oblivious to a fact made inescapable by the balance of payments relationship. This new investment, should it come to fruition, will bring with it future excesses of imports over exports. Foreign demand for U.S. capital assets lifts domestic income and leads to a stronger dollar, both of which boost imports and the trade deficit. The trade deficit will persist even if foreign investment in new factories fully replaces the bloated federal deficit as a use of foreign capital.
Of course, the intent of Trump’s reshoring campaign is for new domestic output to substitute for imports and increase exports. That would bring positive returns for domestic and foreign capital, but rising income and a stronger dollar will stimulate demand for other imports, while exports would flag with the strength of the dollar. In any case, the new investments and a larger capital surplus will increase the trade deficit.

Pingback: Letting Protectionist Nations Tax Themselves | Sacred Cow Chips
Pingback: A Cooked-Up “Crisis” In U.S. Manufacturing | Sacred Cow Chips
Pingback: Fond Hopes For Free Trade Bargaining Were Foolish | Sacred Cow Chips
Pingback: June Budget Surplus and Wishful Tariff Thinking | Sacred Cow Chips