Tags
Brian Albrecht, Data Security, Don Boudreaux, Donald Trump, Economic Security, Health Security, Jeff Jacoby, Job Security, National Security, Protectionism, Ross Douthat, Strategic Goods, Tariffs, Trade Barriers, Tyler Cowen, Veronique de Rugy
Supporters of President Trump’s hard line on trade make so many false assertions that it’s hard to keep up. I’ve addressed several of these in earlier posts and I’ll address two more fallacies here: 1) that the U.S. manufacturing sector is in a state of crisis; and 2) that tariffs played a key role in promoting economic growth in the U.S. during the so-called gilded age of the late 19th and early 20th centuries.
Security
First, let’s revisit one tenet of protectionism: national security demands self-sufficiency. This undergirds the story that we must produce physical “things”, in addition to often higher-valued services, to be a great nation, or even to survive!
Of course, protecting industries critical to national security might seems like a natural concession to make, even for those supportive of liberalized trade. Ross Douthat says this:
“I think trying to reshore some manufacturing and decouple more from China makes sense from a national security standpoint, even if it costs something to G.D.P. and the stock market.“
Unfortunately, this kind of rationale is far too malleable. There is never a clearly defined limiting principle. Someone decides which goods are “critical” to national security, and this deliberation becomes the subject of much political jockeying and favor-seeking. But wait! Economic security is also cited as an adequate excuse for trade protections! And how about data security? Health security? Job security? Always there is insistence that “security” of one sort or another demands that we provide for our own needs. For definitive proof, take a look at this nonsense! Give them an inch and they’ll take a mile.
Pretty soon you “protect” such a wide swath of industries in a quest for self-sufficiency that the entire economy is unmoored from opportunity costs, comparative advantages, and the information about scarcities provided by market prices. Absolute “security” comes at the cost of transforming the economy’s productive machinery into a complacent hulk rivaling the inefficiency of Soviet industrial planning. Competition is the solution, but not limited to firms under the same set of protective trade barriers.
Manufacturing Is Mostly Fine
Trade warriors, including members of Trump’s team, insist that our decline as a nation is being hastened by a crisis in manufacturing. However, value added in U.S. manufacturing is at an all-time high.
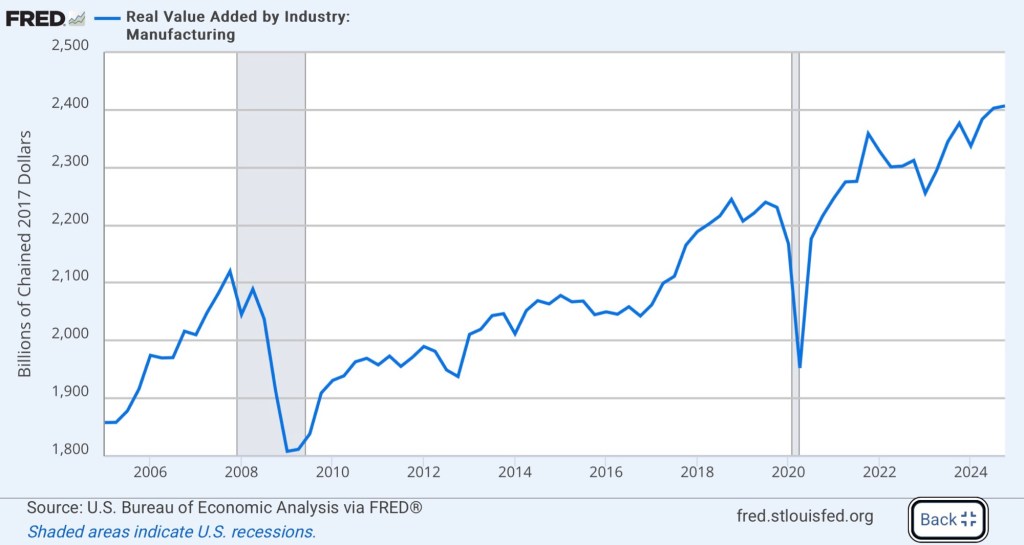
There has been a long-term decline in manufacturing employment, but not manufacturing output. In fact, manufacturing output has doubled since 1980. As Jeff Jacoby notes, “the purpose of manufacturing is to make things, not jobs.” If our overarching social goal was job security, we’d have revolted long ago against the tremendous reduction in agricultural employment experienced over the past century. We’d rely on switchboard operators to load web pages, and we’d dig trenches and tunnels with spoons (to paraphrase Milton Friedman).
The secular decline in manufacturing employment is a consequence of growth in manufacturing productivity. Economy-wide, this phenomenon allows real income and our standard of living to grow.
Take That Job and …
It’s also significant that few Americans have much interest in factory work. It’s typically less dangerous than in times past, but many of today’s factory jobs are still physically challenging and relatively risky. Perhaps that helps explain why nearly half-a-million jobs in manufacturing are unfilled.
Jacoby describes the transition that has changed the face of American manufacturing:
“… US plants have largely turned away from making many of the low-tech, labor-intensive consumer items they once specialized in — sneakers, T-shirts, small appliances, toys. Those jobs have mostly gone overseas, and trying to bring them back by means of a trade war would be ruinous. Yet America remains a global manufacturing powerhouse — highly skilled, highly innovative, and highly efficient.“
And yet, even as wages in manufacturing have grown, many factory jobs do not pay as well as positions requiring far less strenuous toil in the services sector. It’s also true that the best manufacturing jobs in the U.S. today require high-level skills, which are in short supply. These factors help explain why manufacturers believe finding qualified workers is one of their biggest challenges.
Isolating Weak Sectors
There are specific sectors within manufacturing that have fared poorly, including textiles, furniture, metals, and low-end electronics. The loss of competitiveness that drove those sectoral declines is not a new development. It has, however, devastated communities in the U.S. that were heavily dependent on these industries. These misfortunes are regrettable, but trade barriers are not an effective prescription for revitalizing depressed areas.
Meanwhile, other manufacturing sectors have enjoyed growth, such as computers, aerospace, and EVs. While we’ve seen a decline in the number of manufacturing firms, the performance of U.S. manufacturing in the 21st century can be described as mixed at the very worst.
The author of this piece seems to accept the false notion that U.S. manufacturing is moribund, but he knows tariffs aren’t an effective way to strengthen domestic goods production. He has a number of better suggestions, including a commitment to infrastructure investment, reforms to education and health, and reconfiguring certain corporate income tax policies. Unfortunately, his ideas on tariffs are sometimes as mistaken as Trump’s,
The Gilded Age
Finally, the other false assertion noted in the opening paragraph is that tariffs somehow spurred economic growth in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. Brian Albrecht corrects this protectionist fallacy, which lies at the root of many defenses of Trump’s tariffs. Albrecht cites favorable conditions for growth that were sufficient to overwhelm the negative effects of tariffs, including:
“… explosive population growth, mass European immigration, rapid technological innovation, westward expansion, abundant natural resources, high literacy rates, and stable property rights.”
While cross-country comparisons indicate a positive correlation between tariffs and growth during the 1870 – 1920 period, those differences were caused by other forces that dominated tariffs. Cross-industry research discussed by Albrecht indicates that tariffs on manufactured goods during the gilded era reduced labor productivity and stimulated the entry of smaller, less productive firms. Likewise, natural experiments find that tariffs allowed inefficient firms to survive and discouraged innovation.
Conclusion
The U.S. manufacturing sector is not in any sort of crisis, and its future growth won’t be powered by attempts to restore the sort of low-value production offshored over the past several decades. What protectionists interpret as failure is the natural progression of a technically advanced market-based civilization, where high-value services account for greater shares of growing total output. Of course, low-value production is sometimes “crowded out” in this process, depending on its trade-ability and comparative advantages. The logic of the process is encapsulated by Veronique de Rugy’s recent discussion of iPhone production (HT: Don Boudreaux):
“Then there’s [Commerce Secretary Howard] Lutnick, pining for a world where Americans flood back into massive factories to assemble iPhones. This is nostalgic industrial cosplay masquerading as economic strategy. Yes, iPhones aren’t assembled by Americans. But this isn’t a failure; it’s a feature of smart economic specialization. We design the iPhone here. That’s the high-value, high-margin part. The sophisticated chips, software, architecture, and intellectual property are all created in the U.S. The marketing is done here, too. That’s most of the value of the iPhone. The lower-value labor-intensive assembly work is done abroad because those tasks are more efficiently performed abroad.“
There is certainly no crisis in U.S. manufacturing. That narrative is driven by a combination of politics, rent seeking, and misplaced nostalgia.

