Tags
AI Capital Expenditures, Artificially Intelligence, Bradford S. Cohen, Carlyle, central planning, Cronyism, crowding out, Daren Acemoglu, Digital Assets, Federal Deficits, Goldman Sachs, Jason Thomas, Megan Jones, Productivity Growth, Public debt, Scarcity, Seth Benzell, Sovereign Wealth Fund, Stanford Digital Economy Lab, Tyler Cowen
There’s a hopeful narrative making the rounds that artificial intelligence will prove to be such a boon to the economy that we need not worry about high levels of government debt. AI investment is already having a substantial economic impact. Jason Thomas of Carlyle says that AI capital expenditures on such things as data centers, hardware, and supporting infrastructure account for about a third of second quarter GDP growth (preliminarily a 3% annual rate). Furthermore, he says relevant orders are growing at an annual rate of about 40%. The capex boom may continue for a number of years before leveling off. In the meantime, we’ll begin to see whether AI is capable of boosting productivity more broadly.
Unfortunately, even with this kind of investment stimulus, there’s no assurance that AI will create adequate economic growth and tax revenue to end federal deficits, let alone pay down the $37 trillion public debt. That thinking puts too much faith in a technology that is unproven as a long-term economic engine. It would also be a naive attitude toward managing debt that now carries an annual interest cost of almost $1 trillion, accounting for about half of the federal budget deficit.
Boom Times?
Predictions of AI’s long-term macro impact are all over the map. Goldman Sachs estimates a boost in global GDP of 7% over 10 years, which is not exactly aggressive. Daren Acemoglu has been even more conservative, estimating a gain of 0.7% in total factor productivity over 10 years. Tyler Cowen has been skeptical about the impact of AI on economic growth. For an even more pessimistic take see these comments.
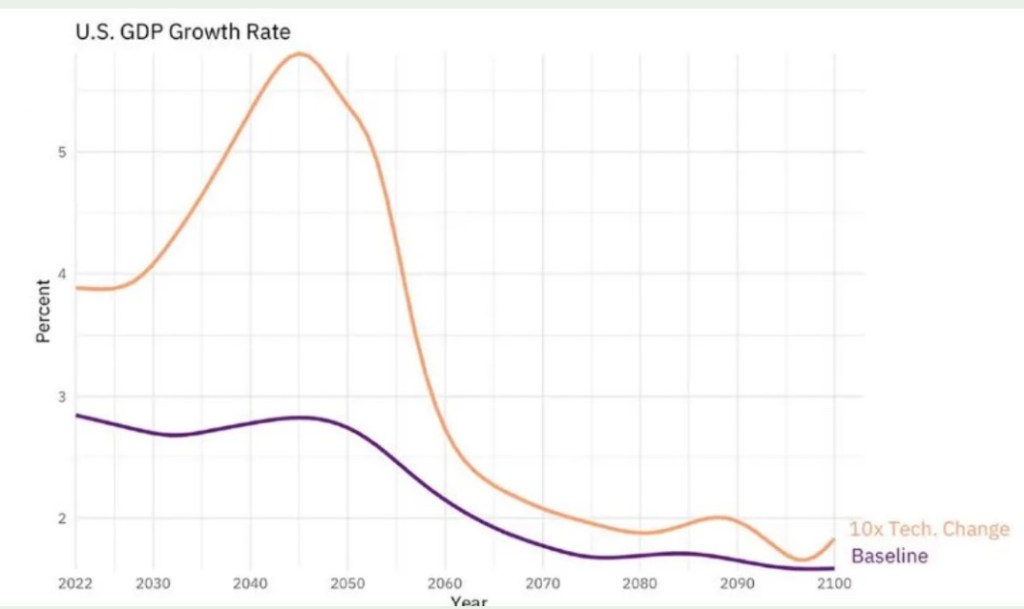
In July, however, Seth Benzell of the Stanford Digital Economy Lab discussed some simulations showing impressive AI-induced growth (see chart at top). The simulations project additional U.S. GDP growth of between 1% – 3% annually over the next 75 years! The largest boost in growth occurs now through the 2050s. This would produce a major advance in living standards. It would also eliminate the federal deficit and cure our massive entitlement insolvency, but the result comes with heavy qualifications. In fact, Benzell ultimately throws cold water on the notion that AI growth will be strong enough to reduce or even stabilize the public debt to GDP ratio.
The Scarcity Spoiler
The big hitch has to do with the scarcity of capital, which I’ve described as an impediment to widespread AI application. Competition for capital will drive interest rates up (3% – 4%, according to Benzell’s model). Ongoing needs for federal financing intensify that effect. But it might not be so bad, according to Benzell, if climbing rates are accompanied by heightened productivity powered by AI. Then, tax receipts just might keep-up with or exceed the explosion in the government’s interest obligations.
A further complication cited by Benzell lurks in insatiable demands for public spending, and politicians who simply can’t resist the temptation to buy votes via public largesse. Indeed, as we’ve already seen, government will try to get in on the AI action, channeling taxpayer funds into projects deemed to be in the public interest. And if there are segments of the work force whose jobs are eliminated by AI, there will be pressure for public support. So even if AI succeeds in generating large gains in productivity and tax revenue, there’s very little chance we’ll see a contagion of fiscal discipline in Washington DC. This will put more upward pressure on interest rates, giving rise to the typical crowding out phenomenon, curtailing private investment in AI.
Playing Catch-Up
The capex boom must precede much of the hoped-for growth in productivity from AI. Financing comes first, which means that rates are likely to rise sooner than productivity gains can be expected. And again, competition from government borrowing will crowd out some private AI investment, slowing potential AI-induced increases in tax revenue.
There’s no chance of the converse: that AI investment will crowd out government borrowing! That kind of responsiveness is not what we typically see from politicians. It’s more likely that ballooning interest costs and deficits generally will provoke even more undesirable policy moves, such as money printing or rate ceilings.
The upshot is that higher interest rates will cause deficits to balloon before tax receipts can catch up. And as for tax receipts, the intangibility of AI will create opportunities for tax flight to more favorable jurisdictions, a point well understood by Benzell. As attorneys Bradford S. Cohen and Megan Jones put it:
“Digital assets can be harder to find and more easily shifted offshore, limiting the tax reach of the U.S. government.”
AI Growth Realism
Benzell’s trepidation about our future fiscal imbalances is well founded. However, I also think Benzell’s modeled results, which represent a starting point in his analysis of AI and the public debt, are too optimistic an assessment of AI’s potential to boost growth. As he says himself,
“… many of the benefits from AI may come in the form of intangible improvements in digital consumption goods. … This might be real growth, that really raises welfare, but will be hard to tax or even measure.”
This is unlikely to register as an enhancement to productivity. Yet Benzell somehow buys into the argument that AI will lead to high levels of unemployment. That’s one of his reasons for expecting higher deficits.
My view is that AI will displace workers in some occupations, but it is unlikely to put large numbers of humans permanently out of work and into state support. That’s because the opportunity cost of many AI applications is and will remain quite high. It will have to compete for financing not only with government and more traditional capex projects, but with various forms of itself. This will limit both the growth we are likely to reap from AI and losses of human jobs.
Sovereign Wealth Fund
I have one other bone to pick with Benzell’s post. That’s in regard to his eagerness to see the government create a sovereign wealth fund. Here is his concluding paragraph:
“Instead of contemplating a larger debt, we should instead be talking about a national sovereign wealth fund, that could ‘own the robots on behalf of the people’. This would both boost output and welfare, and put the welfare system on an indefinitely sustainable path.”
Whether the government sells federal assets or collects booty from other kinds of “deals”, the very idea of accumulating risk assets in a sovereign wealth fund undermines the objective to reduce debt. It will be a struggle for a sovereign wealth fund to consistently earn cash returns to compensate for interest costs and pay down the debt. This is especially unwise given the risk of rising rates. Furthermore, government interests in otherwise private concerns will bring cronyism, displacement of market forces by central planning, and a politicization of economic affairs. Just pay off the debt with whatever receipts become available. This will free up savings for investment in AI capital and hasten the hoped-for boom in productivity.
Summary
AI’s contribution to economic growth probably will be inadequate and come too late to end government budget deficits and reduce our burgeoning public debt. To think otherwise seems far fetched in light of our historical inability to restrain the growth of federal spending. Interest on the federal debt already accounts for about half of the annual budget deficit. Refinancing the existing public debt will entail much higher costs if AI capex continues to grow aggressively, pushing interest rates higher. These dynamics make it pretty clear that AI won’t provide an easy fix for federal deficits and debt. In fact, ongoing federal borrowing needs will sop up savings needed for AI development and diffusion, even as the capital needed for AI drives up the cost of funds to the government. It’s a shame that AI won’t be able to crowd out government.
