Tags
Ample Reserves, Bank Regulation, Discount Window, Fed Balance Sheet, Federal Funds, Federal Open Market Committee, Federal Reserve Board, Interest on Reserves, Kevin Warsh, Lender of Last Resort, Liquidity Backstops, Michelle Bowman, Milton Friedman, Quantitative Tightening, Scarce Reserves, Scott Bessent, Supplementary Leverage Ratio, Too big to fail

Kevin Warsh has been nominated by President Trump as the next Chairman of the Federal Reserve Board. He’d step into the role in May if confirmed by the Senate. Warsh has served on the Board before, from 2006-2011. During that tenure, he was basically opposed to quantitative easing and expansion of the Fed’s balance sheet, though he voted for QE1 in 2010 in deference to then-Chairman Ben Bernanke, while offering a dissenting opinion.
A Chairman Warsh would have allies some at the Fed, but whatever direction he might prefer for policy, it’s not clear that he can or would swing policy decisions. The Board of Governors has seven members, not all of whom would ally with Warsh, while the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC), the main policy-setting arm of the Fed, has 12 voting members. And the influential Fed staff might offer resistance to Warsh’s views. Nevertheless, it’s worth asking how his views would take shape as Fed policy if they held sway.
Warsh has said the Fed’s balance sheet should shrink and that the Fed should reduce its target rate for the federal funds rate. Of course, the latter aligns with Trump’s exhortations. Sharply lower rates are desired by the Administration as a tonic for consumers and businesses. Furthermore, reducing the federal government’s interest costs on the public debt would bring a meaningful reduction in the deficit, or at least give Trump room for new spending initiatives.
Some might wonder whether shrinking the Fed’s balance sheet — selling securities to the public — is consistent with an effort to reduce rates. After all, selling securities on the open market by the Fed is usually associated with higher rates and tighter monetary policy. When the Fed’s balance sheet shrinks, we call it quantitative tightening. And yet Warsh calls for lower rates.
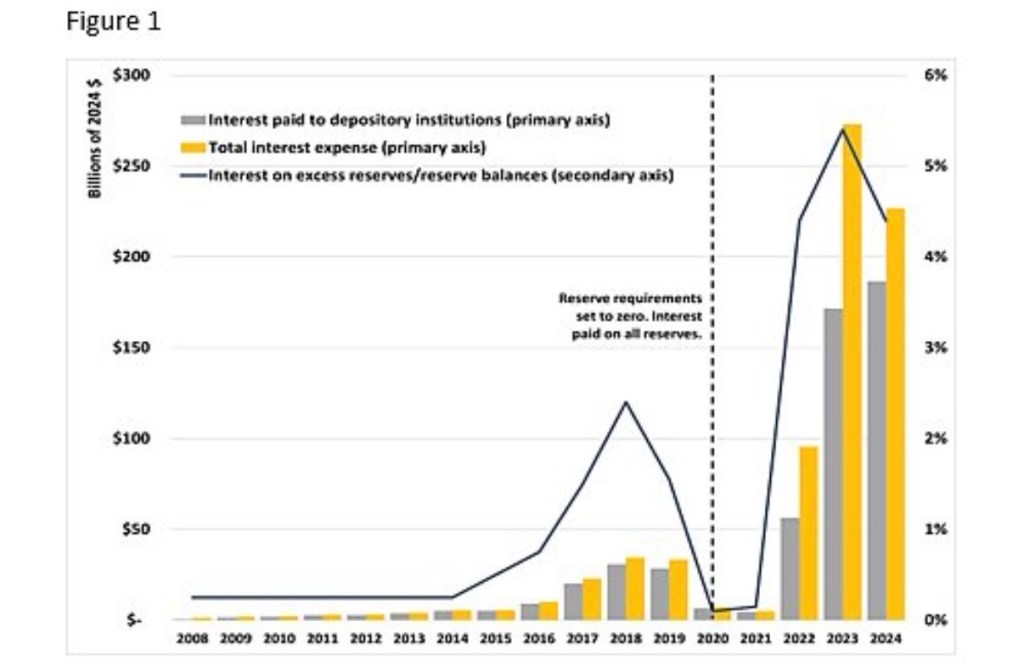
Whether you agree with either of the Warsh objectives, their combination can at least be reconciled. A sharp reduction or prohibition on interest paid by the Fed to banks on their reserves (IOR) would go hand-in-hand with other steps by the Fed to reduce short-term interest rates. Eliminating or reducing the rate earned on reserves would create an incentive for banks to purchase the assets that Warsh would have the Fed divest from its balance sheet. That would also have to be accompanied by the reestablishment of minimum reserve requirements for banks.
Of course, bank incentives matter only to the extent that regulations don’t stand in the way. Currently, bank regulations penalize large banks for investing in Treasuries, despite minimal risk. So-called Supplementary Leverage Ratio (SLR) rules require large banks to hold from 3% up to 6% capital against all assets on their balance sheets. In addition, long-term Treasury securities held by banks can trigger flags for rate-risk exposure, and mark-to-market rules might lead to adverse fluctuations in bank regulatory capital.
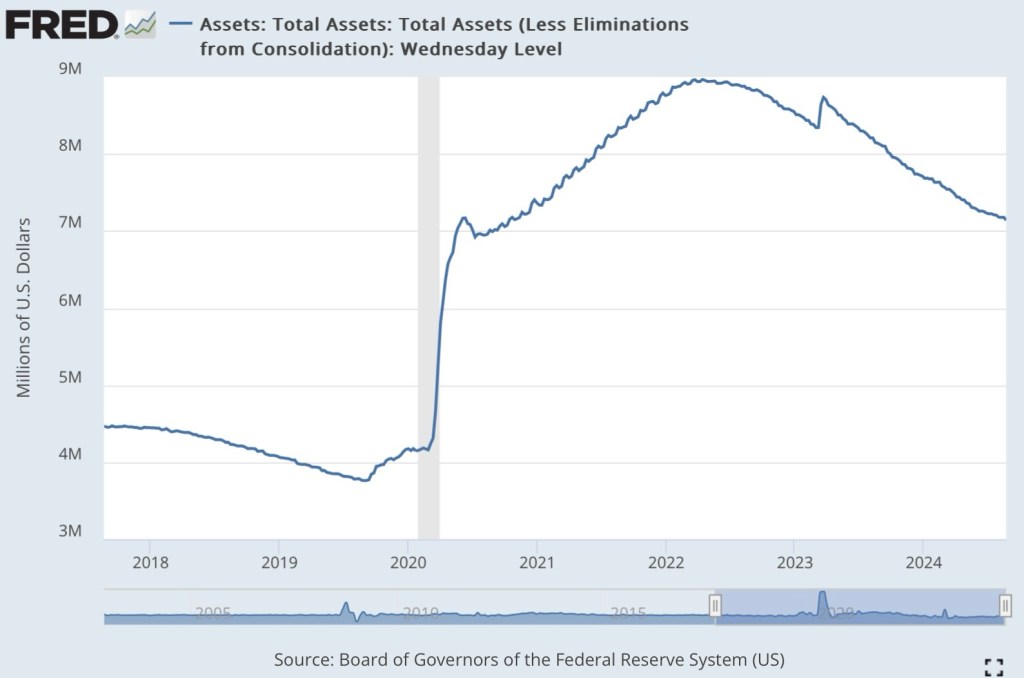
Warsh has been a critic of expansive bank regulation by the Fed. It’s likely that he would support Vice Chairwoman Michelle Bowman’s push for deregulation, and would be in the same corner on that point as Treasury Secretary Scott Bessent. New rules would take time to promulgate and implement, but surely Warsh recognizes that shrinking the Fed’s $6.5 trillion portfolio would have to be a protracted affair in any case. In fact, an effort to reduce the Fed’s balance sheet in 2019 was halted after liquidity became a concern in the repurchase market.
For perspective on the $6.5 trillion portfolio, private U.S. commercial banks currently hold about $25 trillion in assets, but total bank reserves at the Fed are almost $3 trillion, including reserves held by foreign banks. This limits the extent to which the Fed’s balance sheet can be drawn down via uptake by commercial banks.
A potential switch by the Fed from ensuring “ample reserves” to a system of “scarce reserves” sets off alarm bells among many Fed watchers and within the Fed itself. Resistance to the change is based in part on the need for adequate “backstops” to ensure the safety of the banking system under scarce reserves. In this connection, there always were backstops under scarce reserves, including a well-functioning market for overnight loans of reserves between banks (federal funds) as well as the Fed’s own Discount Window, which it operates as lender of last resort. Most importantly, a steady and reliable policy course would minimize economic and financial disruptions and therefore the need for extraordinary measures. Beyond that, in times of volatility or financial stress it’s necessary to take a longer perspective on asset valuation, rather than relying too heavily on short-term market fluctuations, before leaning into “too big to fail” solutions. In fact, Warsh has said the following:
“The Fed, as first-responder, must strongly resist the temptation to be the ultimate rescuer.
And this:
“The Federal Reserve is not a repair shop for broken fiscal, trade or regulatory policies.“
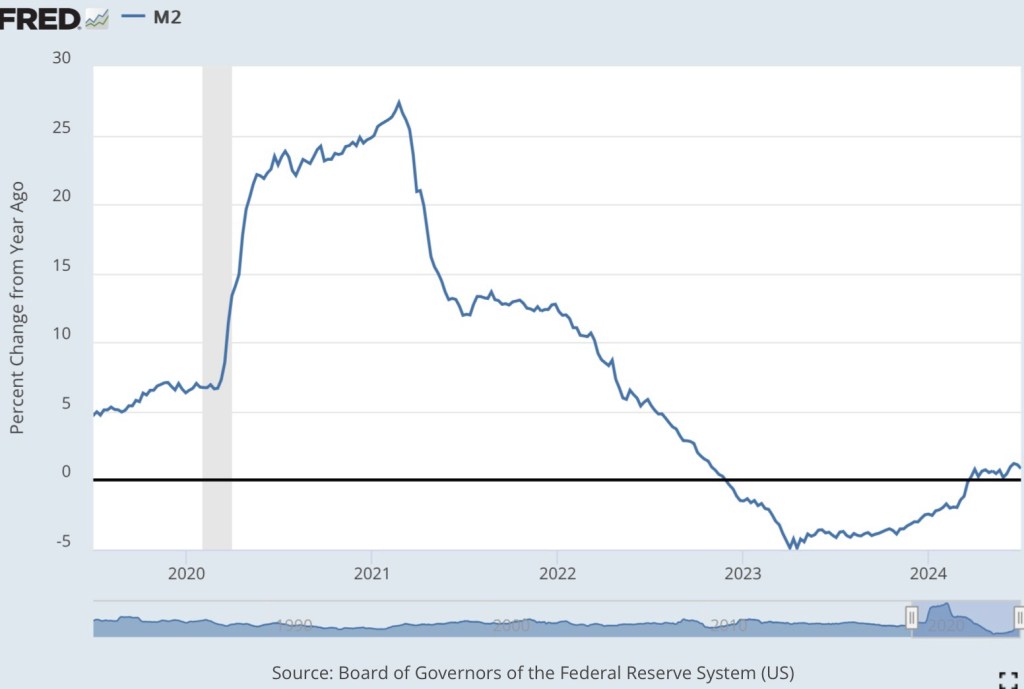
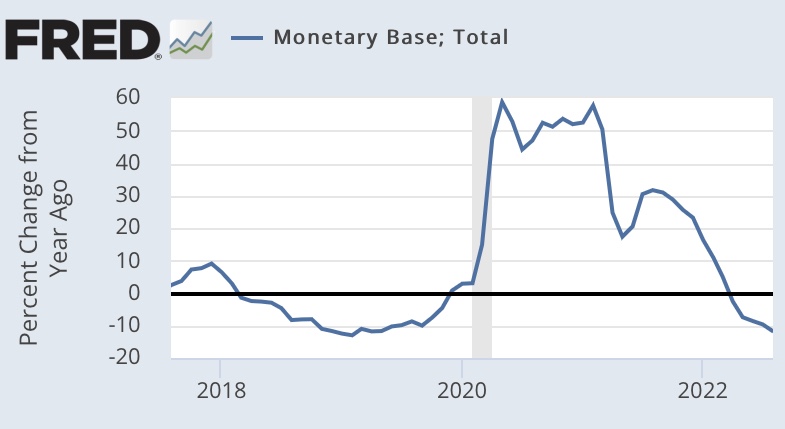
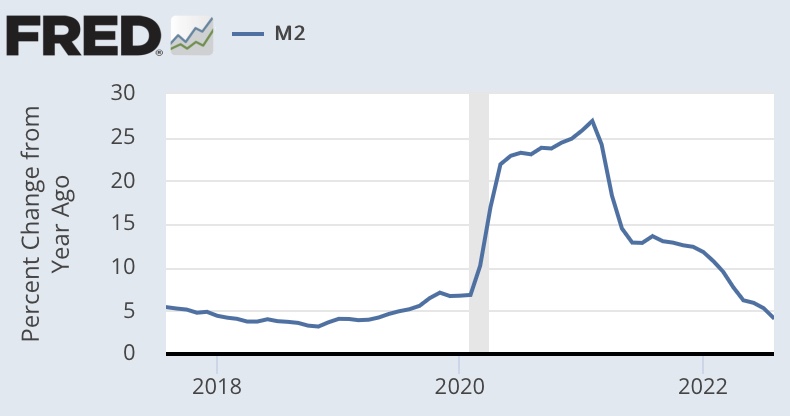
Would this approach, steadily shrinking the Fed’s balance sheet while scaling back IOR, succeed in reducing key interest rates? It could reduce some consumer and business loan rates that are indexed to the fed funds rate or to the prime rate. Long-term rates are another story, as they are governed by fundamentals like expectations of economic growth and inflation. But beyond the evolution of the balance sheet, the rate of IOR, the fed funds rate, and bank reserves, there are measures of greater interest to the full thrust of monetary policy: the rate of growth of the money supply relative to nominal aggregates like GDP.
Warsh has been described as a “inflation hawk”, and has described himself as a “student of Milton Friedman”. That should assuage any fears that a “Warsh Fed” would be inclined to monetary activism for economic or political reasons.
What Trump might want and what Warsh, as Fed Chairman, is willing or able to do are two different things. Trump has loudly called for an immediate cut in the fed funds rate of 100 basis points or more, which is not going to happen. Such a large cut in the target rate (and IOR) would alarm markets, particularly without firmly establishing the Fed’s intentions for both its inflation (or other) target and the transition to a new reserve/balance sheet regime. In fact, any future policy actions should be predicated on inflation and other economic data.
But who knows? Warsh has said that the proliferation of AI will engender massive gains in productivity, which would be a deflationary force. We can only hope! Perhaps that would provide all the rationale Warsh needs for expansionary monetary policy… a smaller balance sheet with rate cuts and non-inflationary money growth.
There have been comments from Warsh and Treasury Secretary Scott Bessent that the Fed can reach some kind of new “accord” with the Treasury with respect to the Fed’s balance sheet and debt issuance. It’s not clear what this might entail, but it could be a simple matter of clearly outlining plans to level-set market expectations. The Fed has reduced the average maturity of its Treasury debt holdings. Perhaps Bessent can persuade Warsh and the Fed to lengthen maturities as the Fed’s portfolio runs off. But there are other avenues for a possible accord, such as guides for action on the provision of liquidity by the Fed, regulatory matters, and bounds around interventions that might influence debt issuance.
Here are a few bullet points to summarize the Warsh policy scenario I outlined above:
- Shrink the Fed’s balance sheet
- End the ample reserves regime
- Reduce or eliminate interest on bank reserves
- Deregulate bank balance sheets
- Guide rates lower and provide monetary accommodation for productivity growth
That’s a lot for a new Fed Chair to bring together. Events might conspire to prevent some of those steps, but that’s stab at a Warsh roadmap for monetary policy.