Tags
Avik Roy, Bernie Sanders, Elizabeth Warren, Health Care Monopolies, Hospital Insurance Trust Fund, Insolvency, J.D. Tuccille, Jacqueline Pohida, John C. Goodman, Medicaid, Medicare Advantage, Medicare Buy-Ins, Medicare For All, Medicare Supplements, Michael F. Cannon, Obamacare, P.J. O'Rourke, Phillip L. Swagel, Public Option, Quality of Care, Reimbursement Rates, Spending Caps. Affordable Care Act, Stephen Green

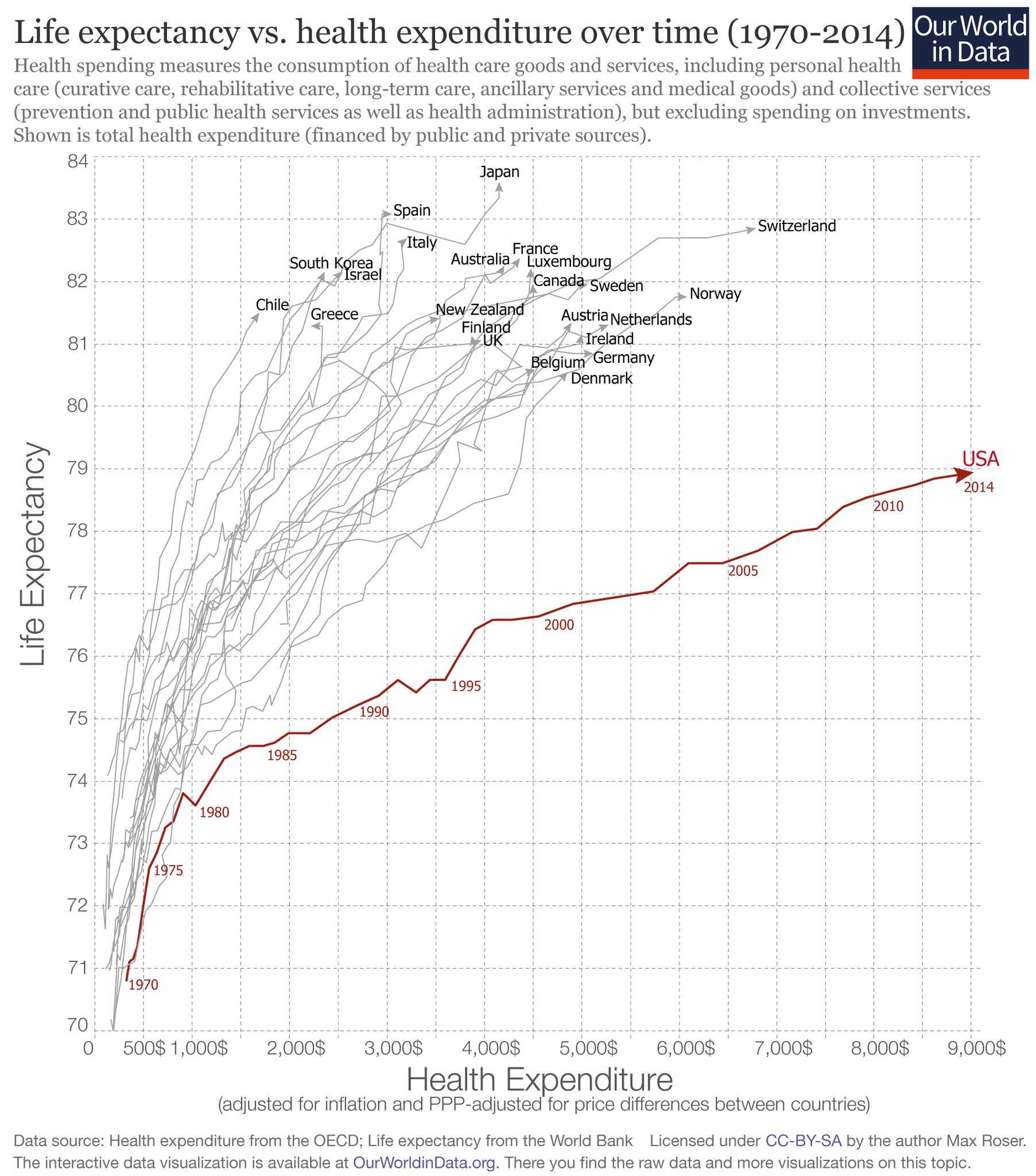
Political humorist P.J. O’Rourke once quipped that if you think health care is expensive now, wait till it’s free! A Stephen Green post reminded me of the source of that wisdom. But there are many who say they don’t understand why we simply don’t offer the Medicare program to everyone … free! Well, the reasons are quite simple: we can’t afford it, and it would be bad policy. In fact, it’s too costly and bad policy even if it isn’t free! Medicare is technically insolvent as it is — broke, in plain language. According to the Medicare Trustees 2022 Report linked above, the Hospital Insurance Trust Fund will be depleted by 2028. That only means the Medicare system has authority to take funds the Treasury borrows to pay ongoing benefits through 2028, so the remaining trust fund balance is little consolation. The long-term actuarial deficit is $700 billion, but it’s possibly as high as $1.5 trillion under an alternative, high-cost scenario shown in the Trustee’s report.
Single Payer Medicare?
Extending free Medicare to the entire population would cost over $30 trillion in the first 10 years, and that’s a conservative estimate. And be forewarned: single-payer health care is government health care, which invariably leads to rationed access and protracted waiting times, poor quality, and escalating costs. For a detailed look at many of the quality problems suffered by Medicare patients, see this paper by Michael Cannon and Jacqueline Pohida. Don’t be deceived by claims that Medicare’s administrative costs are lower than private insurance: The real cost of Medicare is largely hidden through the imposition of low reimbursement rates to providers, while taxpayers get stuck with a significant bill.
Avik Roy has discussed variations on “Medicare For All” (M4A), most of which share very little with today’s Medicare. Not only would they fail to address its shortcomings; they would be much worse. Some do not include the range of private plans currently offered through Medicare Advantage. In fact, under the plans offered by Bernie Sanders and Elizabeth Warren, Medicare Advantage would be terminated, as would all other private insurance for the working-age population. Medicaid would also be eliminated. “Medicare”, in its surviving form, would be the single-payer system, “free” at the point of care and without premiums. Again, a free health care buffet would unleash gluttonous demand, so certain restrictions must be in place to limit pricing and access to care. Think rationing, which should sound ominous to those whose health is failing.
Physician reimbursement rates under traditional Medicare are now only about 60% of private reimbursements, and that filters down to the wages earned by other workers in the health care sector. Naturally, broadening Medicare’s reach will cause providers and their employees to drop-out or cut back. And again, services will be subject to various other forms of rationing. These are unavoidable failings of free or heavily-subsidized health care systems, not to mention the massive burden on taxpayers. And by the way, the “rich” are nowhere near rich enough to pay for all of it.
As to the overall effects, here’s what CBO Director Phillip L. Swagel told the Senate Budget Committee recently, as quoted in Reason by JD Tuccille:
“The increase in demand for personal health care would exceed the increase in supply, resulting in greater unmet demand than the amount under current law. The increase in unmet demand would correspond to increased congestion in the health care system, including delays and forgone care.”
The “increase in supply” mentioned by Swagel is something of a pipe dream.
Buy-Ins and Public Option
There are less drastic proposals than full-blown M4A, such as so-called Medicare buy-ins. For example, those age 50 – 64 might be given the option to “buy-in” to Medicare coverage. It’s not clear whether that would include a choice of Medicare Advantage plans. Many would find the coverage available through traditional Medicare and Medicare Advantage to be inadequate. It is often inferior to private plans, including the lack of dependent coverage and no out-of-pocket maximum for traditional Medicare. Supplemental coverage would be necessary for many individuals choosing the latter.
Another question is how employers would adjust to a segment of their work force in the 50-64 age group opting-out of sponsored coverage. Would the company be required to pick-up the Medicare tab? Would there be compensatory adjustments in wages? Fully compensatory changes are unlikely. Even with partial adjustments, how would an employer adjust company-wide wage scales for younger workers who perform the same or similar duties as those opting into Medicare. And what of the tax-free benefit for workers on employer-paid premiums? Medicare premiums are not tax deductible… at least not yet!
All of the other concerns about low provider reimbursement rates would apply to a Medicare buy-in. The supply of medical care, particularly to the segment buying in, might prove thin. The buy-in option would have very little impact on the number of uninsured individuals. However, several studies have found that the buy-in option would increase premiums for private plans on the individual market (see the last link). That’s largely because providers will try to stick private insurers and patients with the burden of cross-subsidizing Medicare buy-ins.
Another proposal is for a Medicare plan or similar public option to be made available to all in the exchange marketplace. This would take a more massive toll on taxpayers and health care access and quality than the buy-in approach. Moreover, because of pressure for cross-subsidies, private plans will struggle to stay in business. The destruction would be gradual, but the public option would slowly eliminate choice from the marketplace. Cannon and Pohida believe that offering a public option could lead to improvements if the private and public plans are allowed to compete on a level playing field, largely in terms of subsidies and regulatory hurdles, but that is highly unlikely.
Cuts Ahead?
A lesser known issue is the impact of spending caps put in place under the Affordable Care Act. These apply to Medicare and Medicaid as well as federal subsidies on policies purchased on the Obamacare exchanges. When those caps are exceeded, access becomes temporarily restricted, with some practices actually closing their doors for a period of days or weeks. Health economist John Goodman notes that seniors tend to eat into the allowable spending amounts much faster than younger cohorts. That means seniors might be denied costlier forms of care. To the extent that any variation on M4A covers a broader age range, there might be more pressure to curtail certain forms of care for seniors, which would be a most unfortunate case of policy-induced age discrimination.
As for Medicare as it stands now, Goodman describes the potential cuts that are coming. These include the possibility of reduced amenities (e.g., hospital wards with more patients per room and lower-cost meals), and as already mentioned, longer waits and restricted availability of costlier treatments. Goodman states that the necessary cuts to make Medicare whole would be equivalent to the loss of three years of coverage for a 65-year old, and the cuts will affect both traditional Medicare and privately-issued (but publicly subsidized) Advantage plans.
Conclusion
There’s no chance any form of M4A would reduce the cost of care or improve access to care. An expanded Medicare would bear the hallmarks of central planning that have accelerated the monopolization of health care under Obamacare. And like Obamacare, the final form of any M4A plan will be the product of negotiations between self-interested politicians, corporatists and regulators. Big pharmaceutical companies, insurers, large hospital systems, and other interest groups will wrangle for the rents that “reform” legislation might bring. Costs will rise and access to care will be restricted. Taxpayers will be saddled with a large chunk of the cost.
In the end it’s likely to be a mess. Far better to adopt reforms that would bring more innovation, choice, and competition to the markets for health insurance and health care. That includes expanding the range of options available under private Medicare (Advantage). At the same time, Obamacare should be scrapped in favor of a range of a greater range of private options with income-dependent subsidies, including catastrophic coverage only, as well as reduced regulation of insurers and providers.