Tags
80000 Hours, Chris Murray Model, Christopher Monkton, Christopher Murray, Co-morbidity, Confidence Interval, Coronavirus, Covid Tracking Project, Covid-19, Economic Restart, Indur M. Goklany, Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation, Lockdowns, Pending Tests, Positive Test Ratio, Social Distancing, Stay-at-Home Orders, White House Coronavirus Task Force
There were a few encouraging signs of change over the past few days in the course of the coronavirus pandemic in the U.S. This is the third of my quaint efforts to provide perspective on the coronavirus pandemic with “tracking” or “framing” posts. The first two were: Coronavirus: Framing the Next Few Weeks, on March 22, and Framing Update on March 28. In both of those posts, I charted confirmed cases of Covid-19 in the U.S. along with optimistic and pessimistic scenarios. I speculated that over the course of a few weeks, social distancing would lead to a reduction in the daily number of new confirmed cases. Unfortunately, it’s not clear whether that curve has started to “bend” rightward, but new confirmed cases on Sunday, April 5 — the number of those testing positive — was down almost 30% from Saturday.
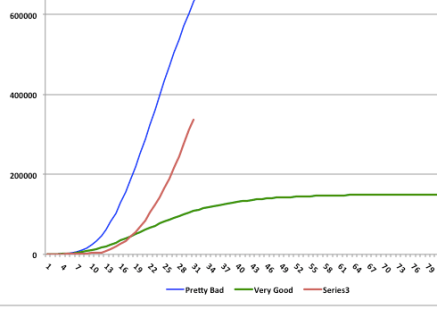
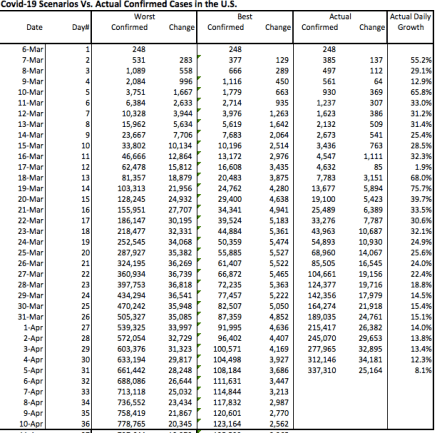
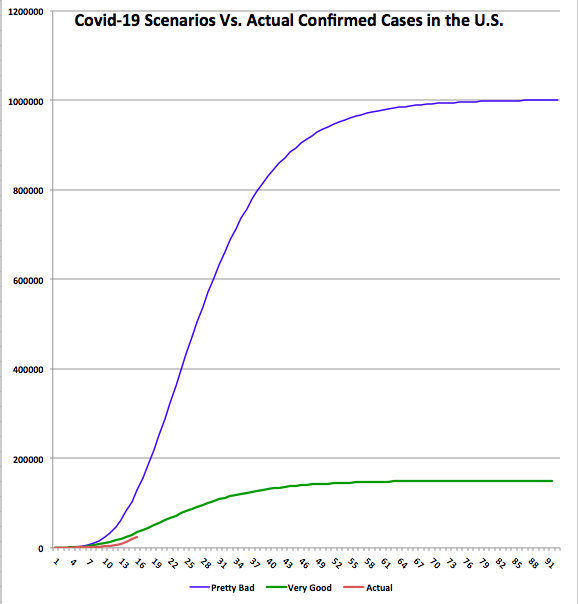
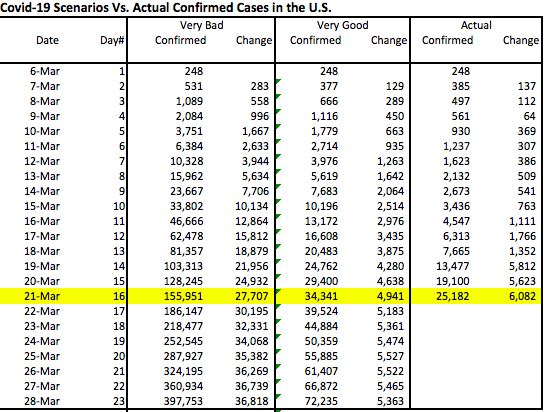
An updated version of the earlier chart appears below, accompanied by a table. The number of confirmed cases (red line) has mounted over the past week, as has the daily increase in confirmed cases, though yesterday’s number was better. The table below the chart shows that the growth rate of confirmed cases (the far right-hand column) has decelerated, but it had leveled off at about 14% over the few days before Sunday. If Sunday’s drop persists it would be encouraging. Unfortunately, even moderate growth rates are destructive when the base of confirmed cases is large. The faster the growth rate declines, the faster the curve will bend.
I did not make any changes to the original “Very Good” and “Pretty Bad” scenarios, deciding that it was better to keep them as a consistent benchmark. As of Sunday, the top of the “Very Good” curve would still be about 2.3x the North Korean experience as of Sunday night, normalized for population. The top of the “Pretty Bad” scenario (which is not visible in this “zoomed-in” version) would be about 1.4x the Italian experience thus far. South Korea’s curve flattened substantially several weeks ago, and now even Italy’s curve is showing a rightward bend. Let’s hope that continues.
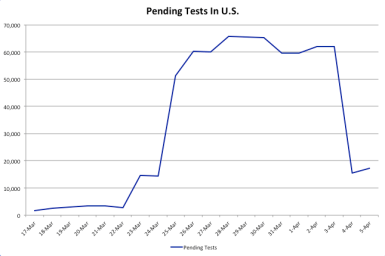
The case count obviously depends on the volume of daily testing, which has been increasing rapidly. As I’ve noted before, there has been a backlog of test requests. In addition, every day there is an overhang of “pending” test results. Interestingly, the number of tests stabilized on Saturday and the number of pending test results plunged (see the next chart, which uses data from the Covid Tracking Project). We’ll see if those developments persist. It would represent a milestone because daily case counts will advance as long as tests do, and the effort to work through the backlog has been inflating the speed of the advance in confirmed cases.
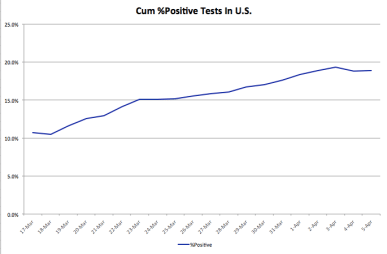
Another interesting development coincident with the drop in pending tests has to do with the cumulative percentage of positive test results: it has stabilized after growing for several weeks. This might mean we’ve reached a point at which the most severe incoming cases are fewer, but we’ll have to see if the flattening persists or even declines, which would be wonderful.
I’ve been grappling with potential weaknesses of the data on confirmed cases: first, the U.S. got a late start on testing, so there was the backlog of patients requiring tests just discussed above. That was presumed to have exaggerated the acceleration in the daily totals for new cases. Second, it’s possible that a continuing transition to more rapid test results would exaggerate the daily counts of new cases. Third, It’s possible that testing criteria are being relaxed, which, despite reducing the positive test rate, would increase growth in the “official” confirmed case count. Suspected cases should be tested, of course, but the change in standards is another factor that distorts the shape of the curve.
Any published statistic has its shortcomings. All test results are subject to false positives and negatives. Hospitalizations of patients with a positive coronavirus diagnosis are subject to the measurement issues as well, though they might be driven more by the severity of symptoms and co-morbidities than a positive Covid diagnosis per se. And hospitalizations of Covid patients might be subject to inconsistencies in reporting, and so might ICU admittances. Coronavirus deaths are subject to vagaries: reporting a cause of death is dictated by various criteria when co-morbidities are involved, and those criteria differ from country to country, or perhaps even hospital to hospital and doctor to doctor! In fact, some go so far as to say that all deaths should be tracked for coronavirus plus its co-morbidities and then compared to an average of the past five to ten years to obtain an estimate of “excess deaths”, which could conceivably be negative or positive. Finally, recoveries are even more impacted by inconsistent reporting, especially because many recoveries occur at home.
I’ll be highlighting coronavirus deaths going forward, and I’ll continue to focus mainly on the U.S. and only lightly on other countries. After all, death is obviously the most negative outcome. Again, however, the count of coronavirus deaths does not account for deaths that would have occurred over the same time frame due to co-morbidities or the effect of deaths that would not have occurred absent co-morbidities.
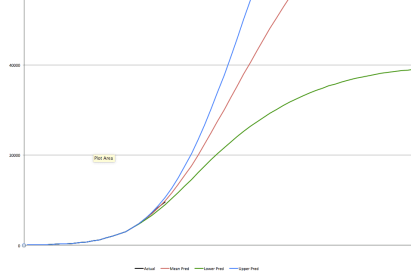
The predictions in the chart below are from the Chris Murray Model, upon which the White House Coronavirus Task Force has focused more recently. This model was developed by Dr. Christopher Murray at the Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation at the University of Washington. I’ll be using the forecast starting from April 2 as the basis for my “framing” of actual deaths over the next few weeks, keeping it “frozen” at that level as a new benchmark. My apologies for the absence of dates on the horizontal axis, but the origin is at March 14 and there is only a single line up through April 1. That line represents actual cumulative Covid deaths recorded in the U.S. The red line is the mean model prediction. Deaths are expected to ramp up over the next week or so, much as we’ve seen in the confirmed case count, as deaths lag behind diagnoses by anywhere from a few days up to 17 days. This model predicts an ultimate death toll of about 94,000 at the top of the mean curve (not visible on the zoomed-in chart). Above and below that line are upper (blue) and lower (green) bounds, respectively, of a “confidence interval”. It’s unlikely we’ll see cumulative deaths breach either of those bounds. The lower bound would place the ultimate death toll at about 40,000; the upper bound would place it at just under 180,000. At this point, as of Sunday, April 5, actual deaths (black) are slightly below the mean or central tendency, but that’s difficult to see in the current chart.
The ongoing lockdowns in the U.S. and around the world are exceedingly controversial. There is a very real tradeoff between the benefits of extending the length of these lockdowns and the benefits of allowing economic activity to “restart”. But do lockdowns work? Christopher Monkton offers aggregate evidence that they truly do reduce the spread of the virus in “Are Lockdowns Working?” That they would work is intuitive, and decisions to scale them back should be made cautiously for certain “high exposure” activities, and in conjunction with isolating and trace-tracking contacts of all infected individuals, as they have done successfully in countries such as Taiwan and Singapore.
There may be signs that a bend in the U.S. case curve is in the offing, perhaps over the next week or two. That timing would roughly comport with the notion that over the past three weeks, efforts at social distancing and stay-at-home orders have allowed the U.S. to limit the spread of coronavirus through the first major “round” of infections and a much more limited second round. Perhaps these efforts will largely stanch a third and subsequent rounds of infection. Ultimately, if the number of coronavirus deaths is in the neighborhood of the mean value predicted by the Murray Model, about 94,000, that would place the severity of the toll at less than two times the severity of a bad flu season, though limiting the Covid death toll will have been achieved at much higher economic cost.
There are signs elsewhere around the globe that the pandemic may be turning a corner toward more favorable trends. See “Good News About COVID-19” at 80,000hours.org for a good review.