Tags
CATO Institute, Federal entitlements, FICA Tax, George W. Bush, Lump Sum vs. Annuity, Michael Tanner, Michigan Retirement Research Center, National Bureau of Economic Research, NBER, payroll taxes, Privatization, retirement, Social Safety Net, Social Security Privatization, Social Security Trust Fund, Treasury Special Purpose Bonds, Welfare Payments
In general parlance, an entitlement is a thing to which one is entitled. If you have paid into Social Security (FICA payroll “contributions”), you should feel entitled to receive benefits one day. Why do I so often hear indignant complaints about the use of the term “entitlement” when applied to Social Security and Medicare? I’ve heard it from both ends of the political spectrum, but more often from the Left. It is usually accompanied by a statement about having “paid for those benefits!”. Exactly, you should feel entitled to them. You are not asking society to pay you alms!
Yet there seems to be resentment of an imagined implication that such “entitlements” are equivalent to “welfare” of some kind. That might be because the definition of an entitlement is somewhat different in the federal budget: it is a payment or benefit for which Congress sets eligibility rules with mandatory funding, as contrasted with discretionary budget items with explicit approval of funding. Because payments are based solely on eligibility, Social Security, Medicare and many forms of welfare benefits are all classified as entitlements in the federal budget. Obviously, those complaining about the use of the term in connection with Social Security believe there is a difference between their entitlement and welfare. But as long as they are willing to leave their “contributions” and future eligibility in the hands of politicians, their claim on future benefits is tenuous. Yes, you will pay FICA TAXES, and then you might be paid benefits (alms?) if you are eligible at that time. Certainly, the government has behaved as if the funds are fair game for use in the general budget.
Having made that minor rant, I can get to another point of this post: the Social Security retirement system offers terrible returns for its “beneficiaries”. Furthermore, it is insolvent, meaning that its long-term promises are, and will remain, unfunded under the current program design. However, there is a fairly easy fix for both problems from an economic perspective, if not from a political perspective.
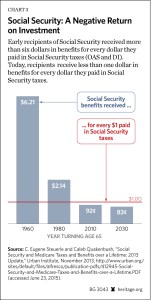
The chart at the top of this post shows that Social Security benefits paid to eligible retirees are less than the payroll taxes those same individuals paid into the system. The chart is a couple of years old, but the facts haven’t changed. It’s boggling to realize that you’ll receive a negative return on the funds after a lifetime of “contributions”. That kind of investment performance should be condemned as unacceptable. However, you should know that the program is not “invested” in your retirement at all! Social Security’s so-called “trust fund” is almost a complete fiction. Most FICA tax revenue is not held “in trust”. Instead, it is paid out as an intergenerational transfer to current retirees. In the past, any surplus FICA tax revenue was invested in U.S. Treasury special purpose bonds, which funded part of the federal deficit. Here is a fairly good description of the process. The article quotes the Clinton Office of Management and Budget in the year 2000:
“These balances are available to finance future benefit payments … only in a bookkeeping sense. They do not consist of real economic assets that can be drawn down in the future to fund benefits. Instead, they are claims on the Treasury that, when redeemed, will have to be financed by raising taxes, borrowing from the public, or reducing benefits, or other expenditures.“
Unfortunately, for the past few years, instead of annual surpluses for the trust fund, deficits have been the rule and they are growing. Retiring baby boomers, longer life expectancies, slow income growth and declining labor force participation are taking a toll and will continue to do so. Something will have to change, but reform of any kind has been elusive. An important qualification is that almost any reform would have to be phased in as a matter of political necessity and fairness to current retirees. Unfortunately, just about every reform proposal I’ve heard has been greeted by distorted claims that it would harm either current retirees or those nearing retirement. In fact, leaving the program unaltered is likely to be a greater threat to everyone down the road.
There are three general categories of reform: higher payroll taxes, lower benefits, and at least partial privatization. Tax increases have obvious economic drawbacks, while straight benefit reductions would be harmful to future recipients even if that entailed means testing: the return on contributions is already negative, especially at the upper end of the income spectrum. Michael Tanner discusses specific options within each of these categories, including raising the normal and early retirement ages. None of the options close the funding gap, but at least higher retirement ages reflect the reality of longer life expectancies.
Early in his presidency, the George W. Bush administration offered a reform plan involving no tax increases or benefit cuts. Instead, the plan would have offered voluntary personal accounts for younger individuals. Needless to say, it was not adopted, but it would have kept the system in better shape than it is today. The key to success of any privatization is that unlike the Social Security Trust Fund, workers with private accounts can earn market returns on their contributions, which are in turn reinvested, allowing the accounts to grow faster over time. Tanner notes that 20 other countries have moved to private accounts including Chile, Australia, Mexico, Sweden, Poland, Latvia, Peru, and Uruguay. This sort of change does not preclude a separate social safety net for those who have been unable to accumulate a minimum threshold of assets, as Chile has done. Tanner’s article lays out details of a tiered plan that would allow participants a wider range of investments as their accumulated assets grow.
Economic research suggests that participants do not place a high value on their future benefits. From a 2007 National Bureau of Economic Research (NBER) paper by John Geanakoplos and Stephen Zeldes entitled “The Market Value of Social Security“:
“We find that the difference between market valuation and ‘actuarial’ valuation is large, especially when valuing the benefits of younger cohorts. … The market value of accrued benefits is only 2/3 of that implied by the actuarial approach.“
An implication is that younger workers who have already made contributions could be offered the choice of a future lump sum that is less than the actuarial present value of their benefits when they become eligible. Such a program could cut the long-term funding gap significantly, if the results found by Geanakoplos and Zeldes can be taken at face value, though it could create additional short-term funding pressure at the time of payment.
Qualified support for such a program seems apparent from another 2007 NBER paper by Jeffrey R. Brown, Marcus D. Casey and Olivia S. Mitchell entitled “Who Values the Social Security Annuity? New Evidence on the Annuity Puzzle“. They find that:
“Our first finding is that nearly three out of five respondents favor the lump-sum payment if it were approximately actuarially fair, a finding that casts doubt on several leading explanations for why more people do not annuitize. Second, there is some modest price sensitivity and evidence consistent with adverse selection; in particular, people in better health and having more optimistic longevity expectations are more likely to choose the annuity. Third, after controlling on education, more financially literate individuals prefer the annuity. Fourth, people anticipating future Social Security benefit reductions are more likely to choose the lump-sum, suggesting that political risk matters.“
Moreover, lump sums may offer an additional advantage from a funding perspective: a 2012 paper from the Michigan Retirement Research Center at the University of Michigan by Jingjing Chai, Raimond Maurer, Olivia S. Mitchell and Ralph Rogalla called “Exchanging Delayed Social Security Benefits for Lump Sums: Could This Incentivize Longer Work Careers?” found that “... workers given the chance to receive their delayed retirement credit as a lump sum payment would boost their average retirement age by l.5-2 years.”
Certainly, it would be difficult for private accounts to fare as badly in terms of returns on contributions than the system has managed to date. The future appears even less promising without reform. There are several advantages to privatization of Social Security accounts beyond the likelihood of higher returns mentioned above: it would avoid some of the labor market distortions that payroll taxes entail, and it would increase the pool of national savings. Perhaps most importantly, over time, it would release the assets (and future benefits) accumulated by workers from the clutches of the state and self-interested politicians. They are not entitled to pursue their political ends with those assets; they are yours!