Tags
Austrian Business Cycle Theory, Boom and bust, CPI, David Beckworth, Federal Funds Rate, Federal Open Market Committee, FOMC, Hard Landing, Hedging, Inflation, Interest Rate Risk, Jason Furman, Jerome Powell, Lender of Last Resort, Liquidity, Money Supply, NBER, Owner’s Equivalent Rent, PCE Deflator, Price Stability, Quantitative Tightening, Rate Targeting, Shelter Costs, Soft Landing

To the great chagrin of some market watchers, the Federal Reserve Open Market Committee (FOMC) increased its target for the federal funds rate in March by 0.25 points, to range of 4.75 – 5%. This was pretty much in line with plans the FOMC made plain in the fall. The “surprise” was that this increase took place against a backdrop of liquidity shortfalls in the banking system, which also had taken many by surprise. Perhaps a further surprise was that after a few days of reflection, the market didn’t seem to mind the rate hike all that much.
Switchman Sleeping
There’s plenty of blame to go around for bank liquidity problems. Certain banks and their regulators (including the Fed) somehow failed to anticipate that carrying large, unhedged positions in low-rate, long-term bonds might at some point alarm large depositors as interest rates rose. Those banks found themselves way short of funds needed to satisfy justifiably skittish account holders. A couple of banks were closed, but the FDIC agreed to insure all of their depositors. As the lender of last resort, the Fed provided banks with “credit facilities” to ease the liquidity crunch. In a matter of days, the fresh credit expanded the Fed’s balance sheet, offsetting months of “quantitative tightening” that had taken place since last June.
Of course, the Fed is no stranger to dozing at the switch. Historically, the central bank has failed to anticipate changes wrought by its own policy actions. Today’s inflation is a prime example. That kind of difficulty is to be expected given the “long and variable lags” in the effects of monetary policy on the economy. It makes activist policy all the more hazardous, leading to the kinds of “boom and bust” cycles described in Austrian business cycle theory.
Persistent Inflation
When the Fed went forward with the 25 basis point hike in the funds rate target in March, it was greeted with dismay by those still hopeful for a “soft landing”. In the Fed’s defense, one could say the continued effort to tighten policy is an attempt to make up for past sins, namely the Fed’s monetary profligacy during the pandemic.
The Fed’s rationale for this latest rate hike was that inflation remains persistent. Here are four CPI measures from the Cleveland Fed, which show some recent tapering of price pressures. Perhaps “flattening” would be a better description, at least for the median CPI:
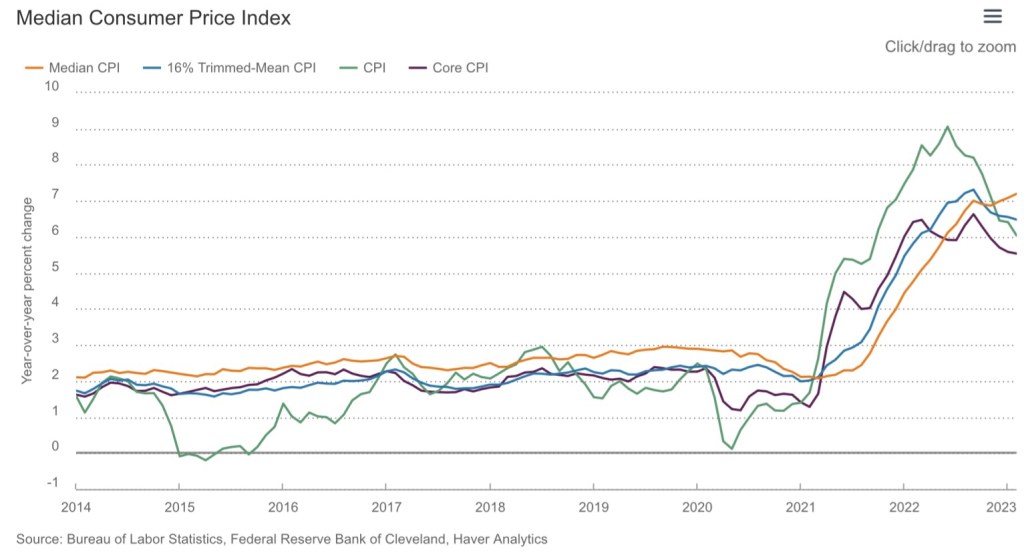
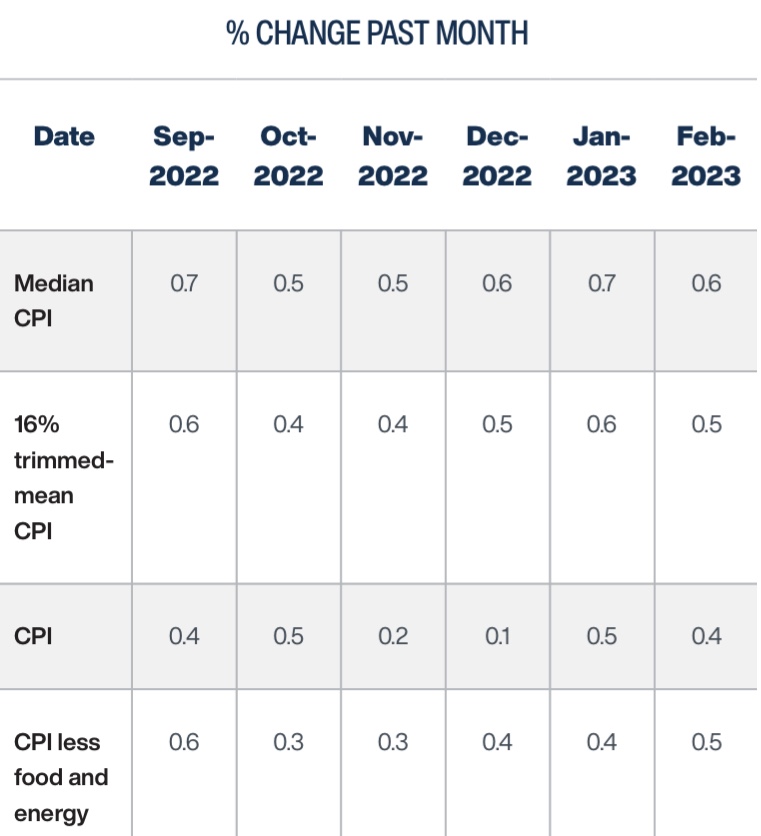
Those are 12-month changes, and just in case you’ve heard that month-to-month changes have tapered more sharply, that really wasn’t the case in January and February:
Jason Furman noted in a series of tweets that the prices of services are driving recent inflation, while goods prices have been flat:
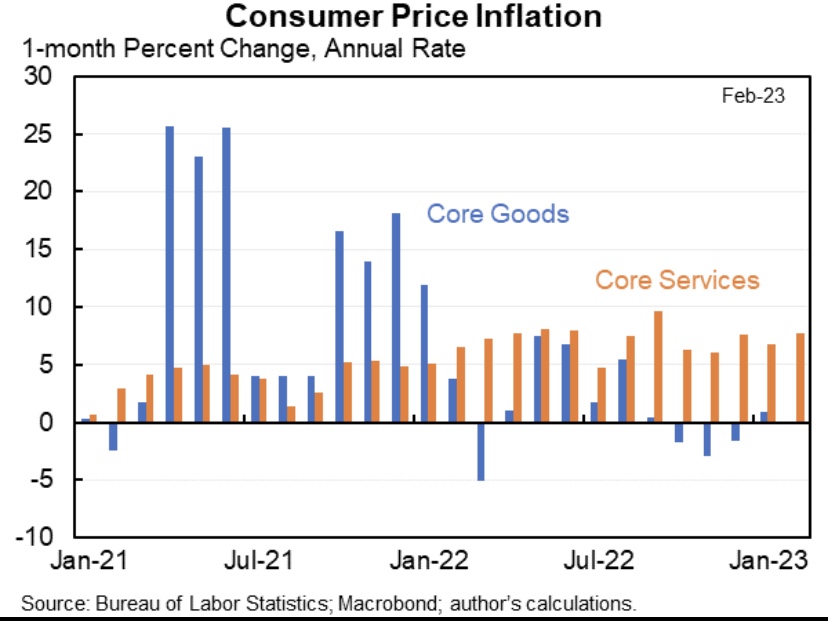
A compelling argument is that the shelter component of the CPI is overstating services inflation, and it’s weighted at more than one-third of the overall index. CPI shelter costs are known as “owner’s equivalent rent” (OER), which is based on a survey question of homeowners as to the rents they think they could command, and it is subject to a fairly long lag. Actual rent inflation has slowed sharply since last summer, so the shelter component is likely to relieve pressure on CPI inflation (and the Fed) in coming months. Nevertheless, Furman points out that CPI inflation over the past 3 -4 months was up even when housing is excluded. Substituting a private “new rent” measure of housing costs for OER would bring measured inflation in services closer the Fed’s comfort zone, however.
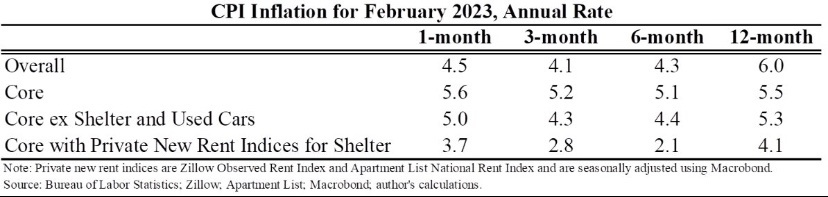
The Fed’s preferred measure of inflation, the deflator for personal consumption expenditures (PCE), uses a much lower weight on housing costs, though it might also overstate inflation within that component. Here’s another chart from the Cleveland Fed:
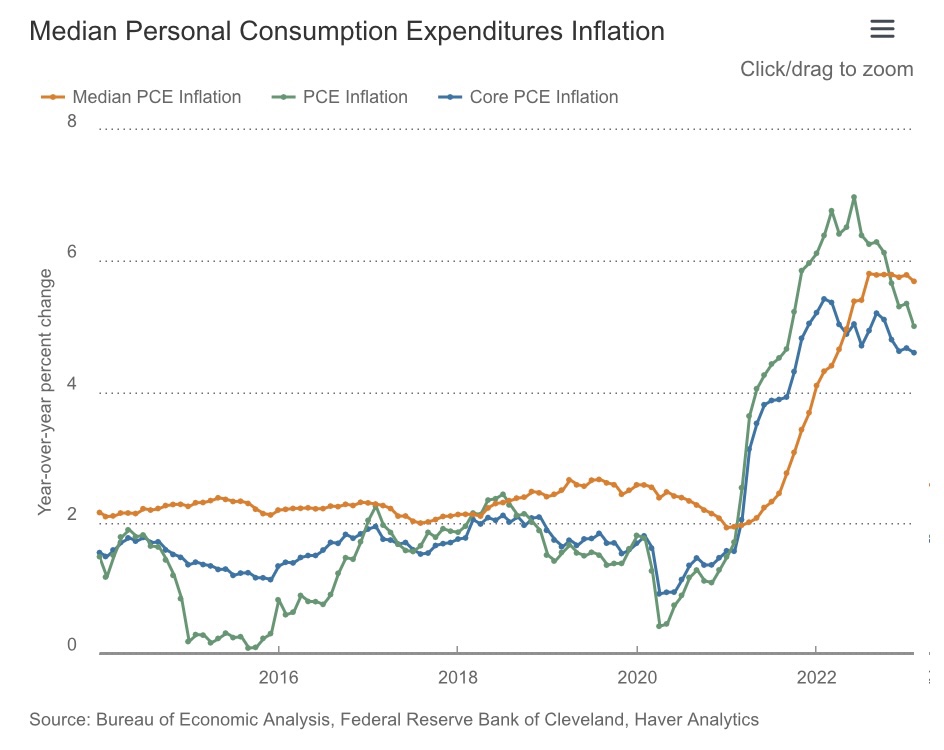
Inflation in the Core PCE deflator, which excludes food and energy prices, looks as if it’s “flattened” as well. This persistence is worrisome because inflation is difficult to stop once it becomes embedded in expectations. That’s exactly what the Fed says it’s trying to prevent.
Rate Targets and Money Growth
Targeting the federal funds rate (FFR) is the Fed’s primary operational method of conducting monetary policy. The FFR is the rate at which banks borrow from one another overnight to meet short-term needs for reserves. In order to achieve price stability, the Fed would do better to focus directly on controlling the money supply. Nevertheless, it has successfully engineered a decline in the money supply beginning last April, and recently the money supply posted year-over-year negative growth.
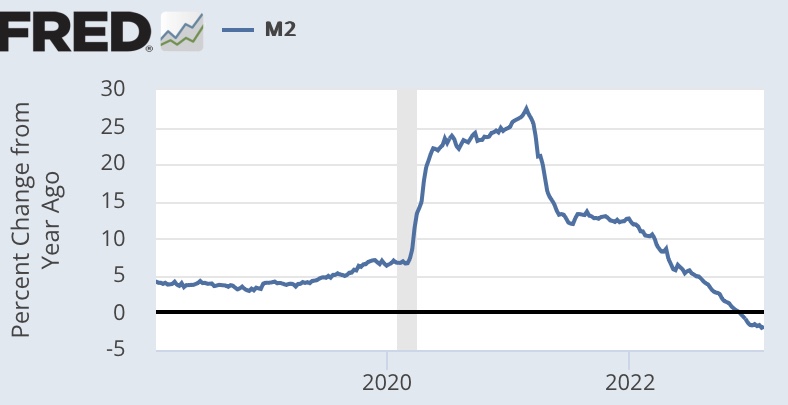
That doesn’t mean money growth has been “optimized” in any sense, but a slowdown in money growth was way overdue after the pandemic money creation binge. You might not like the way the Fed executed the reversal or its operating policy in general, and neither do I, but it did restrain money growth. In that sense, I applaud the Fed for exercising its independence, standing up to the Treasury rather than continuing to monetize yawning federal deficits. That’s encouraging, but at some point the Fed will reverse course and ease policy. We’ll probably hope in vain that the Fed can avoid sending us once again along the path of boom and bust cycles.
In effect, the FFR target is a price control with a dynamic element: the master fiddles with the target whenever economic conditions are deemed to suggest a change. This “controlled” rate has a strong influence on other short-term interest rates. The farther out one goes on the maturity spectrum, however, the weaker is the association between changes in the funds rate and other interest rates. The Fed doesn’t truly “control” those rates of most importance to consumers, corporate borrowers, government borrowers, and investors. It definitely influences those rates, but credit risk, business opportunities, and long-term expectations are often dominant.
The FOMC’s latest rate increase suggests its members don’t expect an immediate downturn in economic activity or a definitive near-term drop in inflation. The Committee may, however, be willing to pause for a period of several meeting cycles (every six weeks) to see whether the “long and variable lags” in the transmission of tighter monetary policy might begin to kick-in. As always, the FOMC’s next step will be “data dependent”, as Chairman Powell likes to say. In the meantime, the economic response to earlier tightening moves is likely to strengthen. Lenders are responding to the earlier rate hikes and reduced lending margins by curtailing credit and attempting to rebuild their own liquidity.
Is It Supply Or Demand?
There’s an ongoing debate about whether monetary policy is appropriate for fighting this episode of inflation. It’s true that monetary policy is ill-suited to addressing supply disruptions, though it can help to stem expectations that might cause supply-side price pressures to feed upon themselves (and prevent them from becoming demand-side pressures). However, profligate fiscal and monetary policy did much to create the current inflation, which is pressure on the demand-side. On that point, David Beckworth leaves little doubt as to where he stands:
“The real world is nominal. And nominal PCE was about $1.6 trillion above trend thru February. Unless one believes in immaculate above-trend spending, this huge surge could 𝙣𝙤𝙩 have happened without support from fiscal and monetary policy.”
In reality, this inflationary episode was borne of a mix of demand and supply-side pressures, and policy either caused or accommodated all of it. Nevertheless, it’s interesting to consider efforts to decompose these forces. This NBER paper attributed about 2/3 of inflation from December 2019 – June 2022 to the demand-side. Given the ongoing tenor of fiscal policy and the typical policy lags, it’s likely that the effects of fiscal and monetary stimulus have persisted well beyond that point. Here is a page from the San Francisco Fed’s site that gives an edge to supply-side factors, as reflected in this breakdown of the Fed’s favorite inflation gauge:
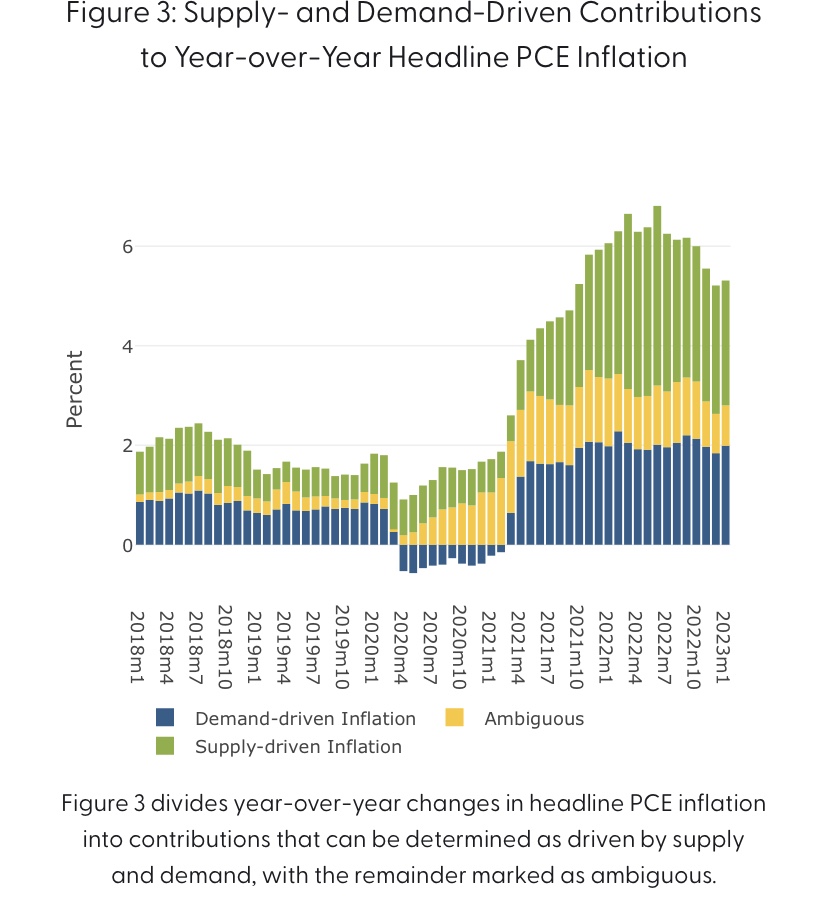
Of course, all of these decompositions are based on assumptions and are, at best, model-based. Nevertheless, to the extent that we still face supply constraints, they would impose limits to the Fed’s ability to manage inflation downward without a “hard landing”.
There’s also no doubt that supply side policies would reduce the kinds of price pressures we’re now experiencing. Regulation and restrictive energy policies under the Biden Administration have eroded productive capacity. These policies could be reversed if political leaders were serious about improving the nation’s economic health.
The Dark Runway Ahead
Will we have a recession? And when? There are no definite signs of an approaching downturn in the real economy just yet. Inventories of goods did account for more than half of the fourth quarter gain in GDP, which may now be discouraging production. There are layoffs in some critical industries such as tech, but we’ll have to see whether there is new evidence of overall weakness in next Friday’s employment report. Real wages have been a little down to flat over the past year, while consumer debt is climbing and real retail sales have trended slightly downward since last spring. Many firms will experience higher debt servicing costs going forward. So it’s not clear that the onset of recession is close at hand, but the odds are good that we’ll see a downturn as the year wears on, especially with credit increasingly scarce in the wake of the liquidity pinch at banks. But no one knows for sure, including the Fed.




