Tags
American Rescue Plan, CBO, Child Tax Credit, CHIPS Act, Debt to GDP, Discretionary Spending, Donald Trump, Emergency Spending, entitlements, Eric Boehm, Inflation Premium, Inflation tax, Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act, Joe Biden, John Cochrane, Medicare, OMB, Promise to Address Comprehensive Toxics Act, Social Security, Soft Default, Student Loan Forgiveness, Supreme Court, Treasury Debt
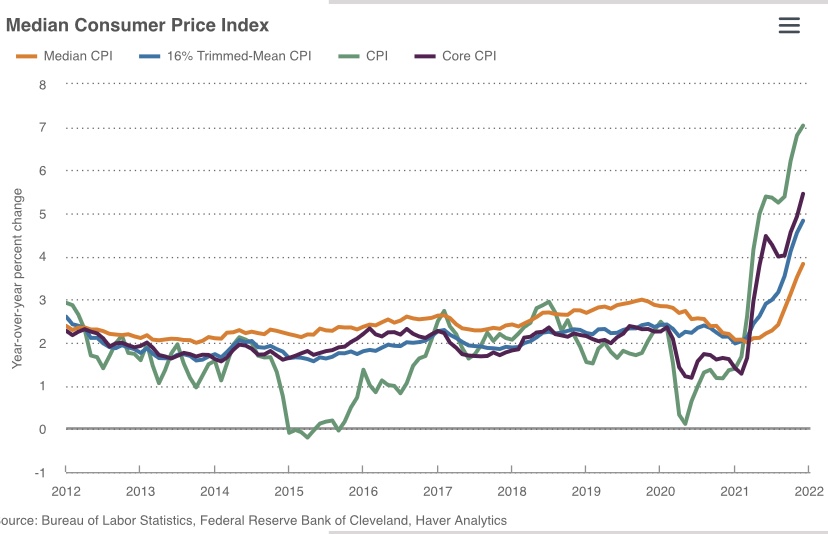
The chart above makes a convincing case that we have a spending problem at the federal level. Really, we’ve had a spending problem for a long time. But at least tax revenue today remains reasonably well-aligned with its 50-year historical average as a share of GDP. Not spending. Even larger deficits opened up during the pandemic and they haven’t returned to pre-pandemic levels.
We’ve seen Joe Biden break spending records. His initiatives, often with questionable merit, have included the $1.8 trillion American Rescue Plan and the nearly $0.8 trillion Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act, along with several other significant spending initiatives such as the Promise to Address Comprehensive Toxics Act and the subsidy-laden CHIPS Act. Meanwhile, emergency spending has become a regular occurrence on Biden’s watch. More recently, he’s made repeated efforts to forgive massive amounts of student loans despite the Supreme Court’s clear ruling that such gifts are unconstitutional.
Indeed, while Biden keeps pretty busy spinning tales of his days driving an 18-wheeler, cannibals devouring his Uncle Bosie Finnegan, his upbringing in black churches, synagogues, or in the Puerto Rican community, he still finds time to dream up ways for the government to spend money it doesn’t have. Or his kindly puppeteers do.
Biden’s New Budget
Eric Boehm expressed wonderment at Biden’s fiscal 2025 budget not long after its release in March. He was also mystified by the gall it took to produce a “fact sheet” in which the White House congratulated itself on fiscal responsibility. That’s how this Administration characterizes deficits projected at $16 trillion over the next ten years. No joke!
Furthermore, the Administration says the record spending will be “paid for”. Well, yes, with tax increases and lots of borrowing! There are a great many fabulist claims made by the White House about the budget. This link from the Office of Management and Budget includes a handy list of propaganda sheets they’ve managed to produce on the virtues of their proposal.
The Congressional Budget Office (CBO) projects ten-year deficits under current law that are $3 trillion higher than Biden’s proposed budget. That’s the basis of the White House’s boast of fiscal restraint. But the difference is basically paid for with a couple of accounting tricks (see below). More charitably, one could say it’s paid for with higher taxes, aided by the assumption of slightly faster economic growth. The latter will be a good trick while undercutting incentives and wages with a big boost to the corporate tax rate.
The revenue projected by the While House from those taxes does not come anywhere close to eliminating the gap shown in the CBO’s chart above. Federal spending under Biden’s budget grows at about 4% annually, just a bit slower than nominal GDP. Thus, the federal share of GDP remains roughly constant and only slightly higher than the CBO’s current projection for 2034. Nevertheless, spending relative to GDP would continue at an historically high rate. Over the next decade, it would average more than 3% higher than its 50-year average. That would be about $1.3 trillion in 2034!
Meanwhile, the ratio of tax revenue to GDP under Biden’s proposal, as they project it, would average slightly higher than its 50-year average, reaching a full percentage point above by 2034 (and higher than the CBO baseline). That’s probably optimistic.
There is little real effort in this budget to reduce federal deficits, with Treasury borrowing rates now near 15-year highs. Interest expense has grown to an alarming share of spending. In fact, it’s expected to exceed spending on defense in 2024! Perhaps not coincidentally, the White House assumes a greater decline in interest rates than CBO over the next 10 years.
Treats or Tricks?
The situation is likely worse than the White House depicts, given that its budget incorporates assumptions that look generous to their claim of fiscal restraint. First, they frontload nondefense discretionary spending, allowing Biden to make extravagant promises for the near-term while pushing off steep declines in budget commitments to the out-years. The sharp reductions in this category of spending pares more than $2 trillion from the 10-year deficit. From the link above:
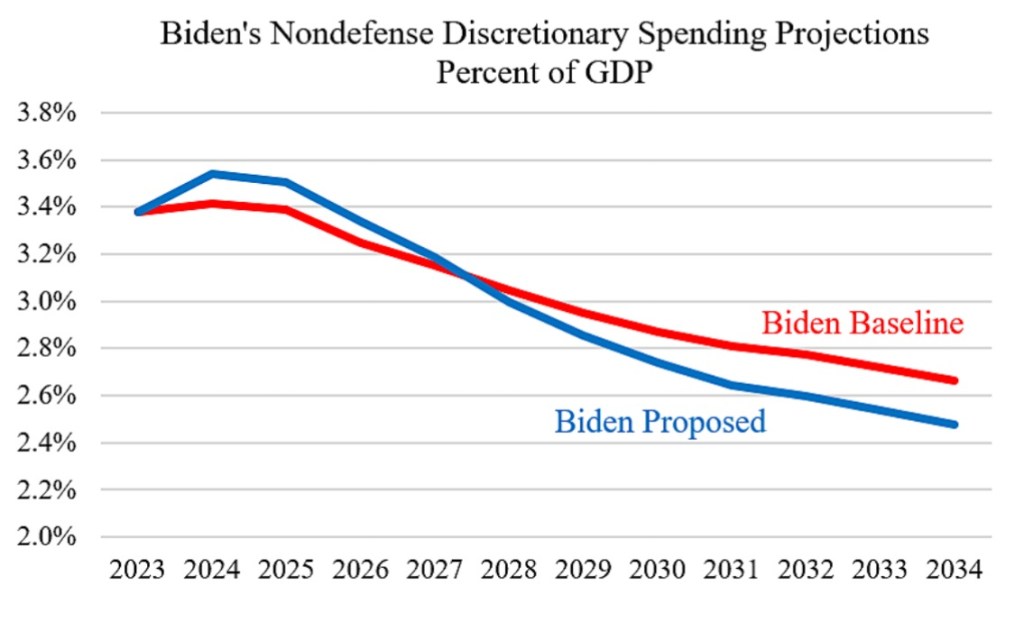
Biden also proposes to restore the expanded the child tax credit — for one year! How handy from a budget perspective: heroically call for an expanded credit (for a year) while avoiding, for the time being, the addition of a couple of trillion to the 10-year deficit.
Code Red
So where does this end? The ratio of federal debt to GDP will resume its ascent after a slight decline from the pandemic high. Here is the CBO’s projection:
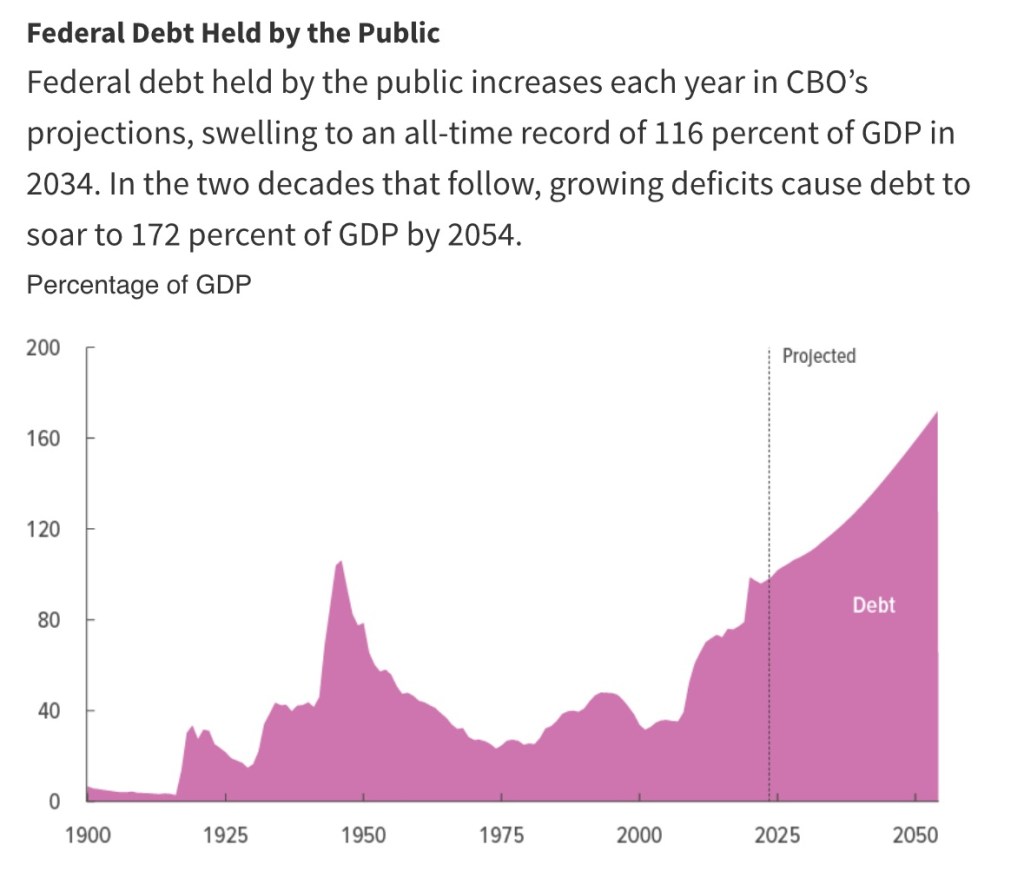
The Biden budget shows a relatively stable debt to GDP ratio through 2034 due to the assumptions of slightly faster GDP growth, lower Treasury borrowing rates, and the aforementioned “fiscal restraint”. But don’t count on it!
The government’s growing dominance over real resources will have negative consequences for growth in the long-term. Purely as a fiscal matter, however, it must be paid for in one of three ways: revenue from explicit taxes, federal borrowing, or an implicit tax on the public more commonly known as the inflation tax. The last two are intimately related.
Bond investors always face at least a small measure of default risk even when lending to the U.S. Treasury. There is almost no chance the government would ever default outright by failing to pay interest or principal when due. However, investors hold an expectation that the value of their bonds will erode in real terms due to inflation. To compensate, they demand an “inflation premium” in the interest rate they earn on Treasury bonds. But an upside surprise to inflation would constitute a “soft default” on the real value of their bonds. This occurred during and after the pandemic, and it was triggered by a burgeoning federal deficit.
Brief Mechanics
John Cochrane has explained the mechanism by which acts of fiscal profligacy can be transmitted to the price of goods. The real value of outstanding federal debt cannot exceed the expected real value of future surpluses (a present value summed across positive and negative surpluses). If expected surpluses are reduced via some emergency or shock such that repayment in real terms is less likely, then the real value of government debt must fall. That means either interest rates or the price level must rise, or some combination of the two.
The Federal Reserve can prevent interest rates from rising (by purchasing bonds and increasing the money supply), but that leaves a higher price level as the only way the real value of debt can come into line. In other words, an unexpected increase in the path of federal deficits would be financed by money printing and an inflation tax. The incidence of this unexpected “implicit” tax falls not only to bondholders, but also on the public at large, who suffer an unexpected decline in the purchasing power of their nominal assets and incomes. This in turn tends to free-up real resources for government absorption.
Government Debt Is Risky
It appears that investors expect the future deficits now projected by the CBO (and the White House) to be paid down someday, to some extent, by future surpluses. That might seem preposterous, but markets apparently aren’t surprised by the projected deficits. After all, fiscal policy decisions can change tremendously over the course of a few years. But it still feels like excessive optimism. Whatever the case, Cochrane cautions that the next fiscal emergency, be it a new pandemic, a war, a recession, or some other crisis, is likely to create another huge expansion in debt and a substantial increase price level. Joe Biden doesn’t seem inclined to put us in a position to deal with that risk very effectively. Unfortunately, it’s not clear that Donald Trump will either. And neither seems inclined to seriously address the insolvencies of Social Security and Medicare. If unaddressed, those mandatory obligations will become real crises over the next decade.