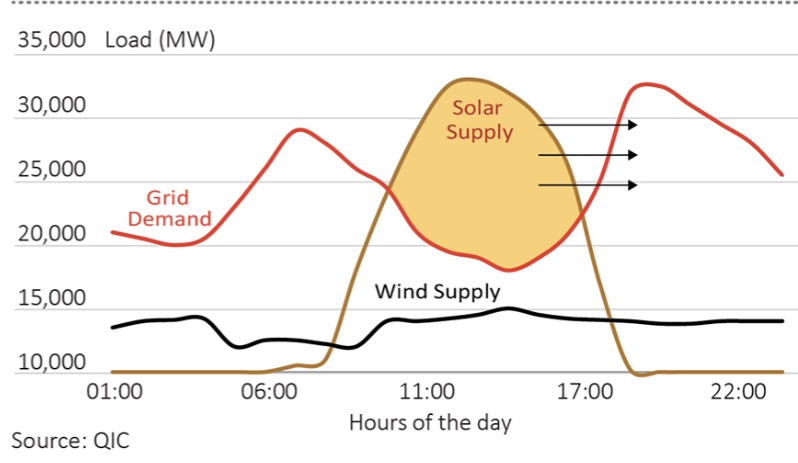
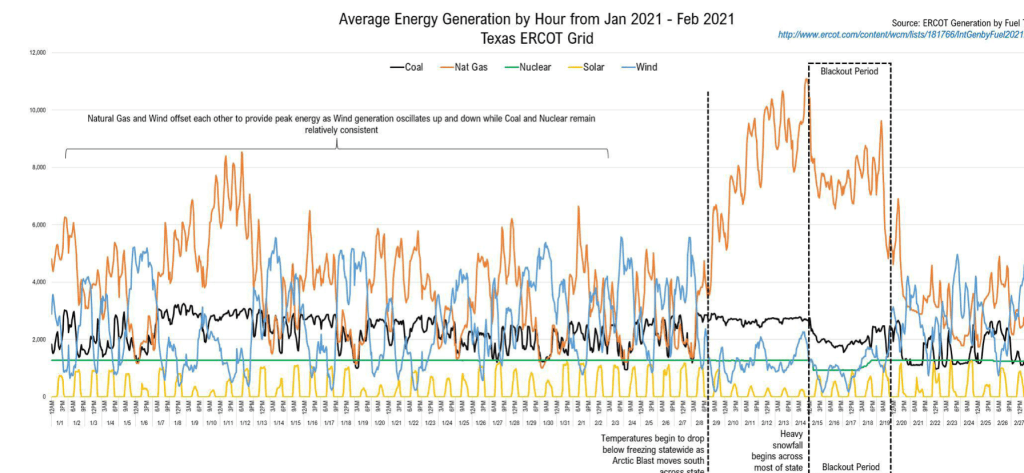
Tags
Assessment Report #6, Carbon Emissions, Cooling the Past, Deforestation, Democratic Republic of Congo, Diablo Canyon, Disparate impact, Economic Development, Energy Poverty, Fossil fuels, Hügo Krüger, Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, IPCC, Jennifer Marohasy, Jim Crow Environmentalism, Joel Kotkin, Judith Curry, Michael Schellenberger, Natural Gas, Net Zero Carbon, Nuclear power, Rare Earth Minerals, Regressive Policy, Remodeled Temperatures, Renewable energy, Steve Koonin

Have no doubt: climate change warriors are at battle with humanity itself, ostensibly on behalf of the natural world. They would have us believe that their efforts to eliminate the use of fossil fuels are necessary to keep our planet from becoming a blazing hothouse. However, the global temperature changes we’ve witnessed over the past 150 years, based on the latest Assessment Report (AR6) from the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), are well within the range of historical variation.
“Remodeled” History
Jennifer Marohasy posted an informative discussion of the IPCC’s conclusions last month, putting them into a broader climatological context and focusing in particular on measurement issues. In short, discussing “global” temperatures with any exactitude is something of a sham. Moreover, the local temperature series upon which the global calculations are based have been “remodeled.” They are not direct observations. I don’t think it’s too crude to say they’ve been manipulated because the changed records are almost always in one direction: to “cool” the past.
Judith Curry is succinct in her criticism of the approach to climate change adopted by alarmist policymakers and many climate researchers:
“In a nutshell, we’ve vastly oversimplified both the problem and its solutions. The complexity, uncertainty, and ambiguity of the existing knowledge about climate change is being kept away from the policy and public debate. The solutions that have been proposed are technologically and politically infeasible on a global scale.”
We need a little more honesty!
The Real Victims
I want to focus here on some of the likely casualties of the war on fossil fuels. Those are, without a doubt, the world’s poor, who are being consigned by climate activists to a future of abject suffering. Joel Kotkin and Hügo Krüger are spot-on in their recent piece on the inhumane implications of anti-carbon ideology.
Energy-poor areas of the world are now denied avenues through which to enhance their peoples’ well being. Attempts to fund fossil-fuel power projects are regularly stymied by western governments and financial institutions in the interests of staving off political backlash from greens. Meanwhile, far more prosperous nations power their economies with traditional carbon-based energy sources. Most conspicuously, China continues to fuel its rapid growth with coal and other fossil fuels, getting little pushback from climate activists. If you’re wondering how the composition of energy output has evolved, this time-lapse chart is a pretty good guide.
One of the most incredible aspects of this situation is how nuclear energy has been spurned, despite its status as a proven and safe solution to carbon-free power. This excellent thread by Michael Schellenberger covers the object lesson in bad public policy offered by the proposed closing of the Diablo Canyon nuclear plant in California.
In both the U.S. and other parts of the world, as Kotkin and Krüger note, it is not just the high up-front costs that lead to the rejection of these nuclear projects. The green lobby and renewable energy interests are now so powerful that nuclear energy is hardly considered. Much the same is true of low-carbon natural gas:
“Sadly, the combination of virtue-signaling companies and directives shaped by green activists in rich countries – often based on wildly exaggerated projections, notes former Barack Obama advisor Steve Koonin – make such a gradual, technically feasible transition all but impossible. Instead, it is becoming increasingly unlikely that developing countries will be able to tap even their own gas.”
Energy is the lifeblood of every economy. Inadequate power creates obstacles to almost any form of production and renders some kinds of production impossible. And ironically, the environmental consequences of “energy poverty” are dire. Many under-developed economies are largely dependent on deforestation for energy. Without a reliable power grid and cheap energy, consumers must burn open fires in their homes for heat and cooking, a practice responsible for 50% of child pneumonia deaths worldwide, according to Kotkin and Krüger.
Green Environmental Degradation
Typically, under-developed countries are reliant on the extraction of natural resources demanded by the developed world:
“The shift to renewables in the West, for example, has increased focus on developing countries as prime sources for critical metals – copper, lithium, and rare-earth minerals, in particular – that could lead to the devastation of much of the remaining natural and agricultural landscape. … Lithium has led to the depletion of water resources in Latin America and the further entrenchment of child labor in the Democratic Republic of the Congoas the search for cobalt continues.”
Unfortunately, the damage is not solely due to dependence on resource extraction:
“The western greens, albeit unintentionally, are essentially turning the Third World into the place they send their dirty work. Already, notes environmental author Mike Shellenberger, Africans are stuck with loads of discarded, highly toxic solar panels that expose both the legions of rag-pickers and the land itself to environmental degradation – all in the name of environmentalism.”
Battering the Poor In the West
Again, wealthy countries are in far better shape to handle the sacrifices required by the climate calamitists, but it still won’t be easy. In fact, lower economic strata will suffer far more than technocrats, managers, and political elites. The environmental left leans on the insidious lever of energy costs in order to reduce demand, but making energy more costly takes a far larger bite out of the budgets of the poor. In another recent piece, “Jim Crow Returns to California,” Kotkin discusses the disparate impact these energy policies have on minorities.
“This surge in prices derives from the state’s obsession — shared by the ruling tech oligarchs — with renewable energy and the elimination of fossil fuels. Yet as a recent Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) report has shown, over-reliance on renewables is costly, because it requires the production of massive (and environmentally unfriendly) battery-storage capacity — the price of which is invariably passed on to the taxpayer.
This is not bad news for the tech oligarchs, who have been prominent among those profiting from ‘clean energy’ investments. But many other Californians, primarily those in the less temperate interior, find themselves falling into energy poverty or are dependent on state subsidies that raise electricity prices for businesses and the middle class. Black and Latino households are already forced to pay from 20 to 43% more of their household incomes on energy than white households. Last year, more than 4 million households in California (30% of the total) experienced energy poverty.”
Kotkin touches on other consequences of these misguided policies to minority and non-minority working people. In addition to jobs lost in the energy sector, a wide variety of wage earners will suffer as their employers attempt to deal with escalating energy costs. The immediate effects are bad enough, but in the long-run the greens’ plans would scale back the economy’s productive machinery in order to eliminate carbon emissions — net zero means real incomes will decline!
Energy costs have a broad impact on consumer’s budgets. Almost every product imaginable is dependent on energy, and consumer prices will reflect the higher costs. In addition, the “green” effort to curtail development everywhere except in high-density transit corridors inflates the cost of housing, inflicting more damage on workers’ standards of living.
Tighten Your Belts
These problems won’t be confined to California if environmental leftists get their version of justice. Be prepared for economic stagnation for the world’s poor and a sharply reduced standard of living in the developed world, but quite unnecessarily. We’ll all pay in the long run, but the poor will pay much more in relative terms.