Tags
Adam Smith, Capitalism, Classical Liberal, Conservatism, Consumer Sovereignty, Corporatism, Free Markets, Freedom of Speech, Friedrich Hayek, Liberalism, Libertarianism, MAGA, monopoly, Monopsony, Nate Silver, Natural Rights, Non-Aggression Principle, Perfect Competition, Progressivism, Property Rights, Public goods, Religious Freedom, Right to Life, Scott Sumner, social engineering, Socialism, State Capacity, State Religion, statism, The Wealth of Nations
Leftism has taken on new dimensions amid its preoccupation with identity politics, victimhood, and “wokeness”. Traditional socialists are still among us, of course, but “wokeists” and “identitarians” have been on the progressive vanguard of late, rooting for the deranged human butchers of Hamas and the dismantling of liberal institutions. This didn’t happen overnight, of course, and traditional socialists are mostly fine with it.
An older story is the rebranding of leftism that took place in the U.S. during the first half of the 20th century, when the word “liberal” was co-opted by leftists. Before that, a liberal orientation was understood to be antithetical to the collectivist mindset long associated with the Left. Note also that liberalism retains its original meaning even today in much of Europe. Often we hear the term “classical liberal” to denote the “original” meaning of liberalism, but the modifier should be wholly unnecessary.
Liberalism Is Not “In-Betweenism”
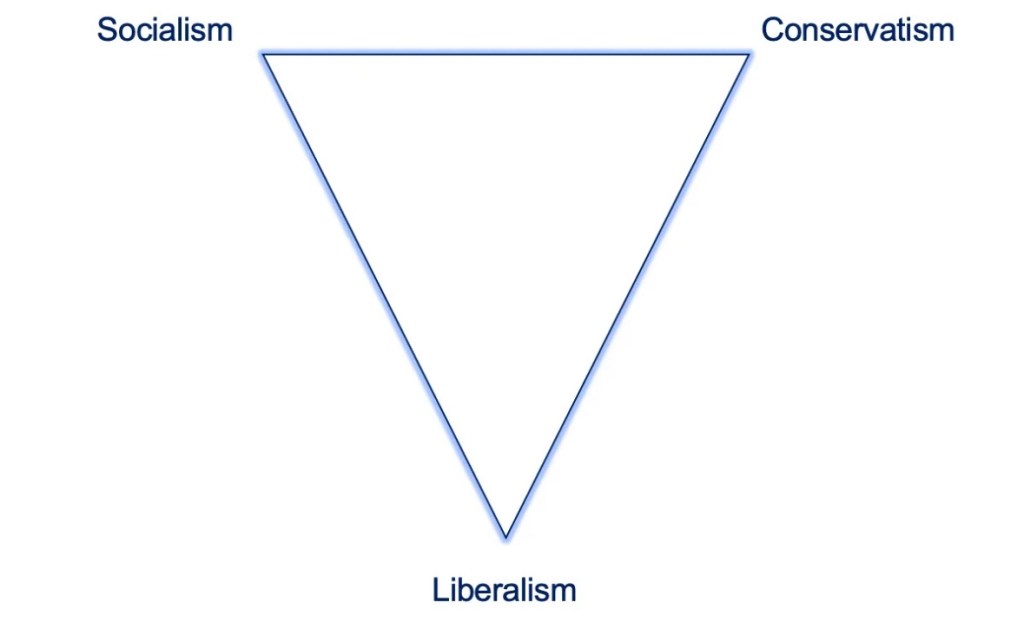
In this vein, Nate Silver presents a basic taxonomy of political orientation in a recent Substack post. It includes the diagram above, which distinguishes between socialism, conservatism, and liberalism. Silver draws on a classic essay written by Friedrich Hayek in 1945, “Why I am Not a Conservative”, in which Hayek discussed the meaning of the word “liberal” (and see here). Liberalism’s true emphasis is a tolerance for individual rights and freedoms, subject to varying articulations of the “nonaggression principle”. That is, “do as you like, but do no harm to others”.
We often see a linear representation distinguishing between so-called progressives on the left and conservatives on the right. Of course, a major hallmark of leftist thinking is extreme interventionism. Leftists or progressives are always keen to detect the slightest whiff of an externality or the slightest departure from the perfectly competitive market ideal. They seem eager to find a role for government in virtually every area of life. While it’s not a limiting case, we can substitute socialism or statism for progressivism on the far left, as Silver does, whereby the state takes primacy in economic and social affairs.
Conservatism, on the other hand, is a deep resistance to change, whether institutional, social, and sometimes economic. Conservatives too often demonstrate a willingness to use the coercive power of the state to prevent change. Hayek noted the willingness of both socialists and conservatives to invoke state power for their own ends.
Similarly, religious conservatives often demand state support beyond that afforded by the freedom to worship in the faith of one’s choice. They might strongly reject certain freedoms held to be fundamental by liberals. Meanwhile, socialists often view mere religious freedom as a threat to the power of the state, or at least they act like it (e.g. see here for an example).
Like conservatives, dedicated statists would doubtless resist change if it meant a loss of their own power. That is, they’d wish to preserve socialist institutions. On this point, witness the vitriol from the Left over what it perceives as threats to the public school monopoly. Witness also the fierce resistance among public employees to reducing the scale of the administrative state, and how advocates of entitlements fiercely resist decreases in the growth rate of those expenditures.
Silver, like Hayek, objects to the traditional, linear framework in which liberals are thought to occupy a range along a line between socialism and conservatism. He objects to that because real liberals value individual liberty as a natural human right, a viewpoint typically abhored by both socialists and conservatives. There is nothing “in between” about it! And of course, conservatives and progressives are equally guilty in their mistaken use of the word “liberal”.
Mapping Political Preferences
Liberty, statism, and conservatism are not exactly orthogonal political dimensions. Larger government almost always means less economic liberty. At a minimum, state dominance implies a social burden associated with public monopoly and monopsony power, as well as tax and welfare-state incentive problems. These features compromise or corrupt the exercise of basic rights. On the other hand, capitalism and its concomitant reliance on consumer sovereignty, individual initiative, free exchange and secure property rights is most in harmony with true liberalism.
For conservatives, resistance to change in support of a traditionally free market economy might offer something of a contradiction. In one sense, it corresponds to upholding market institutions. However, free markets allow new competitors and new technologies to undermine incumbents, who conservatives sometimes wish to defend through regulatory or protectionist measures. And conservatives are almost always too happy to join in the chorus of “price gouging” in response to the healthy operation of the free market in bringing forth supplies.
All that is to say that preferences involving liberty, statism, and traditionalism are not independent of one another. They cannot simply be mapped onto a three-dimensional space. At least the triangular representation gets liberalism out of the middle, but it’s difficult to visualize other ideological positions there. For example, “state religionism” could lie anywhere along the horizontal line at the top or even below it if certain basic liberties are preserved. Facism combines elements of socialism and a deformed version of capitalism that is properly called corporatism, but where would it fall within the triangle?
Big Government Liberalism?
Silver says he leans heavily toward a “big government” version of liberalism, but big government is hard to square with broad liberties. Granted, any well-functioning society must possess a certain level of “state capacity” to defend against private or public violations of individual rights, adjudicate disputes, and provide true public goods. It’s not clear whether Silver’s preferences lie within the bounds of those ambitions. Still, he deserves credit for his recognition that liberalism is wholly different from the progressive, socialist vision. It is the opposite.
The “New” Triangle
Silver attempts to gives the triangular framework a more contemporary spin by replacing conservatism with “MAGA Conservatism” and socialism with “Social Justice Leftism” (SJL), or “wokeism”. Here, I’m treating MAGA as a “brand”. Nothing below is intended to imply that America should not be a great nation.
The MAGA variant of conservatism emphasizes nationalism, though traditional conservatives have never been short on love of nation. For that matter, as a liberal American, it’s easier to forgive nationalist sentiments than it is the “Death to America” refrain we now hear from some SJLs.
The MAGA brand is also centered around a single individual, Donald Trump, whose rhetoric strikes many as nativistic. And Trump is a populist whose policy proposals are often nakedly political and counterproductive.
SJL shares with socialism an emphasis on various forms of redistribution and social engineering, but with a new focus on victimhood based on classes of identity. Of SJL, Silver says:
“Proponents of SJL usually dislike variations on the term ‘woke’, but the problem is that they dislike almost every other term as well. And we need some term for this ideology, because it encompasses quite a few distinctive features that differentiate it both from liberalism and from traditional, socialist-inflected leftism. In particular, SJL is much less concerned with the material condition of the working class, or with class in general. Instead, it is concerned with identity — especially identity categories involving race, gender and sexuality, but sometimes also many others as part of a sort of intersectional kaleidoscope.”
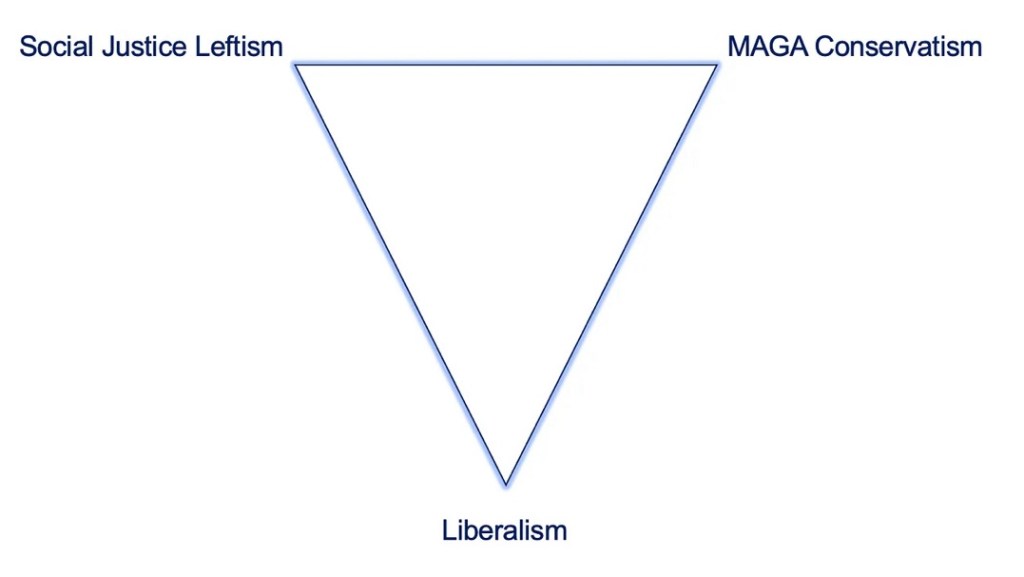
The gulf between liberals and SJLs couldn’t be wider on issues like free speech and “equity”, and equality of opportunity. MAGAns, on the other hand, have some views on individual rights and responsibility that are largely consistent with liberals, but reflexive populism often leads them to advocate policies protecting rents, corporate welfare, and protectionism.
Divided Liberalism
Liberalism emphasizes limited government, individual autonomy, and free exchange. However, there are issues upon which true liberals are of divided opinion. For example, one such area of controversy is the conflict between a woman’s right to choose and the fetal right to life. Many true liberals disagree over whether the rights of a fetus outweigh its mother’s right to choose, but most would concede that the balance shifts to the fetus at some point well short of birth (putting aside potential dangers to the mother’s life). Open borders is another area that can divide true liberals. On one side, the right to unrestricted mobility is thought to supersede any public interest in enforcing borders and limiting the flow of immigrants. On the other side, questions of national sovereignty, national security, as well as social and state capacity to absorb immigrants take primacy.
Don’t Call Lefties “Liberal”… They’re Not!
True liberalism (including most strains of libertarianism) recognizes various roles that a well-functioning state should play, but it also recognizes the primacy of the individual and individual rights as a social underpinning. As Hayek noted, true liberals are not resistant to change per se, unlike conservatives. But modern progressives demand changes of the worst kind: that the state should intervene to pursue their favored objectives, laying claim to an ever-greater share of private resources. This requires government coercion on a massive scale, the antithesis of liberalism. It’s time to recognize that “progressives” aren’t liberals in any sense of the word. For that matter, they don’t even stand for progress.
I’ll close with a quote from Adam Smith that I cribbed from Scott Sumner. Unfortunately, Sumner does not give the full reference, but I’ll take his word that Smith wrote this 20 years before the publication of The Wealth of Nations:
“Little else is requisite to carry a state to the highest degree of opulence from the lowest barbarism, but peace, easy taxes, and a tolerable administration of justice; all the rest being brought about by the natural course of things. All governments which thwart this natural course, which force things into another channel, or which endeavour to arrest the progress of society at a particular point, are unnatural, and to support themselves are obliged to be oppressive and tyrannical.”






