Tags
1619 Project, Abolition, Antebellum South, Capital Deepening, Civil War, Coercion, Emancipation, Juneteenth, Nathan Nunn, Phil Magness, Redistribution, Reparatiins, Rod D. Martin, Slavery, Welfare Loss
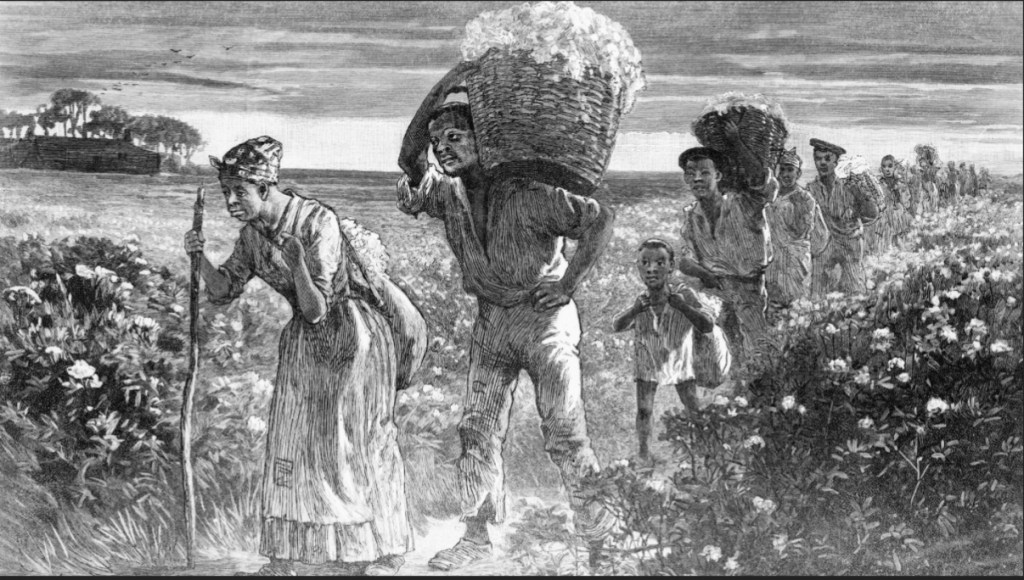

The Juneteenth holiday (June 19th) marks the anniversary of the abolition of slavery in the U.S. It should be viewed as a celebration of basic human rights. However, in purely economic terms, slavery was (and still is in many parts of the world) a complete revocation of property rights (self-ownership). But not only was slave-holding the worst sort of theft, it represented a total suspension of the labor market mechanism and had dire consequences for long-term economic development, especially in the south.
Government sanction of slaveholding in the southern U.S. and an extremely low effective wage for slaves promoted an excessive and inefficient dependence on, and utilization of, the low-cost input: slave labor. As a result, slavery created an obstacle to economic development, innovation, and capital deepening. The overall impact on the U.S. was to reduce economic welfare and development, and the dysfunction was obviously concentrated in the south.
That hasn’t stopped some activists from making the claim that slavery enabled the success of American capitalism. For example, this book contends that:
“… the expansion of slavery in the first eight decades after American independence drove the evolution and modernization of the United States.“
The so-called 1619 Project has promoted this narrative as well. Interestingly, this is similar to claims made prior to emancipation by defenders of slavery.
Of course, one can’t overemphasize the injustices suffered by American slaves, like those of other enslaved peoples throughout history. But it is foolhardy to attribute the long-term economic success of the American economy to slavery. Even today, 160 years after emancipation, it’s a safe bet that most Americans would be better off without its legacy.
To be clear I’ll outline several assertions I’m making here. First, if slaves had been free workers, they would have enjoyed freedoms and captured the value of their labors from the start. (Though it is not clear how many Africans would have come to America voluntarily as free workers, had they been given the opportunity. Some, however, were already enslaved.)
Under this counterfactual, more efficient pricing of labor would have led to deeper capital. At the same time, while many black non-slaves would still have worked in agriculture, blacks would have been more dispersed occupationally, working at tasks that best suited individual skills. The resulting efficiency gains would have been magnified by virtue of working in combination with more capital assets, enhancing productivity. And these workers would have been free to build their own human capital through education and work experience. Meanwhile, government would not have wasted resources enforcing slave ownership, and plantation owners (and other slave holders) would have made more rational resource allocation decisions. All these factors would have produced a net gain in welfare and improved economic development from at least the time of the nation’s founding.
There is no question that enslavement and the welfare losses suffered by slaves (and many of their descendants) far outweighed the gains captured by those who employed slave labor, as well as those who consumed or otherwise made use of the product of slave labor. A proper economic accounting of these losses acknowledges that slaves were denied their worker surplus and their ability to earn an opportunity cost, and they were often punished or tortured as a means of coercing greater effort. This serves to emphasize the implausibility of the argument that the America reaped net economic benefits from slavery.
Slavery was so powerful an institution that it permeated southern culture and perceptions of status. Wealth was tied-up in slave-chattel, and the free labor made for a handsome return on investment. Thus, both economic and cultural factors acted to lock producers into an unending series of short-run input decisions.
Furthermore, as Phil Magness explains in a letter to the Editor in the Wall Street Journal:
“… slavery’s economics … largely depended on government support. Fugitive slave patrols, military expenditures to fend off the threat of slave revolts and censorship of abolitionist materials by the post office were necessary to secure the institution’s economic position. These policies transferred the burden of enforcing the slave system from the plantation masters on to the taxpaying public.“
Meanwhile, the distortions to the cost of labor slowed the adoption of a variety of production techniques, including horse-drawn cultivators and harrows, steel plows, and steam-powered machinery. In other words, planters had little incentive to modernize production. Other technologies commonly used in the north during that era could have been applied in the south, but only to its much smaller share of acreage dedicated to grain crops.
Southern agricultural practices were “frozen in place”, as Rod D. Martin puts it. Ultimately, had southern planters adopted labor-saving technologies, and had southern governments shifted resources away from protecting slavery as an institution toward more diversified economic development, the antebellum economy would have experienced more rapid growth.
Growth in demand for cotton exports was certainly a boon to the south during the years preceding the Civil War, but the reliance on cotton was such that the southern economy was heavily exposed to risks of draught and other shocks. Furthermore, the lack of industrialization meant that southern states captured little of the final value of the textiles produced with cotton. The inadequacy of transportation infrastructure in the south was another serious detriment to long-term growth.
The work of Nathan Nunn, which is cited by Martin, generally supports the hypothesis that slavery retards economic growth. Nunn found a strong negative correlation between slave use and later economic development across different “New World” economies, as well as U.S. states and counties.
Martin goes so far as to say that the Union’s victory over the Confederacy was due in large part to economic under-development attributable to slavery in the south. That narrative has been challenged by a few scholars who claimed that the south was actually wealthier than the north. The owners of large southern plantations were quite well off, of course, but estimates of their wealth are unreliable, and in any case slaves themselves were highly illiquid “assets”. That meant planters would have been hard pressed to raise the capital needed for investment in labor-saving technologies, even if they’d had proper incentives to do so.
On the whole, there is no question the north was far more industrialized, diversified, and prosperous than the south. It was also much larger in terms of population and total output. Thus, Martin’s assertion that slavery explains why the south lost the Civil War is probably a bit too sweeping.
Nevertheless, the slavery “ecosystem” helps explain the south’s historic under-development. It was characterized by artificially cheap labor, illiquidity, a lack of diversification, a rigid social hierarchy based on the aberrant ownership of human chattel, and state subsidization of slave owners. These conditions restricted the supply of investment capital in the south. This was a drag on economic development before the Civil War. Those characteristics, along with the direct costs of the war itself, go a long way toward explaining the south’s lengthy period of depressed conditions after the Civil War as well.
It’s certainly not a knock on the slave population prior to emancipation to say that they were not responsible for the success of American capitalism. It’s a knock on the institution of slavery itself. Our wealth and the bounties produced by today’s economy are not supercharged by the efforts of slave labor in the distant past. If anything, our prosperity would be far greater had slavery never been practiced on U.S. soil.
I oppose reparations as a form of redistribution partly because most prospective payers today have absolutely no connection to slave-holding in antebellum America. It’s ironic that certain activists now argue for reparations based on imagined economic benefits once used to defend slavery itself.