Tags
Anthropocene, Beamed Solar Power, Carbon Capture, Carbon Forcings, Cliff Mass, Common Pool Resources, Elinor Ostrom, Externalities, Fusion Power, Geoengineering, Geothermal Power, global warming, Heat Islands, Interspecies Justice, IPCC, Lula Da Silva, Munger Test, Nuclear power, Orbital Solar Collection, Paris Climate Accords, Planetary Commons, Polycentrism, Private Goods, Property Rights, Public goods, Redistribution, Solar Irradiance, Spillovers, Tipping points

We all share Planet Earth as our home, so there’s a strong sense in which it qualifies as a “commons”. That’s one sensible premise of a new paper entitled “The planetary commons: A new paradigm for safeguarding Earth-regulating systems in the Anthropocene”. The title is a long way of saying that the authors desire broad-based environmental regulation, and that’s what ultimately comes across.
First, a preliminary issue: many resources qualify as commons in the very broadest sense, yet free societies have learned over time that many resources are used much more productively when property rights are assigned to individuals. For example, modern agriculture owes much to defining exclusive property rights to land so that conflicting interests don’t have to compete (e.g,, the farmer and the cowman). Federal land is treated as a commons, however. There is a rich history on the establishment of property rights, but within limits, the legal framework in place can define whether a resource is treated as a commons, a club good, or private property. The point here is that there are substantial economic advantages to preserving strong property rights, rather than treating all resources as communal.
The authors of the planetary commons (PC) paper present a rough sketch for governance over use of the planet’s resources, given their belief that a planetary crisis is unfolding before our eyes. The paper has two main thrusts as I see it. One is to broadly redefine virtually all physical resources as common pool interests because their use, in the authors’ view, may entail some degree of external cost involving degradation of the biosphere. The second is to propose centralized, “planetary” rule-making over the amounts and ways in which those resources are used.
It’s an Opinion Piece
The PC paper is billed as the work product of a “collaborative team of 22 leading international researchers”. This group includes four attorneys (one of whom was a lead author) and one philosopher. Climate impact researchers are represented, who undoubtedly helped shape assumptions about climate change and its causes that drive the PC’s theses. (More on those assumptions in a section below.) There are a few social scientists of various stripes among the credited authors, one meteorologist, and a few “sustainability”, “resilience”, and health researchers. It’s quite a collection of signees, er… “research collaborators”.
Grabby Interventionists
The reasoning underlying a “planetary commons” (PC) is that the planet’s biosphere qualifies as a commons. The biosphere must include virtually any public good like air and sunshine, any common good like waterways, or any private good or club good. After all, any object can play host to tiny microbes regardless of ownership status. So the PC authors characterization of the planet’s biosphere as a commons is quite broad in terms of conventional notions of resource attributes.
We usually think of spillover or external costs as arising from some use of a private resource that imposes costs on others, such as air or water pollution. However, mere survival requires that mankind exploit both public and non-public resources, acts that can always be said to impact the biosphere in some way. Efforts to secure shelter, food, and water all impinge on the earth’s resources. To some extent, mankind must use and shape the biosphere to succeed, and it’s our natural prerogative to do so, just like any other creature in the food chain.
Even if we are to accept the PC paper’s premise that the entire biosphere should be treated is a commons, most spillovers are de minimus. From a public policy perspective, it makes little sense to attempt to govern over such minor externalities. Monitoring behavior would be costly, if not impossible, at such an atomistic level. Instead, free and civil societies rely on a high degree of self-governance and informal enforcement of ethical standards to keep small harms to a minimum.
Unfortunately, the identification and quantification of meaningful spillover costs is not always clear-cut. This has led to an increasingly complex regulatory environment, an increasingly litigious business environment, and efforts by policymakers to manage the detailed inputs and outputs of the industrial economy.
All of that is costly in its own right, especially because the activities giving rise to those spillovers often enable large welfare enhancements. Regulators and planners face great difficulties in estimating the costs and benefits of various “correctives”. The very undertaking creates risk that often exceeds the cost of the original spillover. Nevertheless, the PC paper expands on the murkiest aspects of spillover governance by including “… all critical biophysical Earth-regulating systems and their functions, irrespective of where they are located…” as part of a commons requiring “… additional governance arrangements….”
Adoption of the PC framework would authorize global interventions (and ultimately local interventions, including surveillance) on a massive scale based on guesswork by bureaucrats regarding the evolution of the biosphere.
Ostrom Upside Down
Not only would the PC framework represent an expansion of the grounds for intervention by public authorities, it seeks to establish international authority for intervention into public and private affairs within sovereign states. The authors attempt to rationalize such far-reaching intrusions in a rather curious way:
“Drawing on the legacy of Elinor Ostrom’s foundational research, which validated the need for and effectiveness of polycentric approaches to commons governance (e.g., ref. 35, p. 528, ref. 36, p. 1910), we propose that a nested Earth system governance approach be followed, which will entail the creation of additional governance arrangements for those planetary commons that are not yet adequately governed.”
Anyone having a passing familiarity with Elinor Ostrom’s work knows that she focused on the identification of collaborative solutions to common goods problems. She studied voluntary and often strictly private efforts among groups or communities to conserve common pool resources, as opposed to state-imposed solutions. Ostrom accepted assigned rights and pricing solutions to managing common resources, but she counseled against sole reliance on market-based tools.
Surely the PC authors know they aren’t exactly channeling Ostrom:
“An earth system governance approach will require an overarching global institution that is responsible for the entire Earth system, built around high-level principles and broad oversight and reporting provisions. This institution would serve as a universal point of aggregation for the governance of individual planetary commons, where oversight and monitoring of all commons come together, including annual reporting on the state of the planetary commons.”
Polycentricity was used by Ostrom to describe the involvement of different, overlapping “centers of authority”, such as individual consumers and producers, cooperatives formed among consumers and producers, other community organizations, local jurisdictions, and even state or federal regulators. Some of these centers of authority supersede others in various ways. For example, solutions developed by cooperatives or lower centers of authority must align with the legal framework within various government jurisdictions. However, as David Henderson has noted, Ostrom observed that management of pooled resources at lower levels of authority was generally superior to centralized control. Henderson quotes Ostrom and a co-author on this point:
“When users are genuinely engaged in decisions regarding rules affecting their use, the likelihood of them following the rules and monitoring others is much greater than when an authority simply imposes rules.”
The authors of the PC have something else in mind, and they bastardize the spirit of Ostrom’s legacy in the process. For example, the next sentence is critical for understanding the authors’ intent:
“If excessive emissions and harmful activities in some countries affect planetary commons in other areas—for example, the melting of polar ice—strong political and legal restrictions for such localized activities would be needed.”
Of course, there are obvious difficulties in measuring impacts of various actions on polar ice, assigning responsibility, and determining the appropriate “restrictions”. But in essence, the PC paper advocates for a top-down model of governance. Polycentrism is thus reduced to “you do as we say”, which is not in the spirit of Ostrom’s research.
Planetary Governance
Transcending national sovereignty on questions of the biosphere is key to the authors’ ambitions. At a bare minimum, the authors desire legally-binding commitments to international agreements on environmental governance, unlike the unenforceable promises made for the Paris Climate Accords:
“At present, the United Nations General Assembly, or a more specialized body mandated by the Assembly, could be the starting point for such an overarching body, even though the General Assembly, with its state-based approach that grants equal voting rights to both large countries and micronations, represents outdated traditions of an old European political order.”
But the votes of various “micronations” count for zilch when it comes to real “claims” on the resources of other sovereign nations! Otherwise, there is nothing “voluntary” about the regime proposed in the PC paper.
“A challenge for such regimes is to duly adapt and adjust notions of state sovereignty and self-determination, and to define obligations and reciprocal support and compensation schemes to ensure protection of the Earth system, while including comprehensive stewardship obligations and mandates aimed at protecting Earth-regulating systems in a just and inclusive way.”
So there! The way forward is to adopt the broadest possible definition of market failure and global regulation of any and all private activity touching on nature in any way. And note here a similarity to the Paris Accords: achieving commitments would fall to national governments whose elites often demonstrate a preference for top-down solutions.
Ah Yes, Redistribution
It should be apparent by now that the PC paper follows a now well-established tradition in multi-national climate “negotiations” to serve as subterfuge for redistribution (which, incidentally, includes the achievement of interspecies justice):
“For instance, a more equal sharing of the burdens of climate stabilization would require significant multilateral financial and technology transfers in order not to harm the poorest globally (116).”
The authors insist that participation in this governance would be “voluntary”, but the following sentence seems inconsistent with that assurance:
“… considering that any move to strengthen planetary commons governance would likely be voluntarily entered into, the burdens of conservation must be shared fairly (115).”
Wait, what? “Voluntary” at what level? Who defines “fairness”? The authors approvingly offer this paraphrase of the words of Brazilian President Lula da Silva,
“… who affirmed the Amazon rainforest as a collective responsibility which Brazil is committed to protect on behalf of all citizens around the world, and that deserves and justifies compensation from other nations (117).”
Let Them Eat Cake
Furthermore, PC would require de-growth and so-called “sufficiency” for thee (i.e., be happy with less), if not for those who’ll design and administer the regime.
“… new principles that align with novel Anthropocene dynamics and that could reverse the path-dependent course of current governance. These new principles are captured under a new legal paradigm designed for the Anthropocene called earth system law and include, among others, the principles of differentiated degrowth and sufficiency, the principle of interconnectivity, and a new planetary ethic (e.g., principle of ecological sustainability) (134).”
If we’re to take the PC super-regulators at their word, the regulatory regime would impinge on fertility decisions as well. Just who might we trust to govern humanity thusly? If we’re wise enough to apply the Munger Test, we wouldn’t grant that kind of power to our worst enemy!
Global Warmism
The underlying premise of the PC proposal is that a global crisis is now unfolding before our eyes: anthropomorphic global warming (AGW). The authors maintain that emissions of carbon dioxide are the cause of rising temperatures, rapidly rising sea levels, more violent weather, and other imminent disasters.
“It is now well established that human actions have pushed the Earth outside of the window of favorable environmental conditions experienced during the Holocene…”
“Earth system science now shows that there are biophysical limits to what existing organized human political, economic, and other social systems can appropriate from the planet.”
For a variety of reasons, both of these claims are more dubious than one might suppose based on popular narratives. As for the second of these, mankind’s limitless capacity for innovation is a more powerful force for sustainability than the authors would seem to allow. On the first claim, it’s important to note that the PC paper’s forebodings are primarily based on modeled, prospective outcomes, not historical data. The models are drastically oversimplified representations of the earth’s climate dynamics driven by exogenous carbon forcing assumptions. Their outputs have proven to be highly unreliable, overestimating warming trends almost without exception. These models exaggerate climate sensitivity to carbon forcings, and they largely ignore powerful natural forcings such as variations in solar irradiance, geological heating, and even geological carbon forcings. The models are also notorious for their inadequate treatment of feedback effects from cloud cover. Their predictions of key variables like water vapor are wildly in error.
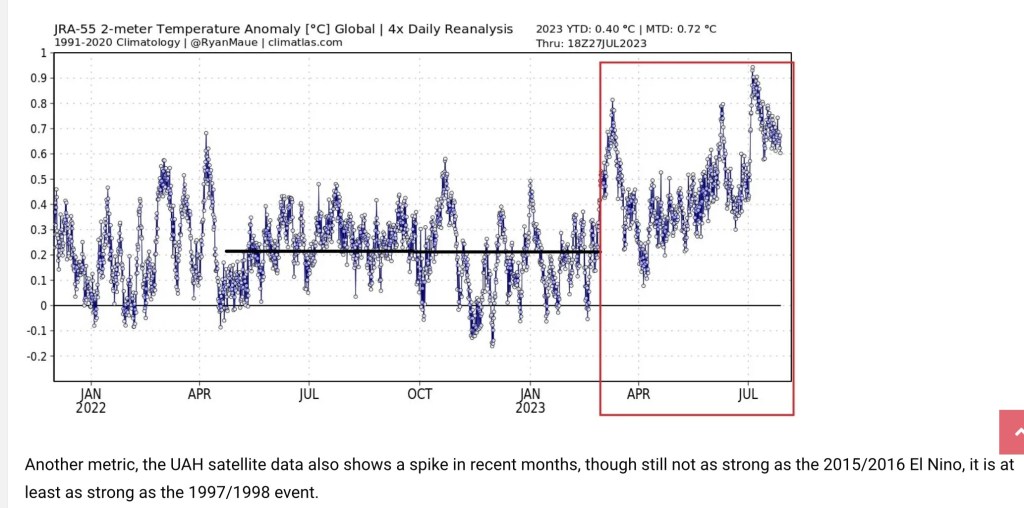
The measurement of the so-called “global temperature” is itself subject to tremendous uncertainty. Weather stations come and go. They are distributed very unevenly across land masses, and measurement at sea is even sketchier. Averaging all these temperatures would be problematic even if there were no other issues… but there are. Individual stations are often sited poorly, including distortions from heat island effects. Aging of equipment creates a systematic upward bias, but correcting for that bias (via so-called homogenization) causes a “cooling the past” bias. It’s also instructive to note that the increase in global temperature from pre-industrial times actually began about 80 years prior to the onset of more intense carbon emissions in the 20th century.
Climate alarmists often speak in terms of temperature anomalies, rather than temperature levels. In other words, to what extent do temperatures differ from long-term averages? The magnitude of these anomalies, using the past several decades as a base, tend to be anywhere from zero degrees to well above one degree Celsius, depending on the year. Relative to temperature levels, the anomalies are a small fraction. Given the uncertainty in temperature levels, the anomalies themselves are dwarfed by the noise in the original series!
Pick Your Own Tipping Point
It seems that “tipping point” scares are heavily in vogue at the moment, and the PC proposal asks us to quaff deeply of these narratives. Everything is said to be at a tipping point into irrecoverable disaster that can be forestalled only by reforms to mankind’s unsustainable ways. To speak of the possibility of other causal forces would be a sacrilege. There are supposed tipping points for the global climate itself as well as tipping points for the polar ice sheets, the world’s forests, sea levels and coastal environments, severe weather, and wildlife populations. But none of this is based on objective science.
For example, the 1.5 degree limit on global warming is a wholly arbitrary figure invented by the IPCC for the Paris Climate Accords, yet the authors of the PC proposal would have us believe that it was some sort of scientific determination. And it does not represent a tipping point. Cliff Mass explains that climate models do not behave as if irreversible tipping points exist.
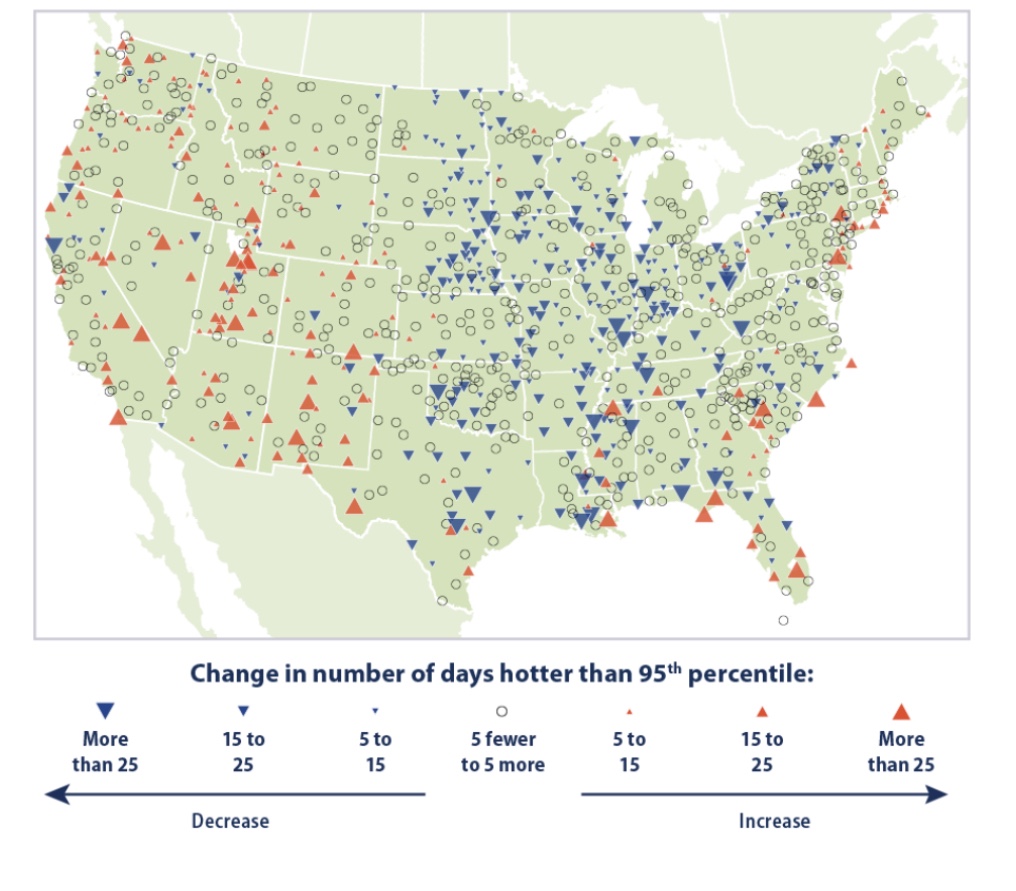
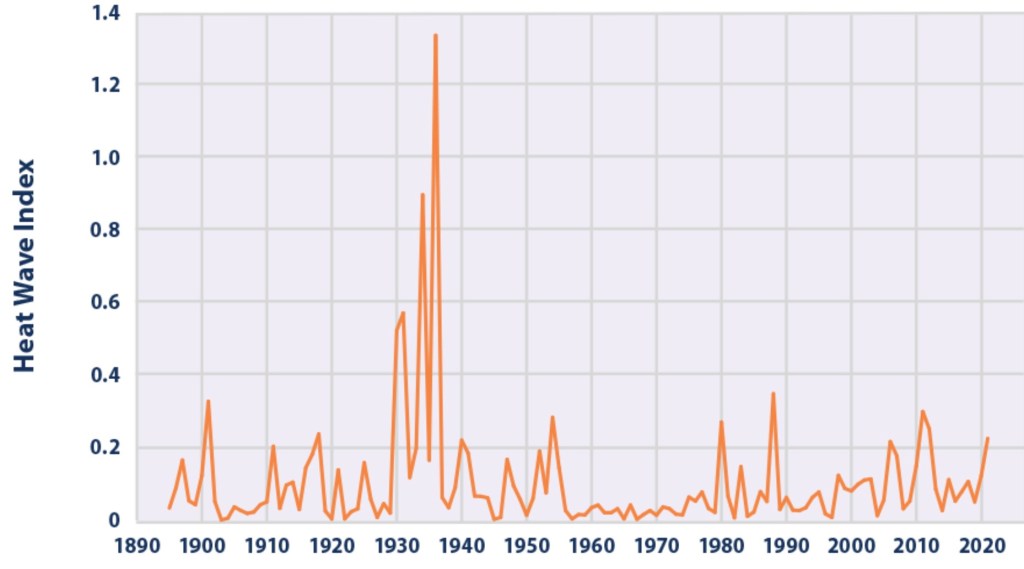
Consider also that there has been absolutely no increase in the frequency or intensity of severe weather.
Likewise, the rise of sea levels has not accelerated from prior trends, so it has nothing to do with carbon forcing.
One thing carbon forcings have accomplished is a significant greening of the planet, which if anything bodes well for the biosphere
What about the disappearance of the polar ice sheets? On this point, Cliff Mass quotes Chapter 3 of the IPCC’s Special Report on the implications of 1.5C or more warming:
“there is little evidence for a tipping point in the transition from perennial to seasonal ice cover. No evidence has been found for irreversibility or tipping points, suggesting that year-round sea ice will return given a suitable climate.”
The PC paper also attempts to connect global warming to increases in forest fires, but that’s incorrect: there has been no increasing trend in forest fires or annual burned acreage. If anything, trends in measures of forest fire activity have been negative over the past 80 years.
Concluding Thoughts
The alarmist propaganda contained in the PC proposal is intended to convince opinion leaders and the public that they’d better get on board with draconian and coercive steps to curtail economic activity. They appeal to the sense of virtue that must always accompany consent to authoritarian action, and that means vouching for sacrifice in the interests of environmental and climate equity. All the while, the authors hide behind a misleading version of Elinor Ostrom’s insights into the voluntary and cooperative husbandry of common pool resources.
One day we’ll be able to produce enough carbon-free energy to accommodate high standards of living worldwide and growth beyond that point. In fact, we already possess the technological know-how to substantially reduce our reliance on fossil fuels, but we lack the political will to avail ourselves of nuclear energy. With any luck, that will soften with installations of modular nuclear units.
Ultimately, we’ll see advances in fusion technology, beamed non-intermittent solar power from orbital collection platforms, advances in geothermal power, and effective carbon capture. Developing these technologies and implementing them at global scales will require massive investments that can be made possible only through economic growth, even if that means additional carbon emissions in the interim. We must unleash the private sector to conduct research and development without the meddling and clumsy efforts at top-down planning that typify governmental efforts (including an end to mandates, subsidies, and taxes). We must also reject ill-advised attempts at geoengineered cooling that are seemingly flying under the regulatory radar. Meanwhile, let’s save ourselves a lot of trouble by dismissing the interventionists in the planetary commons crowd.