Tags
Abundance Agenda, Alex Tabarrok, Baumol's Disease, Beethoven’s String Quartet No. 14, CHIPS, competition, Consumer Sovereignty, Education Cost, Education Grants, Education Productivity, Employer-Paid Coversge, Eric Helland, Exchange subsidies, health care costs, Health Care Productivity, Industrial Concentration, Mark Perry, Medicaid, Medical Technology, Medicare, Obamacare, Peter Suderman, Relative Prices, Slow Productivity Growth, Student Loans, Subsidies, Tax Subsidies, third-party payments, Willian Baumol
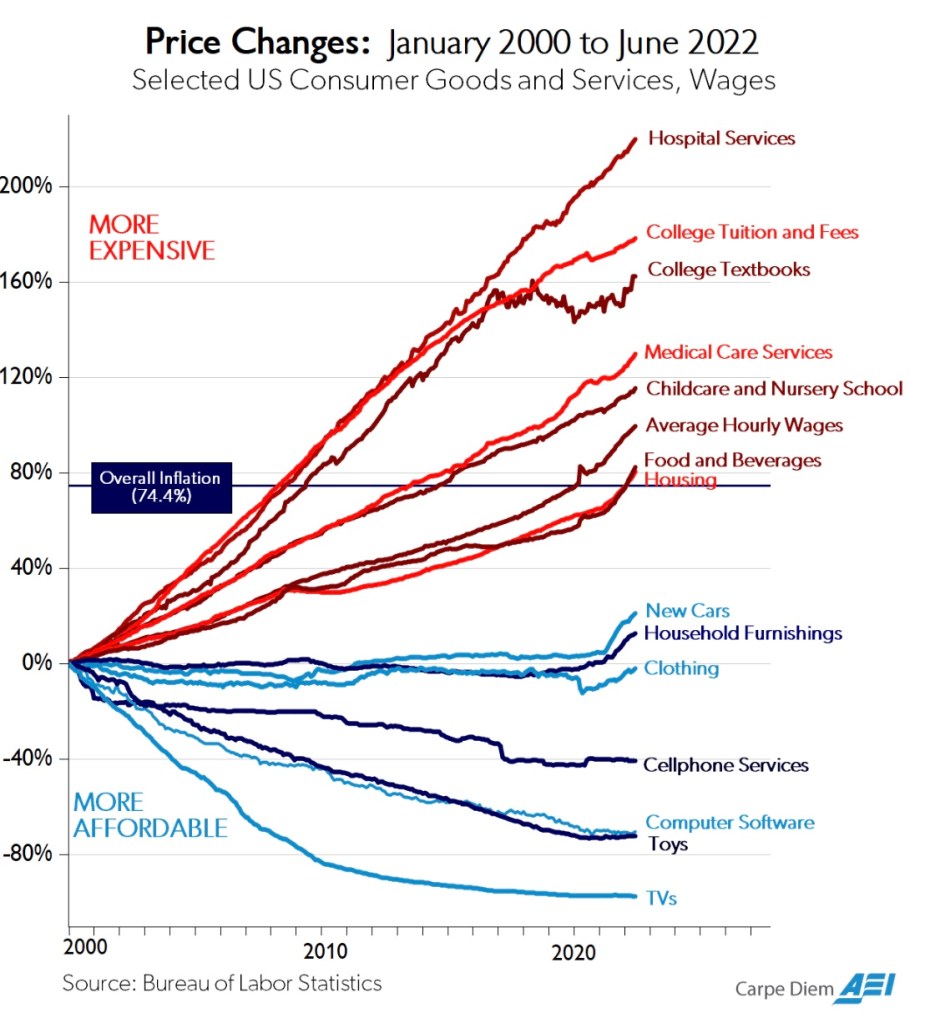
This post is about relative prices in two major sectors of the U.S. economy, both of which are hindered by slow productivity growth while being among the most heavily subsidized: education and health care. Historically, both sectors have experienced rather drastic relative price increases, as illustrated for the past 20 years in the chart from Mark Perry above.
Baumol’s Cost Disease
These facts are hardly coincidental, though it’s likely the relative costs education and health care would have risen even in the absence of subsidies. Over long periods of time, the forces primarily guiding relative price movements are differentials in productivity growth. The tendency of certain industries to suffer from slow growth in productivity is the key to something known among economists as Baumol’s Disease, after the late William Baumol, who first described the phenomenon’s impact on relative prices.
Standards of living improve when a sufficient number of industries enjoy productivity growth. That creates a broad diffusion of new demands across many industries, including those less amenable to productivity growth, such as health care and education. But slow productivity growth and rising demand in these industries are imbalances that push their relative prices upward.
Alex Tabarrok and Eric Helland noted a few years ago that it took four skilled musicians 44 minutes to play Beethoven’s String Quartet No. 14 in 1826 and also in 2010, but the inflation-adjusted cost was 23 times higher. Services involving a high intensity of skilled labor are more prone to Baumol’s Disease than manufactured goods. As well, services for which demand is highly responsive to income or sectors characterized by monopoly power may be more prone to Baumol’s disease.
Tabarrok wonders whether we should really consider manifestations of Baumol’s Disease a blessing, because they show the extent to which productivity and real incomes have grown across the broader economy. So, rather than blame low productivity growth in certain services for their increasing relative prices, we should really blame (or thank) the rapid productivity growth in other sectors.
The Productivity Slog
There are unavoidable limits to the productivity growth of skilled educators, physicians, and other skilled workers in health care. Again, in a growing economy, prices of things in relatively fixed supply or those registering slow productivity gains will tend to rise more rapidly.
Technology offers certain advantages in some fields of education, but it’s hard to find evidence of broad improvement in educational success in the U.S. at any level. In the health care sector, new drugs often improve outcomes, as do advances in technologies such as drug delivery systems, monitoring devices, imaging, and robotic surgery. However, these advances don’t necessarily translate into improved capacity of the health care system to handle patients except at higher costs.
There’s been some controversy over the proper measurement of productivity in the health care sector. Some suggest that traditional measures of health care productivity are so flawed in capturing quality improvements that the meaning of prices themselves is distorted. They conclude that adjusting for quality can actually yield declines in effective health care prices. I’d interject, however, that patients and payers might harbor doubts about that assertion.
Other investigators note that while real advances in health care productivity should reduce costs, the degree of success varies substantially across different types of innovations and care settings. In particular, innovations in process and protocols seem to be more effective in reducing health care expenditures than adding new technologies to existing protocols or business models. All too often, medical innovations are of the latter variety. Ultimately, innovations in health care haven’t allowed a broader population of patients to be treated at low cost.
Superior Goods
Therefore, it appears that increases in the relative prices of education and health care over time have arisen as a natural consequence of the interplay between disparities in productivity growth and rising demand. Indeed, this goes a long way toward explaining the high cost of health care in the U.S. compared to other developed nations, as standards of living in the U.S. are well above nearly all others. In that respect, the cost of health care in the U.S. is not necessarily alarming. People demand more health care and education as their incomes rise, but delivering more health care isn’t easy. To paraphrase Tabarrok, turning steelworkers into doctors, nurses and teachers is a costly proposition.
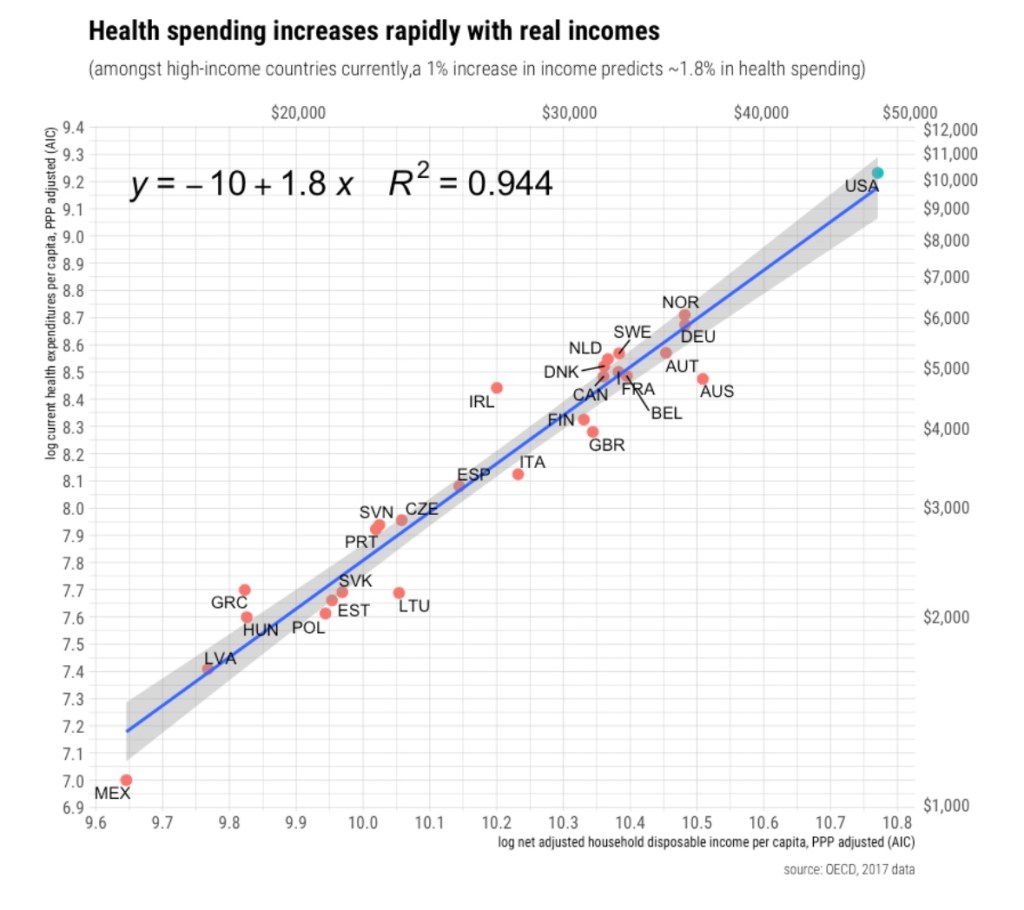
The Role of Subsidies
In the clamor for scarce educational and health care resources, natural tensions over access have spilled into the political sphere. In pursuit of distributing these resources more equitably, public policy has relied heavily on subsidies. It shouldn’t surprise anyone that subsiding a service resistant to productivity gains will magnify the Baumol effect on relative price. One point is beyond doubt: the amounts of these subsidies is breathtaking.
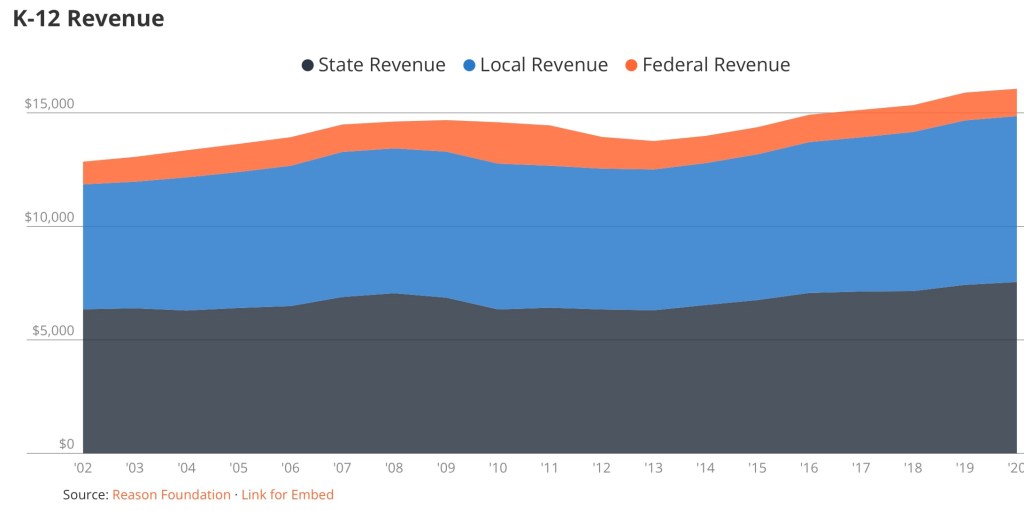
Education: Public K -12 schools are largely funded by local taxpayers. Taxpayer-parents of school-aged children pay part of this cost whether they send their children to public schools or not. If they don’t, they must pay the additional cost of private or home schooling. This severely distorts the link between payments and the value assigned by actual users of public schools. It also confers a huge degree of market power to public schools, thus insulating them economically from performance pressures.
Public K – 12 schools are also heavily subsidized by state governments and federal grants. The following chart shows the magnitude and growth of K – 12 revenue per student over the past couple of decades.
Subsidies for higher education take the form of student aid, including federal student loans, grants to institutions, as well as a variety of tax subsidies. Here’s a nice breakdown:
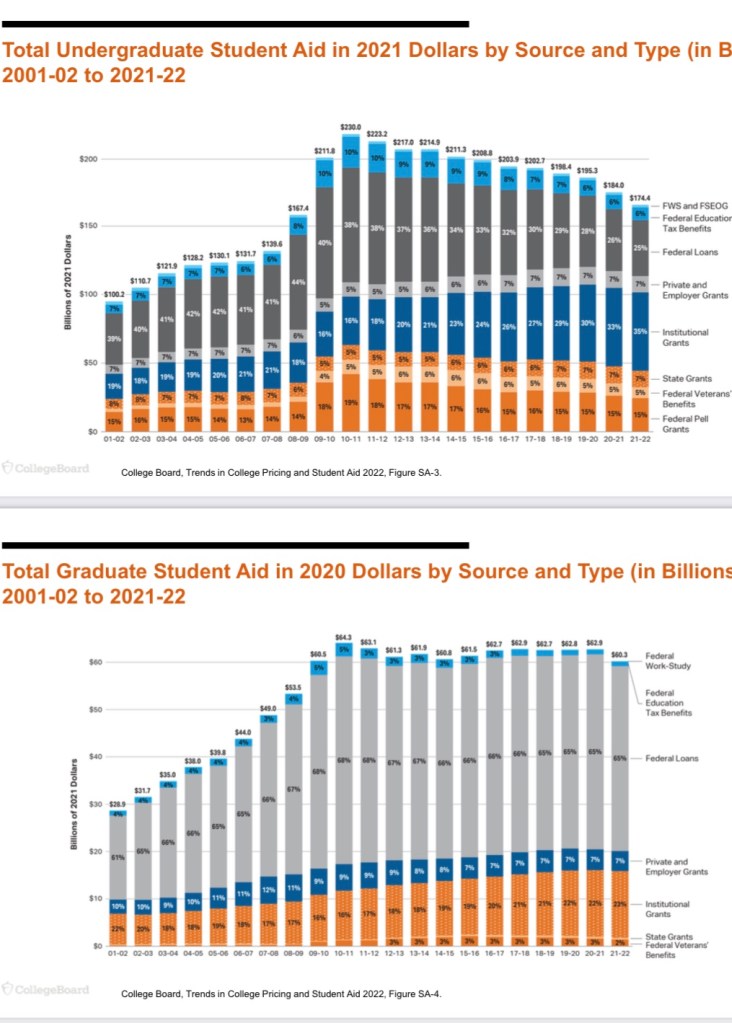
This represents a mix of buyer and seller subsidies. That suggests less upward pressure on price and more stimulus to output, but we still run up against the limits to productivity growth noted above. Moreover, other constraints limit the effectiveness of these subsidies, such as lower academic qualifications in a broader student population and the potential for rewards in the job market to diminish with a potential excess of graduates.
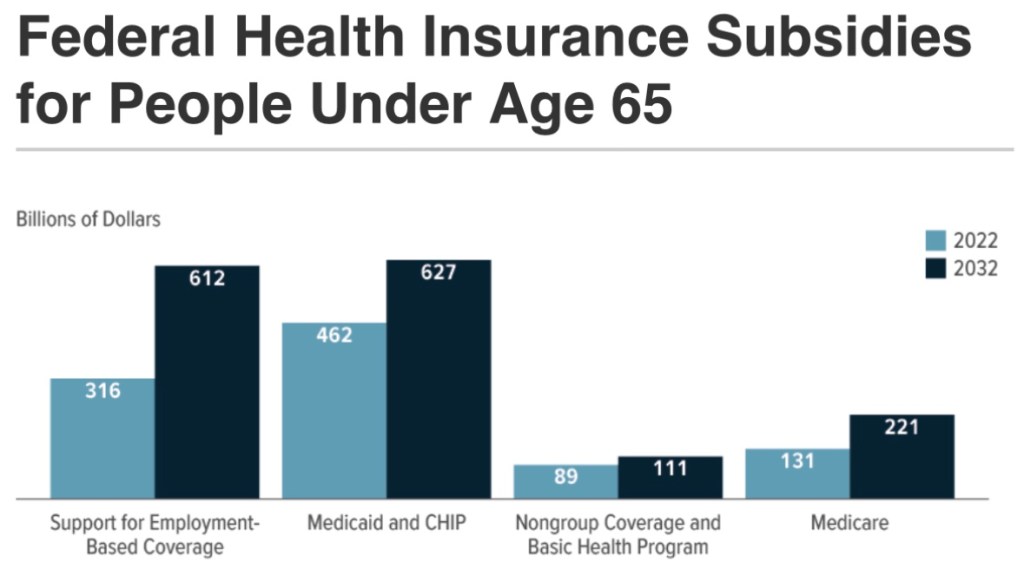
Health care: Subsidies here are massive and come in a variety of forms. They often directly provide or reduce the cost of health insurance coverage: Medicaid, the Children’s Health Insurance Program (CHIP), Obamacare exchange subsidies, Medicare savings programs, tax-subsidies on employer-paid health coverage, and medical expense tax deductions. Within limits, these subsidies reduce the marginal cost of care patients are asked to pay, thus contributing to over-utilization of various kinds of care.
The following are CBO projections from June 2022. They are intended here to give an idea of the magnitude of health care insurance subsidies:
Still Other Dysfunctions
There are certainly other drivers of high costs in the provision of health care and education beyond a Baumol effect magnified by subsidies. The third-party payment system has contributed to a loss of price discipline in health care. While consumers are often responsible for paying at least part of their health insurance premiums, the marginal cost of health care to consumers is often zero, so they have little incentive to manage their demands.
Another impediment to cost control is a regulatory environment in health care that has led to a sharply greater concentration of hospital services and the virtual disappearance of independent provider practices. Competition has been sorely lacking in education as well. Subsidies flowing to providers with market power tend to exacerbate behaviors that would be punished in competitive markets, and not just pricing.
Summary
Baumol’s Disease can explain a lot about the patterns of relative prices shown in the chart at the top of this post. That pattern is a negative side effect of general growth in productivity. Unfortunately, it also reflects a magnification engendered by the payment of subsidies to sectors with slow productivity growth. The intent of these subsidies is to distribute health care and education more equitably, but the impact on relative prices undermines these objectives. The approach forces society to exert wasted energy, like an idiotic dog chasing its tail.
Peter Suderman wrote an excellent piece in which he discussed health care and education subsidies in the context of the so-called “abundance agenda”. His emphasis is on the futility of this agenda for the middle class, for which quality education and affordable health care always seem just out of reach. The malign effects of “abundance” policies are reinforced by anti-competitive regulation and payment mechanisms, which subvert market price discipline and consumer sovereignty. We’d be far better served by policies that restore consumer responsibility, deregulate providers, and foster competition in the delivery of health care and education.









