Tags
2024 Election, Abortion, Abraham Accords, Barack Obama, Capitalism, Climate Change, Corporatism, DEI, Dobbs, Donald Trump, Elon Musk, fascism, Federal Reserve, First Amendment, Fossil fuels, Housing, Hysteria, Immigration, Inflation, Israel, Joe Biden, Kamala Harris, Medicaid, Medicare, Obamacare, Renewable energy, Second Amendment, Social Security, Supreme Court, Tariffs, Tax Policy, Ukraine, Vladimir Putin

Wow! We’re less than a week from Election Day! I’d hoped to write a few more detailed posts about the platforms and policies of Kamala Harris and Donald Trump, but I was waylaid by Hurricane Milton. It sent us scrambling into prep mode, then we evacuated to the Florida Panhandle. The drive there and back took much longer than expected due to the mass exodus. On our return we found the house was fine, but there was significant damage to an exterior structure and a mess in the yard. We also had to “de-prep” the house, and we’ve been dealing with contractors ever since. It was an exhausting episode, but we feel like we were very lucky.
Now, with less than a week left till the election, I’ll limit myself to a summary of the positions of the candidates in a number of areas, mostly but not all directly related to policy. I assign “grades” in each area and calculate an equally-weighted “GPA” for each candidate. My summaries (and “grades”) are pretty off-the-cuff and not adequate treatments on their own. Some of these areas are more general than others, and I readily admit that a GPA taken from my grade assignments is subject to a bit of double counting. Oh well!
Role of Government: Kamala Harris is a statist through and through. No mystery there. Trump is more selective in his statist tendencies. He’ll often favor government action if it’s politically advantageous. However, in general I think he is amenable to a smaller role for the public than the private sector. Harris: F; Trump: C
Regulation: There is no question that Trump stands for badly needed federal regulatory reform. This spans a wide range of areas, and it extends to a light approach to crypto and AI regulation. Trump plans to appoint Elon Musk as his “Secretary of Cost Cutting”. Harris, on the other hand, seems to favor a continuation of the Biden Administration’s heavy regulatory oversight. This encourages a bloated federal bureaucracy, inflicts high compliance costs on the private sector, stifles innovation, and tends to concentrate industrial power. Harris: F; Trump: A
Border Policy: Trump wants to close the borders (complete the wall) and deport illegal immigrants. Both are easier said than done. Except for criminal elements, the latter will be especially controversial. I’d feel better about Trump’s position if it were accompanied by a commitment to expanded legal immigration. We need more legal immigrants, especially the highly skilled. For her part, Harris would offer mass amnesty to illegals. She’d continue an open border policy, though she claims to want certain limits on illegal border crossings going forward. She also claims to favor more funds for border control. However, it is not clear how well this would translate into thorough vetting of illegal entrants, drug interdiction at the border, or sex trafficking. Harris: D; Trump: B-
Antitrust: Accusations of price gouging by American businesses? Harris! Forty three corporations in the S&P 500 under investigation by the DOJ? The Biden-Harris Administration. This reflects an aggressively hostile and manipulative attitude toward the business community. Trump, meanwhile, might wheedle corporations to act on behalf of certain of his agendas, but he is unlikely to take such a broadly punitive approach. Harris: F; Trump: B-
Foreign Policy: Harris is likely to continue the Biden Administration’s conciliatory approach to dealing with America’s adversaries. The other side of that coin is an often tepid commitment to longtime allies like Israel. Trump believes that dealing from a position of strength is imperative, and he’s willing to challenge enemies with an array of economic and political sticks and carrots. He had success during his first term in office promoting peace in the Middle East. A renewed version of the Abraham Accords that strengthened economic ties across the region would do just that. Ideally, he would like to restore the strength of America’s military, about which Harris has less interest. Trump has also shown a willingness to challenge our NATO partners in order to get them to “pay their fair share” toward the alliance’s shared defense. My major qualification here has to do with the candidates’ positions with respect to supporting Ukraine in its war against Putin’s mad aggression. Harris seems more likely than Trump to continue America’s support for Ukraine. Harris: D+; Trump: B-
Trade: Nations who trade with one another tend to be more prosperous and at peace. Unfortunately, neither candidate has much recognition of these facts. Harris is willing to extend the tariffs enforced during the Biden Administration. Trump, however, is under the delusion that tariffs can solve almost anything that ails the country. Of course, tariffs are a destructive tax on American consumers and businesses. Part of this owes to the direct effects of the tax. Part owes to the pricing power tariffs grant to domestic producers. Tariffs harm incentives for efficiency and the competitiveness of American industry. Retaliatory action by foreign governments is a likely response, which magnifies the harm.
To be fair, Trump believes he can use tariffs as a negotiating tool in nearly all international matters, whether economic, political, or military. This might work to achieve some objectives, but at the cost of damaging relations more broadly and undermining the U.S. economy. Trump is an advocate for not just selective, punitive tariffs, but for broad application of tariffs. Someone needs to disabuse him of the notion that tariffs have great revenue-raising potential. They don’t. And Trump is seemingly unaware of another basic fact: the trade deficit is mirrored by foreign investment in the U.S. economy, which spurs domestic economic growth. Quashing imports via tariffs will also quash that source of growth. I’ll add one other qualification below in the section on taxes, but I’m not sure it has a meaningful chance.
Harris: C-; Trump: F
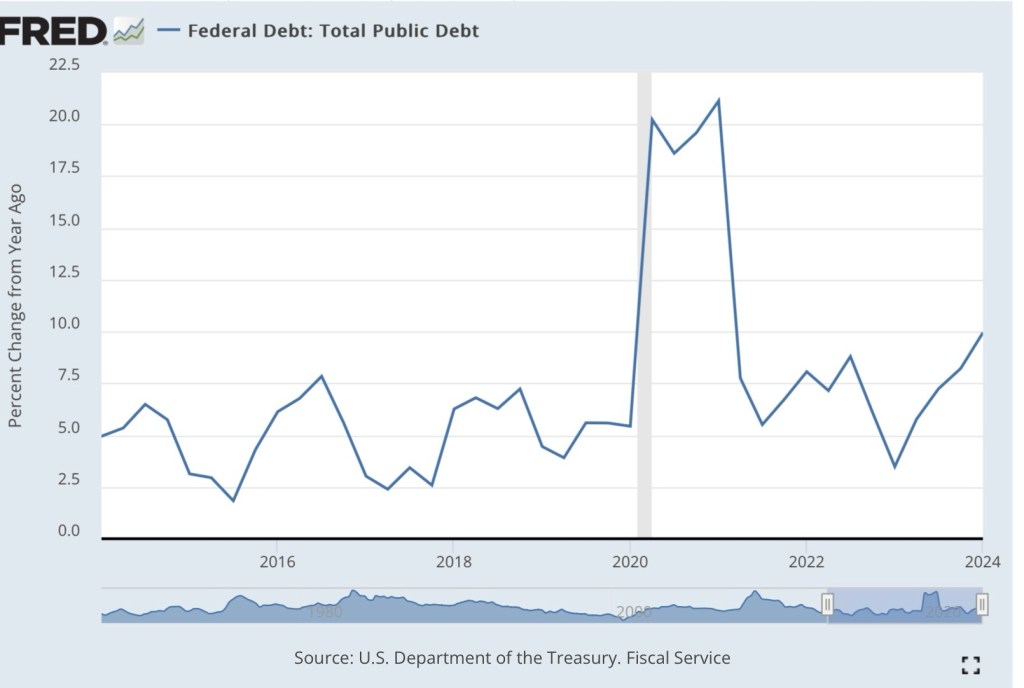
Inflation: This is a tough one to grade. The President has no direct control over inflation. Harris wants to challenge “price gougers”, which has little to do with actual inflation. I expect both candidates to tolerate large deficits in order to fulfill campaign promises and other objectives. That will put pressure on credit markets and is likely to be inflationary if bond investors are surprised by the higher trajectory of permanent government indebtedness, or if the Federal Reserve monetizes increasing amounts of federal debt. Deficits are likely to be larger under Trump than Harris due in large part to differences in their tax plans, but I’m skeptical that Harris will hold spending in check. Trump’s policies are more growth oriented, and these along with his energy policies and deregulatory actions could limit the inflationary consequences of his spending and tax policies. Higher tariffs will not be of much help in funding larger deficits, and in fact they will be inflationary. Harris: C; Trump: C
Federal Reserve Independence: Harris would undoubtedly like to have the Fed partner closely with the Treasury in funding federal spending. Her appointments to the Board would almost certainly lead to a more activist Fed with a willingness to tolerate rapid monetary expansion and inflation. Trump might be even worse. He has signaled disdain for the Fed’s independence, and he would be happy to lean on the Fed to ease his efforts to fulfill promises to special interests. Harris: D; Trump: F
Entitlement Reform: Social Security and Medicare are both insolvent and benefits will be cut in 2035 without reforms. Harris would certainly be willing to tax the benefits of higher-income retirees more heavily, and she would likely be willing to impose FICA and Medicare taxes on incomes above current earning limits. These are not my favorite reform proposals. Trump has been silent on the issue except to promise no cuts in benefits. Harris: C-; Trump: F
Health Care: Harris is an Obamacare supporter and an advocate of expanded Medicaid. She favors policies that would short-circuit consumer discipline for health care spending and hasten the depletion of the already insolvent Medicare and Medicaid trust funds. These include a $2,000 cap on health care spending for Americans on Medicare, having Medicare cover in-home care, and extending tax credits for health insurance premia. She supports funding to address presumed health care disparities faced by black men. She also promises efforts to discipline or supplant pharmacy benefit managers. Trump, for his part, has said little about his plans for health care policy. He is not a fan of Obamacare and he has promised to take on Big Pharma, whatever that might mean. I fear that both candidates would happily place additional controls of the pricing of pharmaceuticals, a sure prescription for curtailed research and development and higher mortality. Harris: F; Trump: D+
Abortion: The Supreme Court’s 2022 decision in Dobbs v. Jackson essentially relegated abortion law to individual states. That’s consistent with federalist principles, leaving the controversial balancing of abortion vs. the unborn child’s rights up to state voters. Geographic differences of opinion on this question are dramatic, and Dobbs respects those differences. Trump is content with it. Meanwhile, Harris advocates for the establishment of expanded abortion rights at the federal level, including authorization of third trimester abortions by “care providers”. And Harris does not believe there should be religious exemptions for providers who do not wish to offer abortion services. No doubt she also approves of federally funded abortions. Harris: F; Trump: A
Housing: The nation faces an acute housing shortage owing to excessive regulation that limits construction of new or revitalized housing. These excessive rules are primarily imposed at the state and local level. While the federal government has little direct control over many of these decisions, it has abetted this regulatory onslaught in a variety of ways, especially in the environmental arena. Harris is offering stimulus to the demand side through a $25,000 housing tax credit for first-time home buyers. This will succeed in raising the cost of housing. She has also called for heavier subsidies for developers of low-income housing. If past is prologue, this might do more to line the pockets of developers than add meaningfully to the stock of affordable housing. Harris also favors rent controls, a sure prescription for deterioration in the housing stock, and she would prohibit software allowing landlords to determine competitive neighborhood rents. Trump has called for deregulation generally and would not favor rent controls. Harris: F; Trump B
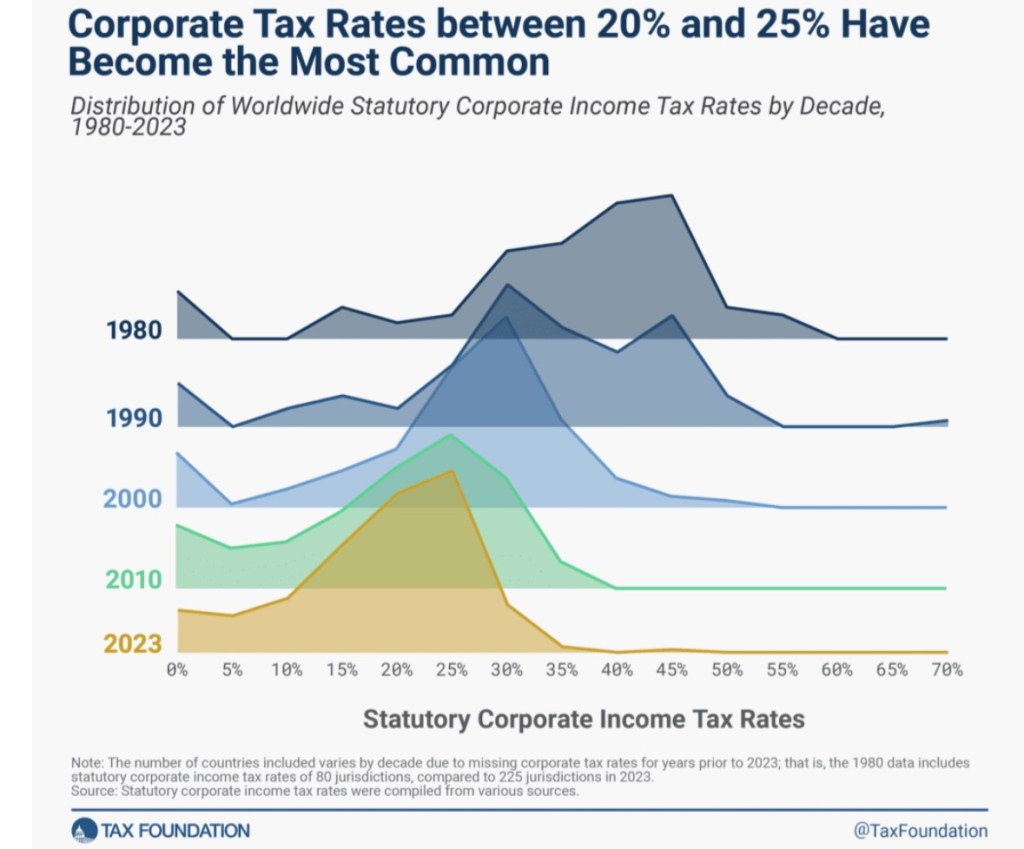
Taxes: Harris has broached several wildly destructive tax proposals. Perhaps the worst of these is to tax unrealized capital gains, and while she promises it would apply only to extremely wealthy taxpayers, it would constitute a wealth tax. Once that line is crossed, the threat of widening the base becomes a very slippery slope. It would also be a strong detriment to domestic capital investment and economic growth. Harris would increase the top marginal personal tax rate and the corporate tax rate, which would discourage investment and undermine real wage growth. She’d also increase estate tax rates. As discussed above, she unwisely calls for a $25,000 tax credit for first-time homebuyers. She also wants to expand the child care tax credit to $6,000 for families with newborns. A proposed $50,000 small business tax credit would allow the federal government to subsidize and encourage risky entrepreneurial activity at taxpayers’ expense. I’m all for small business, but this style of industrial planning is bonkers. She would sunset the Trump (TCJA) tax cuts in 2026.
Finally, Harris has mimicked Trump in calling for no taxes on tips. Treating certain forms of income more favorably than others is a recipe for distortions in economic activity. Employers of tip-earning workers will find ways to shift employees’ income to tips that are mandatory for patrons. It will also skew labor supply decisions toward occupations that would otherwise have less economic value. But Trump managed to find an idea so politically seductive that Harris couldn’t resist.
Trump’s tax plans are a mixed bag of good and bad ideas. They include extending his earlier tax cuts (TCJA) and restoring the SALT deduction. The latter is an alluring campaign tidbit for voters in high-tax states. He would reduce the corporate tax rate, which I strongly favor. Corporate income is double-taxed, which is a detriment to growth as well as a weight on real wages. He would eliminate taxes on overtime income, another example of favoring a particular form of income over others. Wage earners would gain at the expense of salaried employees, so one could expect a transition in the form employees are paid over time. Otherwise, the classification of hours as “overtime” would have to be standardized. One could expect existing employees to work longer hours, but at the expense of new jobs. Finally, Trump says Social Security benefits should not be taxed, another kind of special treatment by form of income. This might encourage early retirement and become an additional drain on the Social Security Trust Fund.
The higher tariffs promised by Trump would collect some revenue. I’d be more supportive of this plank if the tariffs were part of a larger transition from income taxes to consumption taxes. However, Trump would still like to see large differentials between tariffs and taxes imposed on the consumption of domestically-produced goods and services.
Harris: F; Trump C+
Climate Policy: This topic has undergone a steep decline in relative importance to voters. Harris favors more drastic climate interventions than Trump, including steep renewable subsidies, EV mandates, and a panoply of other initiatives, many of which would carry over from the Biden Administration. Harris: F; Trump: B
Energy: Low-cost energy encourages economic growth. Just ask the Germans! Consistent with the climate change narrative, Harris wishes to discourage the use of fossil fuels, their domestic production, and even their export. She has been very dodgy with respect to restrictions on fracking. Her apparent stance on energy policy would be an obvious detriment to growth and price stability (or I should say a continuing detriment). Trump wishes to encourage fossil fuel production. Harris: F; Trump: A
Constitutional Integrity: Harris has supported the idea of packing the Supreme Court, which would lead to an escalating competition to appoint more and more justices with every shift in political power. She’s also disparaged the Electoral College, without which many states would never have agreed to join the Union. Under the questionable pretense of “protecting voting rights”, she has opposed steps to improve election integrity, such voter ID laws. And operatives within her party have done everything possible to register non-citizens as voters. Harris: F; Trump: A
First Amendment Rights: Harris has called for regulation and oversight of social media content and moderation. A more descriptive word for this is censorship. Trump is generally a free speech advocate. Harris: F; Trump A-
Second Amendment Rights: Harris would like to ban so-called “assault weapons” and high-capacity magazines, and she backs universal background checks for gun purchases. Trump has not called for any new restrictions on gun rights. Harris: F; Trump: A
DEI: Harris is strongly supportive of diversity and equity initiatives, which have undermined social cohesion and the economy. That necessarily makes her an enemy of merit-based rewards. Trump has no such confusion. Harris: F; Trump: A
Hysteria: The Harris campaign has embraced a strategy of demonizing Donald Trump. Of course, that’s not a new approach among Democrats, who have fabricated bizarre stories about Trump escapades in Russia, Trump as a pawn of Vladimir Putin, and Russian manipulation of the 2016 Trump campaign. Congressional democrats spent nearly all of Trump’s first term in office trying to find grounds for impeachment. Concurrently, there were a number of other crazy and false stories about Trump. The current variation on “Orange Man Bad” is that Trump is a fascist and a Nazi, and that all of his supporters are Nazis. And that Trump will use the military against his domestic political opponents, the so-called “enemy within”. And that Trump will send half the country’s populace to labor camps. The nonsense never ends, but could anything more powerfully ignite the passions of violent extremists than this sort of hateful rhetoric? Would it not be surprising if at least a few leftists weren’t interested in assassinating “Hitler” himself. This is hysteria, and one has to wonder if that is not, in fact, the intent.
Can any of these people actually define the term fascist? Most fundamentally, a fascist desires the use of government coercion for private gain (of wealth or power) for oneself and/or one’s circle of allies. By that definition, we could probably categorize a great many American politicians as fascists, including Barack Obama, Joe Biden, Donald Trump, and a majority of both houses of Congress. That only demonstrates that corporatism is fundamental to fascist politics. Less-informed definitions of fascism conflate it with everything from racism (certainly can play a part) and homophobia (certainly can play a part) to mere capitalism. But take a look at the demographics of Trump’s supporters and you can see that most of these definitions are inapt.
Is the Trump campaign suffering from any form of hysteria? It’s shown great talent at poking fun at the left. Of course, Trump’s reactions to illegal immigration, crime, and third-trimester abortions are construed by leftists to be hysterical. I mean, why would anyone get upset about those kinds of things?
Harris: F; Trump: A
“Grade Point Average”
I’m sure I forgot an area or two I should have covered. Anyway, the following are four-point “GPAs” calculated over 20 categories. I’m deducting a quarter point for a “minus” grade and adding a quarter point for a “plus” grade. Here’s what I get:
Harris: 0.44; Trump: 2.68
Hmmm