Tags
Asian Flu, Comorbidities, Coronavirus, Covid-19, Get Outside, Hong Kong Flu, Imperial College Model, Italy, Lockdowns, Mortality by Age, Mortality Rates, Neil Ferguson, New York, Organ Failure, Pandemic, Public Health, Slow the Spread, South Korea, Spanish Flu, Suicide Hotlines, Vitamin D Deficiency
Step back in time six months and ask any health care professional about the consequences of suspending delivery of most medical care for a period of months. Forget about the coronavirus for a moment and just think about that “hypothetical”. These experts would have answered, uniformly, that it would be cataclysmic: months of undiagnosed cardiac and stroke symptoms; no cancer screenings, putting patients months behind on the survival curve; deferred procedures of all kinds; run-of-the-mill infections gone untreated; palsy and other neurological symptoms anxiously discounted by victims at home; a hold on treatments for all sorts of other progressive diseases; and patients ordinarily requiring hospitalization sent home. And to start back up, new health problems must compete with all that deferred care. Do you dare tally the death and other worsened outcomes? Both are no doubt significant.
What you just read has been a reality for more than two months due to federal and state orders to halt non-emergency medical procedures in the U.S. The intent was to conserve hospital capacity for a potential rush of coronavirus patients and to prevent others from exposure to the virus. That might have made sense in hot spots like New York, but even there the provision of temporary capacity went almost completely unused. Otherwise, clearing hospitals of non-Covid patients, who could have been segregated, was largely unnecessary. The fears prompted by these orders impacted delivery of care in emergency facilities: people have assiduously avoided emergency room visits. Even most regular office visits were placed on hold. And as for the reboot, there are health care facilities that will not survive the financial blow, leaving communities without local sources of care.
A lack of access to health care is one source of human misery, but let’s ask our health care professional about another “hypothetical”: the public health consequences of an economic depression. She would no doubt predict that the stresses of joblessness and business ruin would be acute. It’s reasonable to think of mental health issues first. Indeed, in the past two months, suicide hotlines have seen calls spike by multiples of normal levels (also see here and here). But the stresses of economic disaster often manifest in failing physical health as well. Common associations include hypertension, heart disease, migraines, inflammatory responses, immune deficiency, and other kinds of organ failure.
The loss of economic output during a shutdown can never be recovered. Goods don’t magically reappear on the shelves by government mandate. Running the printing press in order to make government benefit payments cannot make us whole. The output loss will permanently reduce the standard of living, and it will reduce our future ability to deal with pandemics and other crises by eroding the resources available to invest in public health, safety, and disaster relief.
What would our representative health care professional say about the health effects of a mass quarantine, stretching over months? What are the odds that it might compound the effects of the suspension in care? Confinement and isolation add to stress. In an idle state of boredom and dejection, many are unmotivated and have difficulty getting enough exercise. There may be a tendency to eat and drink excessively. And misguided exhortations to “stay inside” certainly would never help anyone with a Vitamin D deficiency, which bears a striking association with the severity of coronavirus infections.
But to be fair, was all this worthwhile in the presence of the coronavirus pandemic? What did health care professionals and public health officials know at the outset, in early to mid-March? There was lots of alarming talk of exponential growth and virus doubling times. There were anecdotal stories of younger people felled by the virus. Health care professionals were no doubt influenced by the dire conditions under which colleagues who cared for virus victims were working.
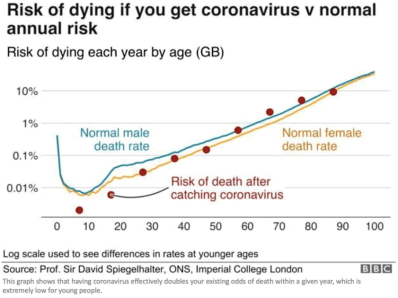
Nevertheless, a great deal was known in early March about the truly vulnerable segments of the population, even if you discount Chinese reporting. Mortality rates in South Korea and Italy were heavily skewed toward the aged and those with other risk factors. One can reasonably argue that health care professionals and policy experts should have known even then how best to mitigate the risks of the virus. That would have involved targeting high-risk segments of the population for quarantine, and treatment for the larger population in-line with the lower risks it actually faced. Vulnerable groups require protection, but death rates from coronavirus across the full age distribution closely mimic mortality from other causes, as the chart at the top of this chart shows.
The current global death toll is still quite small relative to major pandemics of the past (Spanish Flu, 1918-19: ~45 million; Asian Flu, 1957-58: 1.1 million; Hong Kong flu, 1969: 1 million; Covid-19 as of May 22: 333,000). But by mid-March, people were distressed by one particular epidemiological model (Neil Ferguson’s Imperial College Model, subsequently exposed as slipshod), predicting 2.2 million deaths in the U.S. (We are not yet at 100,000 deaths). Most people were willing to accept temporary non-prescription measures to “slow the spread“. But unreasonable fear and alarm, eagerly promoted by the media, drove the extension of lockdowns across the U.S. by up to two extra months in some states, and perhaps beyond.
The public health and policy establishment did not properly weigh the health care and economic costs of extended lockdowns against the real risks of the coronavirus. I believe many health care workers were goaded into supporting ongoing lockdowns in the same way as the public. They had to know that the suspension of medical care was a dire cost to pay, but they fell in line when the “experts” insisted that extensions of the lockdowns were worthwhile. Some knew better, and much of the public has learned better.