Tags
Aerosols, Antibody Response, Biden Administration, Case Counts, City Journal, Covid-19, Delta Variant, Follow the Science, Hope-Simpson, Hospitalizations, Israeli Vaccinations, Jeffrey H. Anderson, Jeffrey Morris, Mask Mandates, Moderna, mRNA Vaccines, Pfizer, Randomized Control Trials, Reproduction Rates, The American Reveille, Transmissability, Vaccinations, Vaccine Efficacy

If this post has an overarching theme, it might be “just relax”! That goes especially for those inclined to prescribe behavioral rules for others. People can assess risks for themselves, though it helps when empirical information is presented without bias. With that brief diatribe, here are a few follow-ups on COVID vaccines, the Delta wave, and the ongoing “mask charade”.
Israeli Vax Protection
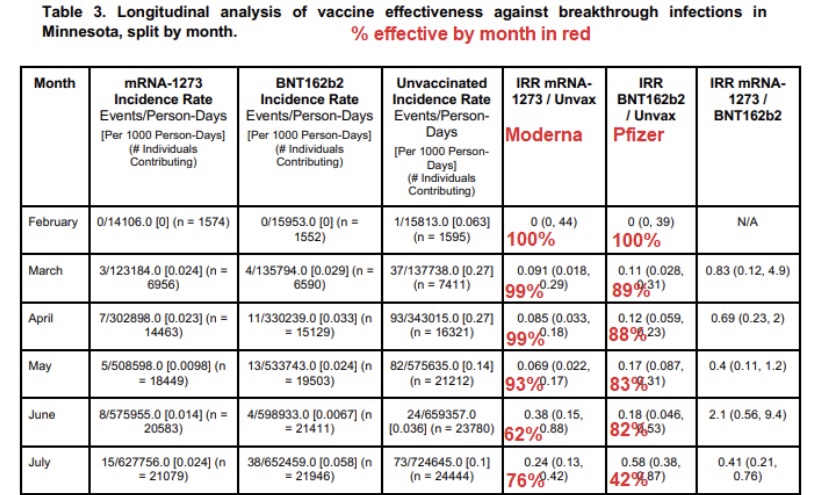
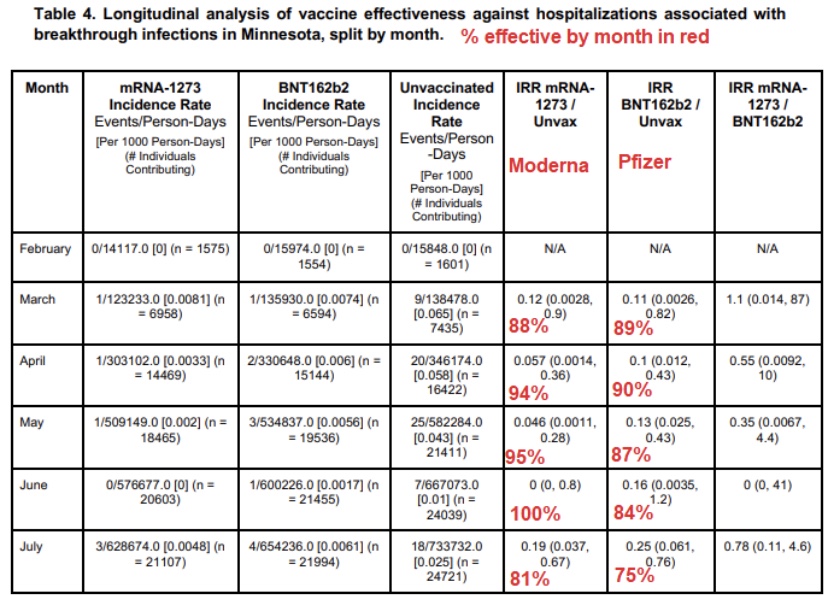
Here is Jeffrey Morris’ very good exposition as to why the Israeli reports of COVID vaccine inefficacy are false. First, he shows the kind of raw data we’ve been hearing about for weeks: almost 60% of the country’s severe cases are in vaccinated individuals. This is the origin of the claim that the vaccines don’t work.
Next, Morris notes that 80% of the Israeli population 12 years and older are vaccinated (predominantly if not exclusively with the Pfizer vaccine). This causes a distortion that can be controlled by normalizing the case counts relative to the total populations of the vaccinated and unvaccinated subgroups. Doing so shows that the unvaccinated are 3.1 times more likely to have contracted a severe case than the vaccinated. Said a different way, this shows that the vaccines are 67.5% effective in preventing severe disease. But that’s not the full story!
Morris goes on to show case rates in different age strata. For those older than 50 (over 90% of whom are vaccinated and who have more co-morbidities), there are 23.6 times more severe cases among the unvaccinated than the vaccinated. That yields an efficacy rate of 85.2%. Vaccine efficacy is even better in the younger age group: 91.8%.
These statistics pertain to the Delta variant. However, it’s true they are lower than the 95% efficacy rate achieved in the Pfizer trials. Is Pfizer’s efficacy beginning to fade? That’s possible, but this is just one set of results and declining efficacy has not been proven. Israel’s vaccination program got off to a fast start, so the vaccinated population has had more time for efficacy to decay than in most countries. And as I discussed in an earlier post, there are reasons to think that the vaccines are still highly protective after a minimum of seven months.
Biden Boosters
IIn the meantime, the Biden Administration has recommended that booster shots be delivered eight months after original vaccinations. There is empirical evidence that boosters of similar mRNA vaccine (Pfizer and Moderna) might not be a sound approach, both due to side effects and because additional doses might reduce the “breadth” of the antibody response. We’ll soon know whether the first two jabs are effective after eight months, and my bet is that will be the case.
Is Delta Cresting?
Meanwhile, the course of this summer’s Delta wave appears to be turning a corner. The surge in cases has a seasonal component, mimicking the summer 2020 wave as well as the typical Hope-Simpson pattern, in which large viral waves peak in mid-winter but more muted waves occur in low- to mid-latitudes during the summer months.
Therefore, we might expect to see a late-summer decline in new cases. There are now 21 states with COVID estimated reproduction rates less than one (this might change by the time you see the charts at the link). In other words, each new infected person transmits to an average of less than one other person, which shows that case growth may be near or beyond a peak. Another 16 states have reproduction rates approaching or very close to one. This is promising.
Maskholes
Finally, I’m frustrated as a resident of a county where certain government officials are bound and determined to impose a mask mandate, though they have been slowed by a court challenge. The “science” does NOT support such a measure: masks have not been shown to mitigate the spread of the virus, and they cannot stop penetration of aerosols in either direction. This recent article in City Journal by Jeffrey H. Anderson is perhaps the most thorough treatment I’ve seen on the effectiveness of masks. Anderson makes this remark about the scientific case made by mask proponents:
“Mask supporters often claim that we have no choice but to rely on observational studies instead of RCTs [randomized control trials], because RCTs cannot tell us whether masks work or not. But what they really mean is that they don’t like what the RCTs show.”
Oh, how well I remember the “follow-the-science” crowd insisting last year that only RCTs could be trusted when it came to evaluating certain COVID treatments. In any case, the observational studies on masks are quite mixed and by no means offer unequivocal support for masking.
A further consideration is that masks can act to convert droplets to aerosols, which are highly efficient vehicles of transmission. The mask debate is even more absurd when it comes to school children, who are at almost zero risk of severe COVID infection (also see here), and for whom masks are highly prone to cause developmental complications.
Closing Thoughts
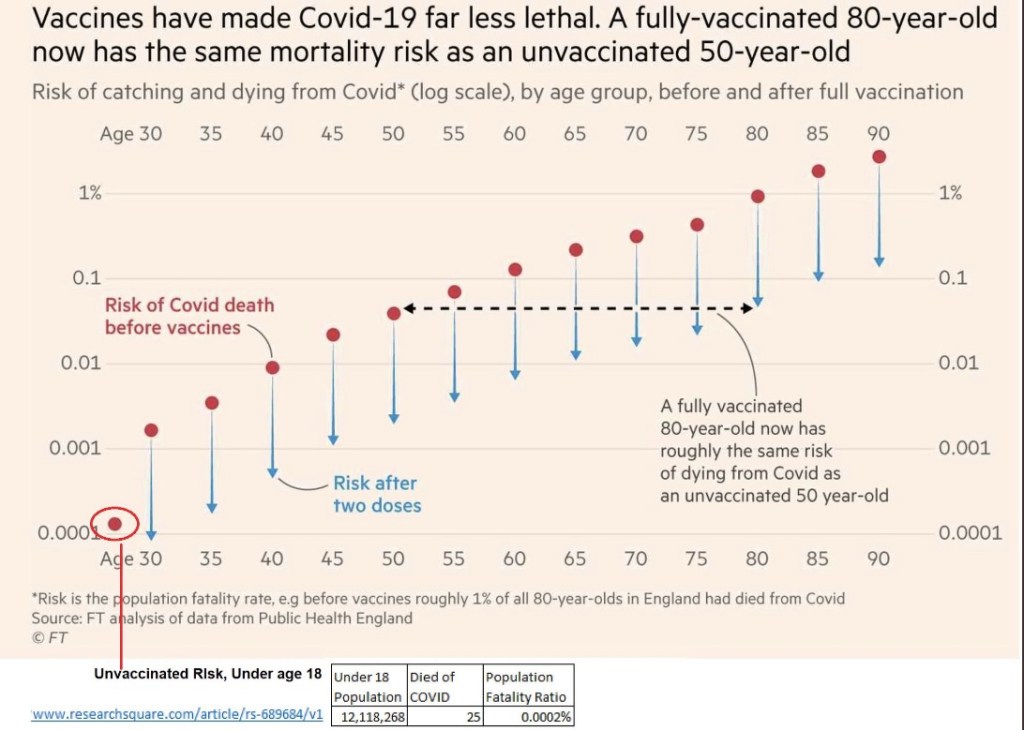
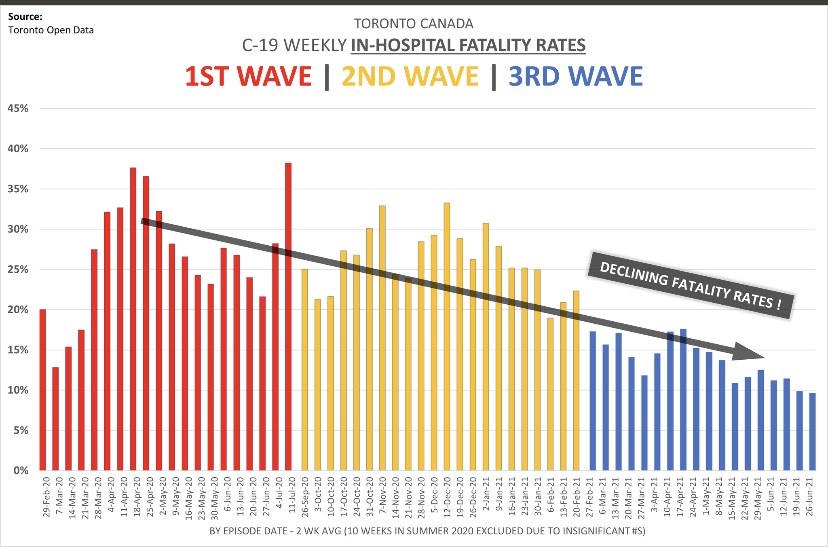
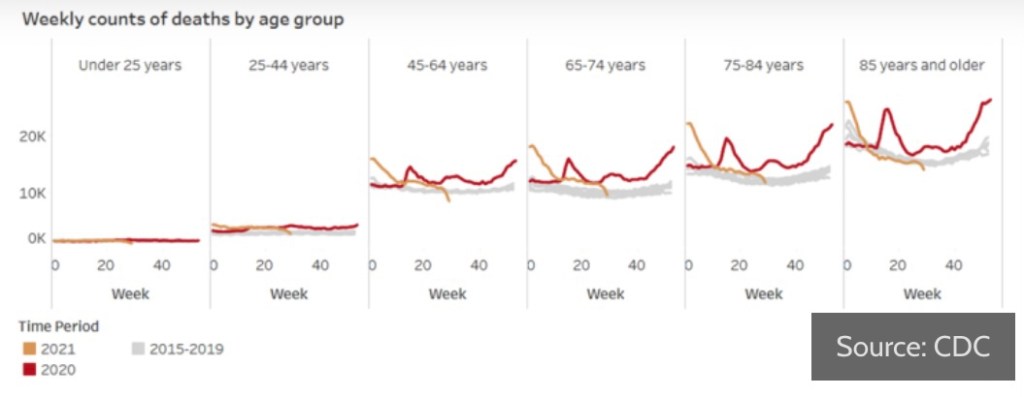
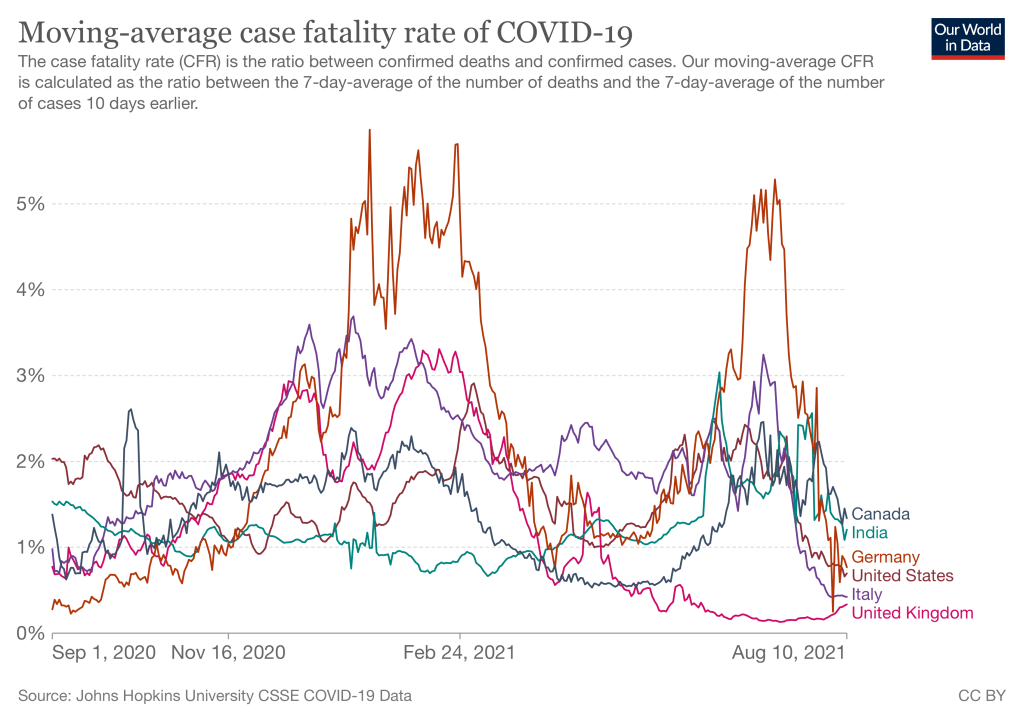
The vaccines are still effective. Data purporting to show otherwise fails to account for the most obvious of confounding influences: vaccination rates and age effects. In fact, the Biden Administration has made a rather arbitrary decision about the durability of vaccine effects by recommending booster shots after eight months. The highly transmissible Delta variant has struck quickly but the wave now shows signs of cresting, though that is no guarantee for the fall and winter season. However, Delta cases have been much less severe on average than earlier variants. Masks did nothing to protect us from those waves, and they won’t protect us now. I, for one, won’t wear one if I can avoid it.