Tags
Big Beautiful Bill, Budget Baseline, Budget Reconciliation, Congressional Budget Office, Deficit Reduction, DOGE, Dominic Pino, Donald Trump, Elon Musk, EV Subsidies, filibuster, Homeland Security, Mandatory Spending, Medicaid, No Tax On Overtime, No Tax On Tips, Rand Paul, SALT Deduction, Senior Deduction, Social Security, Supplemental Nutritional Assistance Program, Tax Cuts and Jobs Act

The GOP’s “Big Beautiful Bill” (BBB) has generated its share of controversy, not least between President Trump and his erstwhile ally Elon Musk. It is a budget reconciliation bill that was passed by a single vote in the House of Representatives. It’s now up to the Senate, which is sure to alter some of the bill’s provisions. That will require another vote in the House before it can head to Trump’s desk for a signature.
Slim But “Reconciled” Majority
As a reconciliation bill, the BBB is not subject to filibuster in the Senate, and only a simple majority is required for approval, not a 60% supermajority. Obviously, that’s why the GOP used the reconciliation process.
I hate big bills, primarily because they tend to provide cover for all sorts of legislative mischief and pork. However, the reconciliation process imposes limits on what kinds of budgetary changes can be included in a bill. A reconciliation bill can alter only mandatory spending programs like Medicaid and other entitlements, but not discretionary or non-mandatory spending. Social Security is an entitlement, but it would be off limits in a typical reconciliation bill (owing to an arcane rule). Reconciliation bills can also address changes in revenue and the debt limit.
The BBB includes provisions to reduce Medicaid outlays such as work requirements, denial of benefits to illegal aliens, and controls on fraud. These are projected to cut spending by nearly $700 billion. Of course, this is a controversial area, but efforts to impose better controls on entitlements are laudable.
Elon Musk criticized the bill’s failure to aggressively rein-in deficit spending, prompting what was probably his first public feud with Trump. At the time, it wasn’t clear whether Musk really understood the limits of reconciliation. If he had, he might at least have been mollified by the effort to tackle Medicaid waste and fraud. Entitlement programs like Medicaid are, after all, at the very root of our fiscal imbalances.
Extending Trump’s Tax Cuts
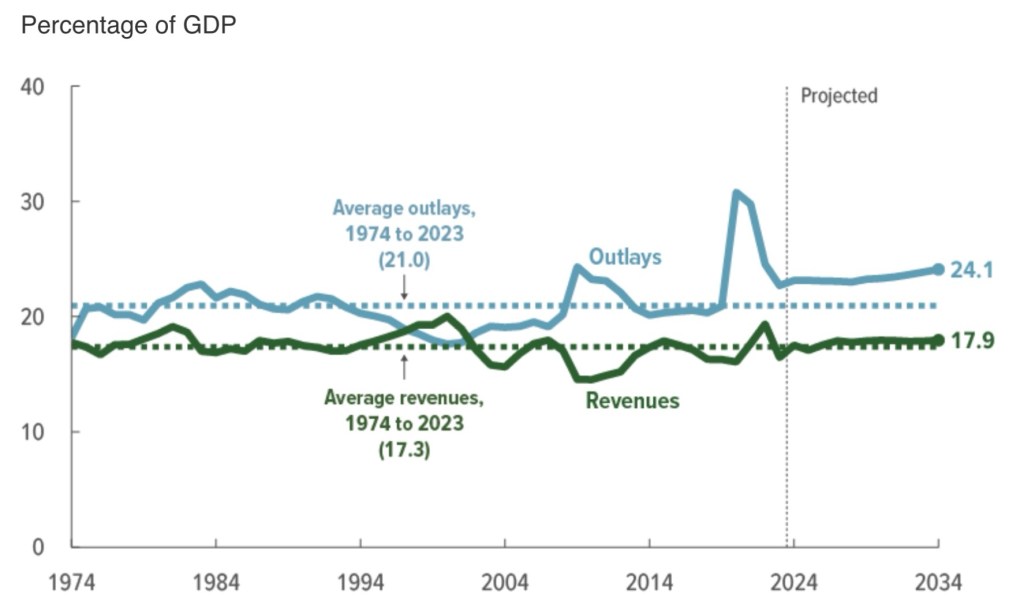
The Congressional Budget Office (CBO) says that BBB will reduce tax revenue by $3.8 trillion over the next ten years. The Trump tariffs are not addressed in the BBB, but those won’t come close to offsetting this projected revenue loss.
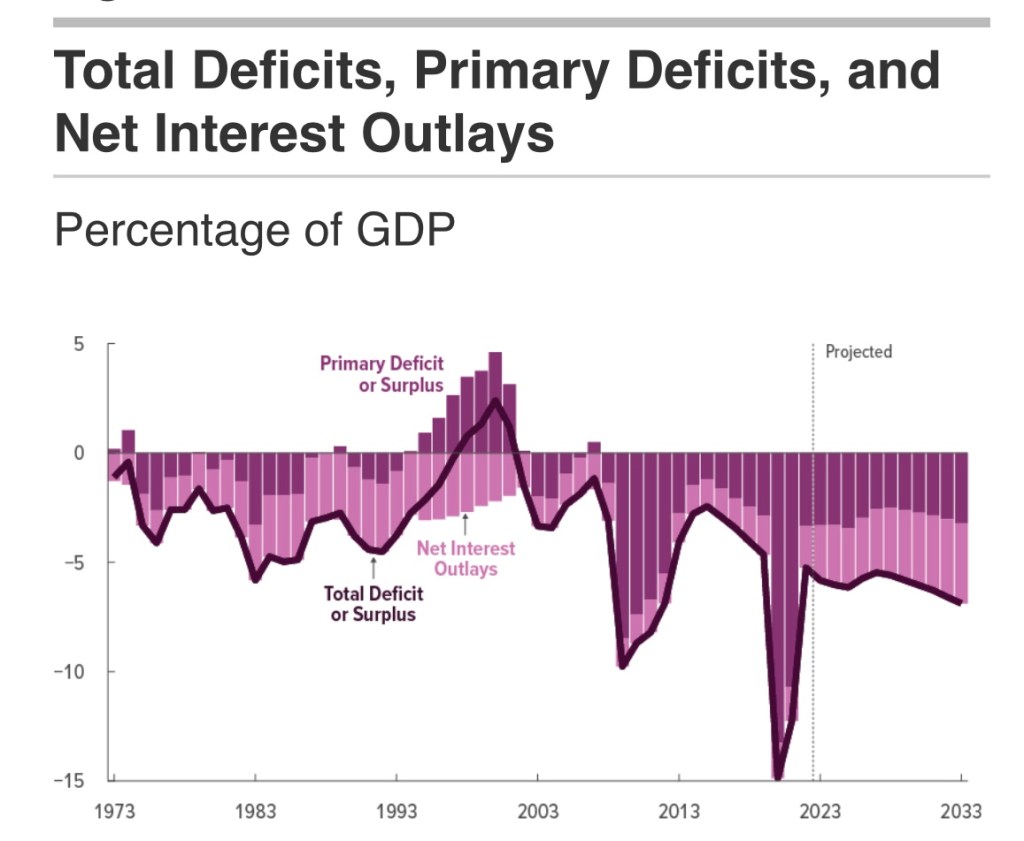
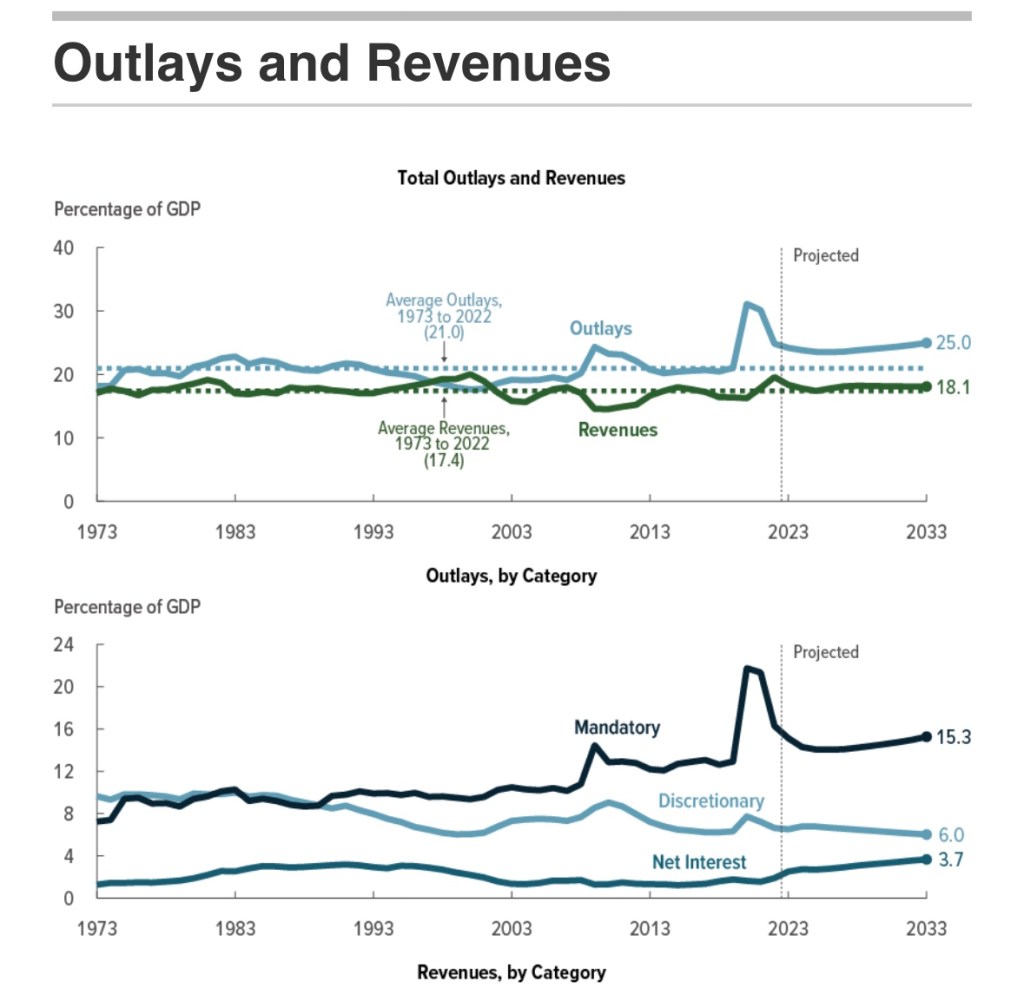
The CBO’s score compares spending and tax revenue to “current law”. Thus, the baseline assumes that the 2017 tax cuts under the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA) expire in 2026. With spending cuts under the BBB, primary federal deficits (non-interest) are projected to rise $2.4 billion over that time. With interest costs on the higher federal debt, the increase in deficits rises to about $3 trillion. I’ll briefly address some of the major provisions below, including their budget impacts.
Spending Cuts
In addition to Medicaid, other significant cuts in spending in the BBB include reductions in benefits under the Supplemental Nutritional Assistance Program (food stamps, -$267b). This includes tighter work requirements, eligibility rules, and higher matching requirements for states. Also included in BBB are more stringent student loan repayment rules and changes in other education funding programs (-$350b).
Other spending categories would increase. The bill would authorize an additional $144 billion for Armed Services and $79 billion for Homeland Security, including $50 billion for the border wall. Senator Rand Paul has called the border security provisions excessive, though many of those favoring greater fiscal discipline also believe defense is underfunded, so they probably don’t oppose these particular items.
Voting Tax Incentives
In terms of revenue, the BBB would extend the provisions of the TCJA. The deduction for state and local taxes (SALT) would be extended and increased to $40,000 at incomes less than $500,000. This would have a combined revenue impact of -$787 billion. No wonder deficit hawks are upset! A larger SALT deduction creates an even greater subsidy for states imposing high tax burdens on their residents. There’s an expectation, however, that this provision will be dialed back to some extent in the Senate version of the BBB.
There are also provisions to eliminate taxes on overtime (-$124b) and tip income (-$40b), and to increase the standard deduction for seniors (-$66b). As I’ve written before, these are all terribly distortionary policies. They would treat different kinds of income differently, create incentives to reclassify income, and impose a highly complex administrative burden on the IRS. The senior deduction creates an incremental revenue hole as a function of Social Security benefit payments. This is the wrong way to address the needs of a system that is insolvent. These policies were selected primarily with vote buying in mind.
The timing of some of these provisions differs. Some would expire after 2028, while others would be permanent. Apparently, the Senate version of the bill is likely to include immediate and permanent expensing of business investment, which would encourage economic growth.
Another notable change would eliminate subsidies and tax credits for EVs (+$191b). Some claim this was at the heart of Musk’s diatribes against the BBB. However, Musk has supported elimination of both EV subsidies and mandates for many years. He stated as much to legislators on Capital Hill last December, so this theory regarding Musk’s opposition to BBB doesn’t wash.
Defining a Baseline
Advocates of extending the TCJA say the CBO’s baseline case is inappropriate, and that the proper baseline should incorporate the continued tax provisions of the TCJA. Again, the extension increases the ten-year deficit by $3.8 trillion, but that total includes the revenue effects of other provisions. Perhaps $3 trillion might be a more accurate upward adjustment to baseline deficits. In that case, the BBB would actually reduce ten-year deficits by $0.2 trillion.
Another criticism is that the CBO does not attempt to estimate dynamic changes in revenue induced by policy. Those in support of extending the TCJA believe that this static treatment unfairly discounts the revenue potential of pro-growth policies.
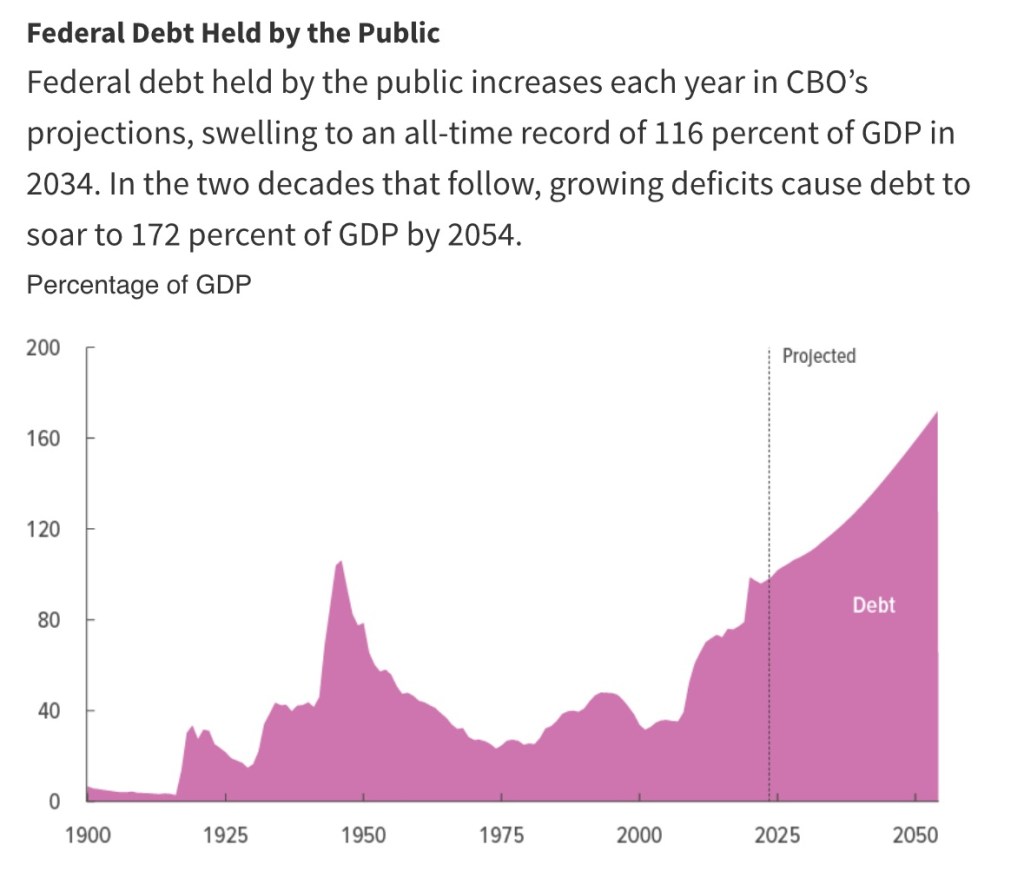
I don’t have a problem with the alternative baseline, but the fact is that deficits will still be problematic. Over the 2025-2034 time frame, a baseline incorporating an extension of TCJA would yield deficits in excess of $20 trillion. That includes mounting interest costs, which might overwhelm serious efforts at fiscal discipline in the unlucky event of an updraft in interest rates. Of course, these large, ongoing deficits raise the likelihood of inflationary pressure. The recent downgrade in the credit rating assigned to U.S. Treasuries by Moody’s is an acknowledgement that bondholder wealth could well be undermined by future attempts to “inflate away” the real value of the debt.
Debt Ceiling
In addition to its direct budgetary effects, the BBB calls for a $5 trillion increase of the federal debt limit. I admit to mixed feelings about this large increase in borrowing authority. Frequent debt limit negotiations tend to create lots of political theater and chew up scarce legislative time. Moreover, it’s easy to conclude that they usually accomplish little in terms of restraining deficit spending. Dominic Pino argues otherwise, citing historical examples in which the debt limit “was paired with” reforms and spending restraint. In other words, despite its apparent impotence, Pino asserts that deficits would have been much higher without it. I’m still skeptical, however, that frequent showdowns over the debt ceiling have much value given entitlements that are seemingly beyond legislative control. In the end, elected representatives must respect the judgement of credit markets and face consequences at the ballot box.
Final Thoughts on BBB
Superficially, the Big Beautiful Bill looks like an abomination to deficit hawks. The GOP decided to structure it as a reconciliation bill to strengthen its odds of passage. That decision sharply limited its potential for spending restraint. Other legislation will be required to make the kinds of rescissions necessary to eliminate wasteful spending identified by DOGE.
As for the bill itself, the effort to extend the 2017 Trump tax cuts was widely expected. That, in and of itself, is neutral with respect to a more reasonable baseline assumption. Elimination of EV tax subsidies is a big plus, as are the permanent incentives for business investment. Unfortunately, Trump and his congressional supporters also propose to create the additional fiscal burdens of no taxes on tips and overtime pay, as well as an increased standard deduction for seniors. The ill-advised increase in the SALT deduction was a compromise to ensure the support of certain blue-state republicans, but with any luck it will be curtailed by the Senate.
On the spending side, the big item is Medicaid. Reforms are long past due for a system so riddled with waste. In addition, there are new rules in the BBB that would reduce SNAP outlays and increase student loan repayments. Outlays for defense, Homeland Security, and border security would increase, but these were known to be Trump priorities. Too bad they’ve been paired with several wasteful tax policies.
But even with those flaws, the BBB would reduce deficits marginally relative to a baseline that incorporates extension of the TCJA. Yes, excessive ongoing deficits still have to be dealt with, but spending reductions on the discretionary side of the budget were out of the question this time due to reconciliation rules. They will have to come later, but that sort of legislation will face tough political headwinds, as will Social Security and Medicare reform. arever introduced.