Tags
Acquired Immunity, Aerosols, AstraZeneca, Border Control, Breakthrough Infections, Case Counts, Covid-19, Delta Variant, Endemicity, Herd Immunity, Hospitalizations, Immunity, Lockdowns, Mask Mandates, Oxford University, Paul Hunter, PCR Tests, School Closings, ScienceAlert, Sir Andrew Pollard, T-Cell Immunity, Transmissability, University of East Anglia, Vaccinations, Vaccine Hesitancy

My last post had a simple message about the meaning of immunity: you won’t get very sick or die from an infection to which you are immune, including COVID-19. Like any other airborne virus, that does NOT mean you won’t get it lodged in your eyeballs, sinuses, throat, or lungs. If you do, you are likely to test positive, though your immunity means the “case” is likely to be inconsequential.
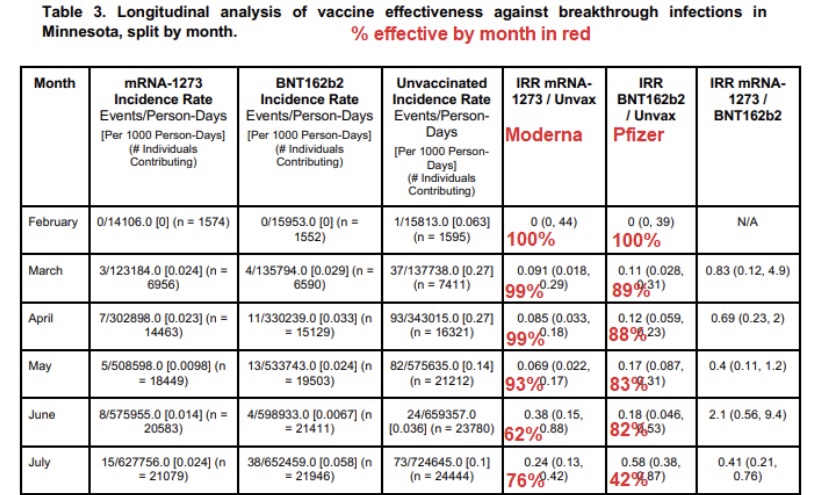
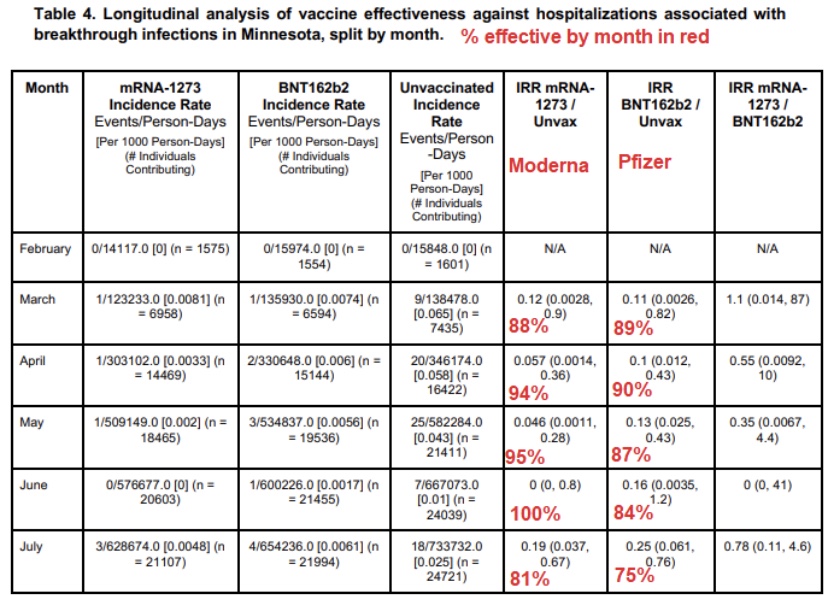
As noted in that last post, we’ve seen increasing COVID case counts with the so-called Delta variant, which is more highly transmissible than earlier variants. (This has been abetted by an uncontrolled southern border as well.) However, as we’d expect with a higher level of immunity in the population, the average severity of these cases is low relative to last year’s COVID waves. But then I saw this article in ScienceAlert quoting Sir Andrew Pollard, a scientist affiliated AstraZeneca and the University of Oxford. He says with Delta, herd immunity “is not a possibility” — everyone will get it.
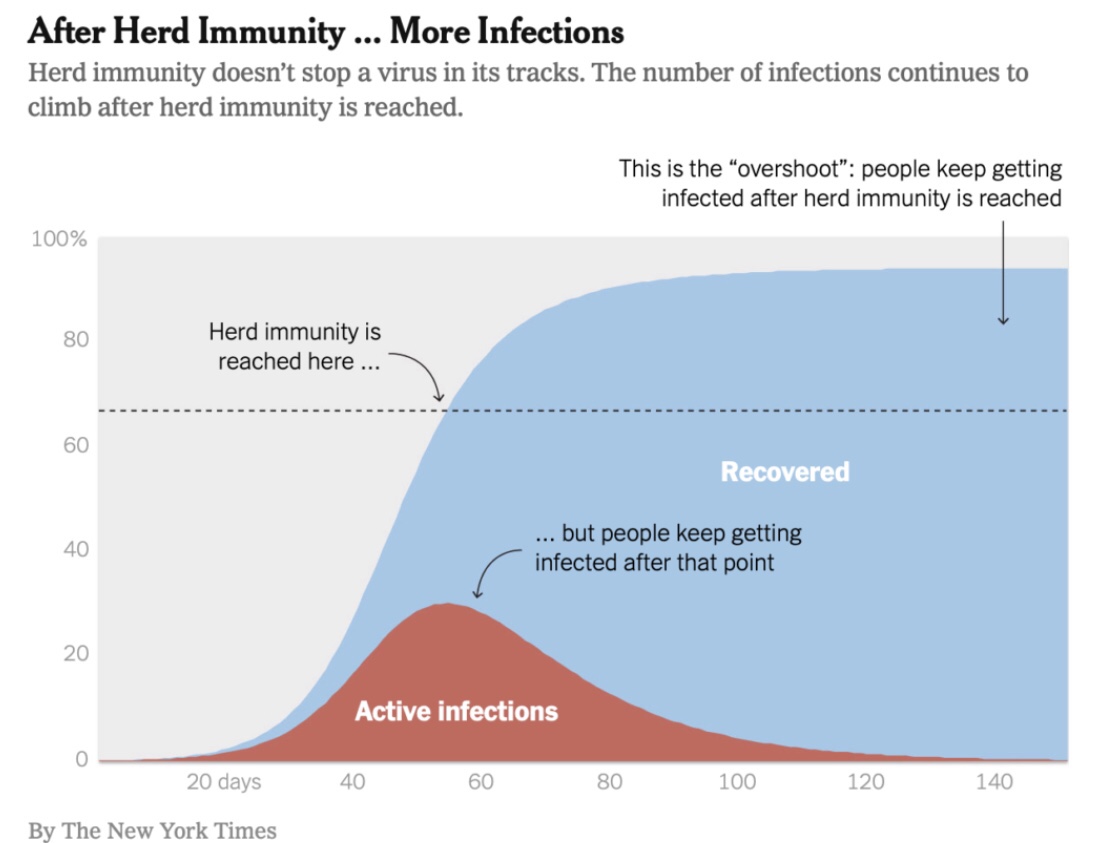
Maybe everyone will, but that doesn’t mean everyone will get sick. His statement raises an obvious question about the meaning of herd immunity. If our working definition of the term is that the virus simply disappears, then Pollard is correct: we know that COVID is endemic. But the only virus that we’ve ever completely eradicated is polio. Would Pollard say we’ve failed to achieve herd immunity against all other viruses? I doubt it. Endemicity and herd immunity are not mutually exclusive. The key to herd immunity is whether a virus does or does not remain a threat to the health of the population generally.
Active COVID infections will be relatively short-lived in individuals with “immunity”. Moreover, viral loads tend to be lower in immune individuals who happen to get infected. Therefore, the “infected immune” have less time and less virus with which to infect others. That creates resistance to further contagion and contributes to what we know as herd immunity. While immune individuals can “catch” the virus, they won’t get sick. Likewise, a large proportion of the herd can be immune and still catch the virus without getting sick. That is herd immunity.
One open and controversial question is whether uninfected individuals will require frequent revaccination to maintain their immunity. A further qualification has to do with asymptomatic breakthrough infections. Those individuals won’t see any reason to quarantine, and they may unwittingly transmit the virus.
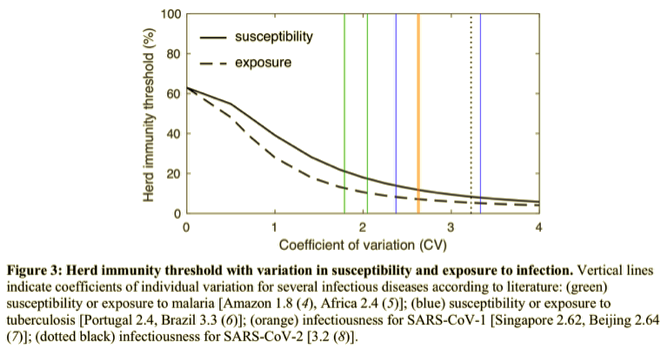
I also acknowledge that the concept of herd immunity is often discussed strictly in terms of transmission, or rather its failure. The more contagious a new virus, like the Delta variant, the more difficult it is to achieve herd immunity. Models predicting low herd immunity thresholds due to heterogeneity in the population are predicated on a given level of transmissibility. Those thresholds would be correspondingly higher given greater transmissibility.
A prominent scientist quoted in this article is Paul Hunter of the University of East Anglia. After backing-up Pollard’s dubious take on herd immunity, Hunter drops this bit of real wisdom:
“We need to move away from reporting infections to actually reporting the number of people who are ill. Otherwise we are going to be frightening ourselves with very high numbers that don’t translate into disease burden.”
Here, here! Ultimately, immunity has to do with the ability of our immune systems to fight infections. Vaccinations, acquired immunity from infections, and pre-existing immunity all reduce the severity of later infections. They are associated with reductions in transmission, but those immune responses are more basic to herd immunity than transmissability alone. Herd immunity does not mean that severe cases will never occur. In fact, more muted seasonal waves will come and go, inflicting illness on a limited number of vulnerables, but most people can live their lives normally while viral reproduction is contained. Herd immunity!
Sadly, we’re getting accustomed to hearing misstatements and bad information from public health officials on everything from mask mandates, lockdowns, and school closings to hospital capacity and vaccine hesitancy. Dr. Pollard’s latest musing is not unique in that respect. It’s almost as if these “experts” have become victims of their own flawed risk assessments insofar as their waning appeal to “the herd” is concerned. Professor Hunter’s follow-up is refreshing, however. Public health agencies should quit reporting case counts and instead report only patients who present serious symptoms, COVID ER visits, or hospitalizations.