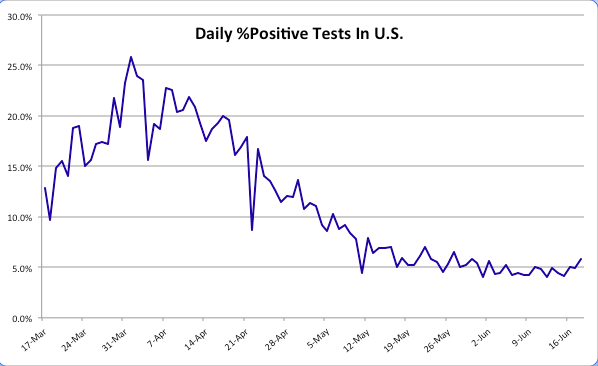
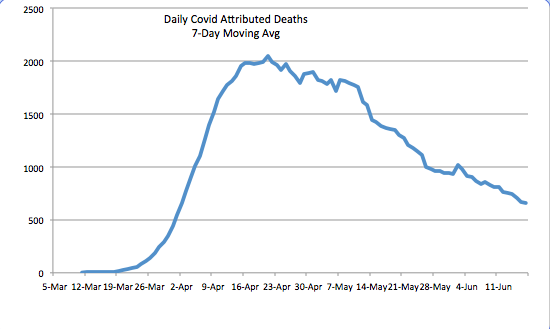
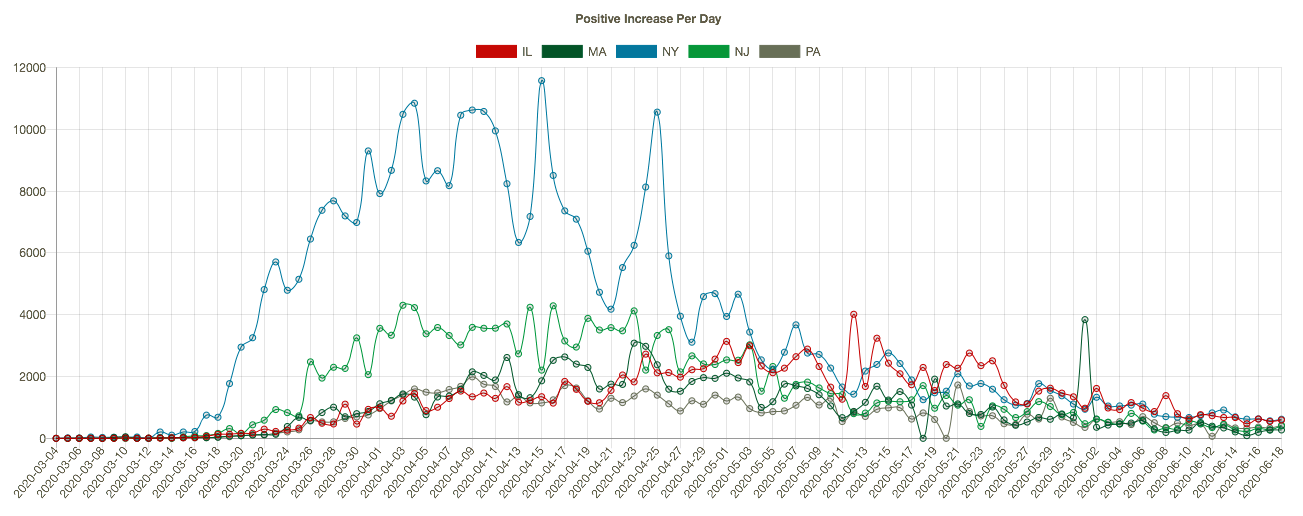
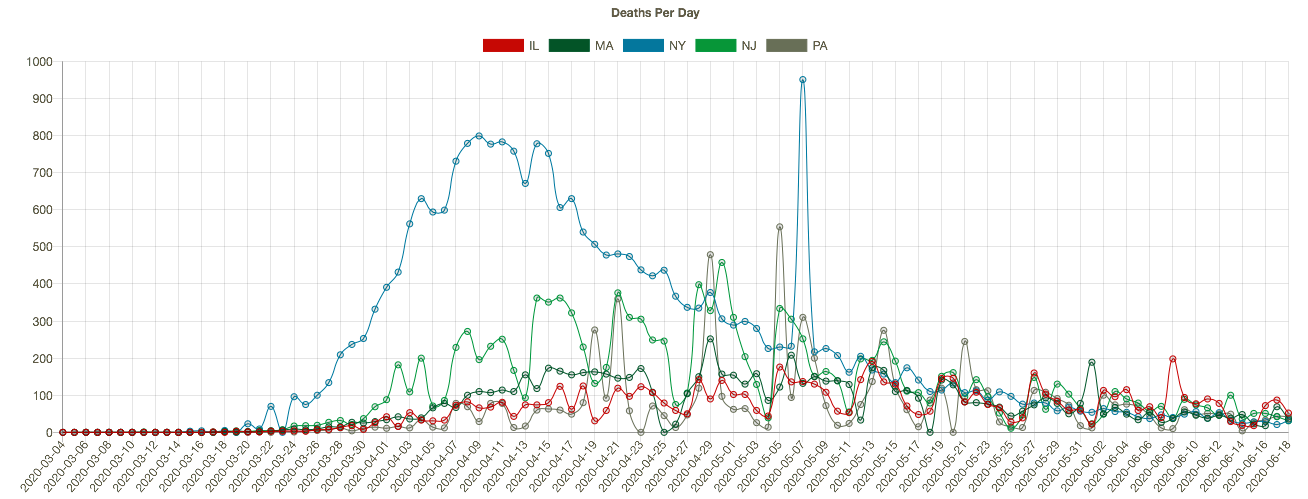
It’s a bit early to fully evaluate President Trump’s performance in dealing with the coronavirus pandemic, but there are a number of criteria on which I might assign marks. I’ll address some of those below, but in so doing I’m reminded of Jerry Garcia’s quip that he was “shopping around for something no one will like.” That might be how this goes. Of course, many of the sub-topics are worthy of lengthier treatment. The focus here is on the pandemic and not more general aspects of his performance in office, though there is some unavoidable overlap.
General “Readiness”
Many have criticized the Trump Administration for not being “ready” for a pandemic. I assign no grade on that basis because absolutely no one was ready, at least not in the West, so there is no sound premise for judgement. I also view the very general charge that Trump did not provide “leadership” as code for either “I don’t like him”, or “he refused to impose more authoritarian measures”, like a full-scale nationwide lockdown. Such is the over-prescriptive instinct of the Left.
Equally misleading is the allegation that Trump had “disbanded” the White House pandemic response team, and I have addressed that here. First, while the NSC would play a coordinating role, pandemic response is supposed to be the CDC’s job, when it isn’t too busy with diseases of social injustice to get it done. Second, it was John Bolton who executed a reorganization at the NSC. There were two high profile departures from the team in question at the time, and one one was a resignation. Most of the team’s staff remained with the NSC with the same duties as before the reirganization.
Finally, there was the matter of a distracting impeachment on false charges. This effort lasted through the first three years of Trump’s administration, finally culminating in January 2020. Perhaps the Administration would have had more time to focus on what was happening in China without the histrionics from the opposition party. So whatever else I might say below, these factors weigh toward leniency in my appraisal of Trump’s handing of the virus.
Messaging: C
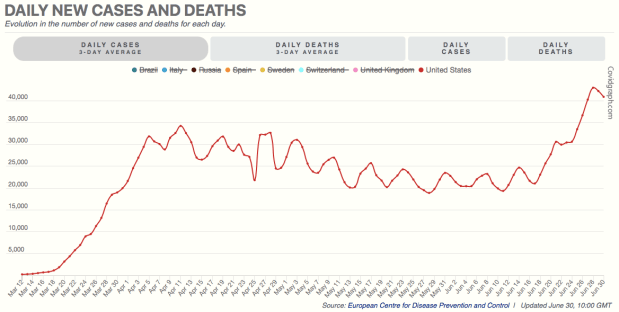
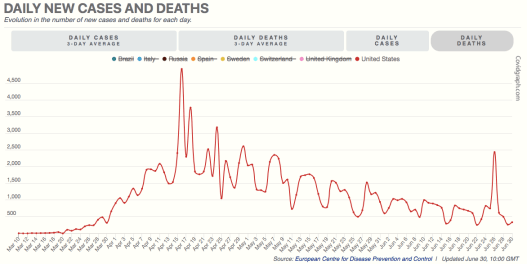
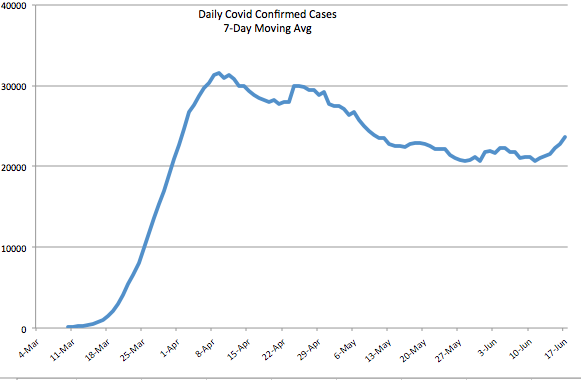
As usual, Trump’s messaging during the pandemic was often boorish and inarticulate. His appearances at coronavirus briefings were no exception, often cringeworthy and sometimes featuring misinterpretations of what his team of experts was saying. He was inconsistent in signaling optimism and pessimism, as were many others such as New York Governor Andrew Cuomo and New York City Mayor Bill De Blasio. It shifted from “the virus is about like the flu” in February to a more sober assessment by mid-March. This was, however, quite consistent with the messaging from Dr. Anthony Fauci over the same time frame, as well as the World Health Organization (WHO). Again, no one really knew what to expect, so it’s understandable. A great deal of that can be ascribed to “the fog of war”.
Delegation and Deference: B
Trump cannot be accused of ignoring expert advice through the episode. He was obviously on-board with Fauci, Dr. Deborah Birx, Dr. Robert Redfield, and other health care advisors on the “15 Days to Slow the Spread” guidelines issued on March 16. His messaging wavered during those 15 days, expressing a desire to fully reopen the nation by Easter, which Vice President Michael Pence later described as “aspirational”. Before the end of March, however, Trump went along with a 30-day extension of the guidelines. Finally, by mid-April, the White House released guidelines for “Opening Up America Again“, which was a collaboration between Trump’s health care experts and the economic team. Trump agreed that the timeline for reopening should be governed by “the data”. There is no question, however, that Trump was chomping at the bit for reopening at several stages of this process. I see value in that positioning, as it conveys an intent to reopen asap and that people should have confidence in progress toward that goal.
International Travel Bans: A
If anyone wonders why the world was so thoroughly blindsided by the coronavirus, look no further than China’s failure to deliver a proper warning as 2019 drew to a close. Wuhan, China was ground zero; the virus spread to the rest of the world with travelers out of Wuhan and other Chinese cities. The White House announced severe restrictions on flights from China on January 31, including a two-week quarantine for returning U.S. citizens. In retrospect, it wasn’t a minute too soon, yet for that precaution, Trump was attacked as a racist by the Left. In early February, WHO actually said travel bans were unnecessary, among other missteps. Other bans were instituted on entry from Iran and Brazil, as well as entry from Europe in early March, as countries around the globe closed their borders. Trump’s actions on incoming travelers were prescient, so I’ll score this one for Trump. Some of these travel restrictions can and should be eased now, and certainly that is expected in coming months, so we’ll see how well that process is managed.
Deference to States: A-
As a federalist, I was pleased that Trump and his team left most of the specifics on closures and bans on public gatherings up to state and local governments. That allowed more targeted mitigation efforts as dictated by local conditions and, to some extent, public opinion. This is a classic case of “laboratory federalism” whereby the most effective policies can be identified, though as we’ve seen, there’s no guarantee less successful states will emulate them. I grade Trump well on this one.
On reopening, too, Trump has been a consistent advocate of allowing flexility where local conditions permit, though he wrongly claimed he had “total authority” over ending social distancing rules. It’s hard to square that remark with his general stand on the issue of autonomy except as a tactic to strong-arm certain governors on other points.
CDC/FDA Snafus: D
I applaud the Administration for its emphasis on the salutary effects of deregulation, but Trump went along with some major pieces of “expert advice” that were not only poor from regulatory perspective, but an affront to federalism. One was a directive issued by the CDC to delay “all elective surgeries, non-essential medical, surgical, and dental procedures during the 2019 Novel Coronavirus (COVID-19) outbreak“. (See my post “Suspending Medical Care in the Name of Public Health“.)
This is exactly the kind of “one size fits all” regulatory policy that has proven so costly, sacrificing not just economic activity but lives and care for the sick, creating avoidable illnesses and complications. The idea was to assure that adequate health care resources were available to treat an onslaught of coronavirus patients, but that was unneeded in most jurisdictions. And while the contagion was in it’s early “exponential” phase at the time, a more nuanced approach could have been adopted to allow different geographic areas and facilities more discretion, especially for different kinds of patients, or perhaps something less than a complete suspension of care. In any case, the extensions into May were excessive. I must grade Trump poorly for allowing this to happen, despite what must have been extreme pressure to follow “expert advice” on the point and the others discussed earlier.
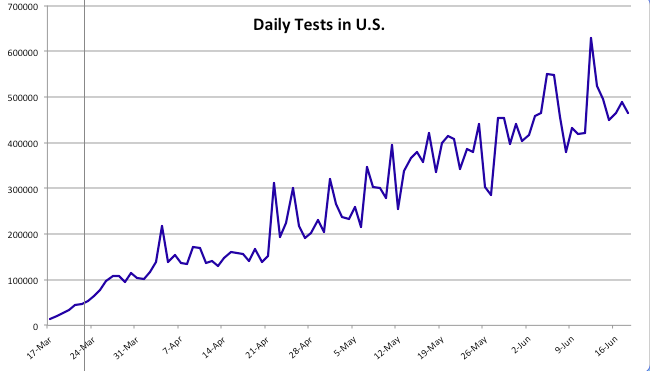
That’s not the only point on which I blame Trump for caving to the CDC. In a case of massive regulatory failure, the CDC and FDA put the U.S. well over a month behind on testing when the first signs of the virus appeared here. Not only did they prohibit private labs and universities from getting testing underway, insisting on exclusive use of the CDC’s own tests, they also distributed faulty tests in early February that took over a month to replace. The FDA also enforced barriers to imported N95-type masks during the pandemic. Trump tends to have a visceral understanding of the calcifying dangers of regulation, but he let the so-called “experts” call the shots here. Big mistake, and Trump shares the blame with these agencies.
Health Resources: B-
Managing the emergency distribution of PPE and ventilators to states did not go as smoothly as might have been hoped. The shortage itself left FEMA with the unenviable task of allocating quantities that could never satisfy all demands. A few states were thought to have especially acute needs, but there was also an obligation to hold stockpiles against potential requests from other states. In fact, a situation of this kind creates an incentive for states to overstate their real needs, and there are indications that such was the case. Trump sparred with a few governors over these allocations. There is certainly blame to be shared, but I won’t grade Trump down for this.
Vaccines and Treatments: C+
The push to develop vaccines might not achieve success soon, if ever, but a huge effort is underway. Trump gets some of the credit for that, as well as the investment in capacity now to produce future vaccine candidates in large quantities. As for treatments, he was very excited about the promise of hydroxychloraquine, going so far as to take it himself with zinc, a combination for which no fully randomized trial results have been reported (the recent study appearing in the Lancet on HCQ taken by itself has been called into question). Trump also committed an unfortunate gaffe when the DHS announced the results of a study showing that sunlight kills coronavirus in a matter of minutes, as do bleach and other disinfectants. Trump mused that perhaps sunlight or some form of disinfectant could be used as a treatment for coronavirus patients. He might have been thinking about an old and controversial practice whereby blood is exposed to UV light and then returned to the body. Later, he said he used the term “disinfectant” sarcastically, but he probably meant to say “euphemistically” …. I’m not sure he knows the difference. In any case, his habit of speculating on such matters is often unhelpful, and he loses points for that.
Fiscal Policy: B
The several phases of the economic stimulus program were a collaboration between the Trump Administration and Congress. A reasonably good summary appears here. The major parts were the $2.3 trillion CARES Act in late March and a nearly $500 billion supplemental package in late April. These packages were unprecedented in size. Major provisions were direct cash payments and the Paycheck Protection Program (PPP), which provides loans and grants to small businesses. The execution of both was a bit clunky, especially PPP, which placed a burden on private banks to extend the loans but was sketchy in terms of qualifications. The extension of unemployment compensation left some workers with more benefits than they earned in their former jobs, which could be an impediment to reopening. There were a number of other reasonable measures in these packages and the two smaller bills that preceded them in March. A number of these measures were well-targeted and inventive, such as waiving early withdrawal penalties from IRA and 401(k) balances. The Trump Administration deserves credit for helping to shape these efforts as well as others taken independently by the executive branch.
Trump’s proposal to suspend payroll taxes did not fly, at least not yet. The idea is to reduce the cost of hiring and increase the return to work, if only temporarily. This is not a particularly appealing idea because so much of the benefits would flow to those who haven’t lost their jobs. It could be improved if targeted at new hires and rehires, however.
Trump’s proposal to grant liability waivers to reopened private businesses is extremely contentious, but one I support. Lockdowns are being eased under the weight of often heavy public and private regulation of conduct. As John Cochrane says in “Get Ready for the Careful Economy“:
“One worry on regulation is that it will provide a recipe for a wave of lawsuits. That may have been a reason the Administration tried to hold back CDC guidance. A long, expensive, and impractical list of things you must do to reopen is catnip when someone gets sick and wants to blame a business. Show us the records that you wiped down the bathrooms every half hour. A legal system that can sue over talcum powder is not above this.”
Indeed, potential liability might represent a staggering cost to many businesses, one that might not be insurable. Accusations of negligence, true or false, can carry significant legal costs. Customers and employees, not just businesses, must accept some of the burden of risks of doing business. I give Trump good marks for this one, but we’ll see if it goes anywhere.
Some of the proposals for new stimulus legislation from democrats are much worse, including diversity initiatives, massive subsidies for “green” technologies, and bailouts for state and local government for unfunded pension liabilities. None of these has anything to do with the virus. The burden of pension shortfalls in some states should not fall on taxpayers nationwide, but on the states that incurred them. The Trump Administration and congressional Republicans should continue resisting these opportunistic proposals.
The Grade
Without assigning weights to the sub-topics covered above, I’d put the overall grade for Trump and his Administration’s handling of matters during the pandemic at about a B-, thus far. When it comes to politics, it’s often unfair to credit or blame one side for the promulgation of an overall set of policies. Nevertheless, I think it’s fair to say that Trump, could have done much better and could have done much worse. We will learn more with the passage of time, the continued evolution of the virus, the development of treatments or vaccines, and the course of the economy.