Tags
@Humble_Analysis (PLC), CLI, COVID Vaccines, Covid-19, COVID-Like Illness, Date of Death, False Positives, Herd Immunity, ILI, Influenza-Like Illness, Justin Hart, PCR Tests, Reported Deaths
My pre-Thanksgiving optimism about a crest in the fall wave of the coronavirus has been borne out for the Midwest and Mountain states in the U.S. These regions were the epicenter of the fall wave through October and most of November, but new cases in those states have continued to decline. Cases in a number of other states began to climb in November, however, contributing to a continuing rise in total new cases nationally. Some of these states are still in the throes of this wave, with the virus impacting subsets of the population that were relatively unscathed up till now.
My disclaimer: COVID is obviously a nasty virus. I don’t want to get it. However, on the whole, it is not a cataclysm on the order of many pandemics of the past. In fact, excess deaths this year will add just over 10% to projections of total deaths based on a five-year average. That level puts us in line with average annual deaths of about twenty years ago. And many of those excess deaths have been caused by our overreaction to the pandemic, not by the virus itself. As my endocrinologist has said, this is the greatest overreaction in all medical history. Unfortunately, a fading pandemic does not mean we can expect an end to the undue panic, or pretense for panic, on the part of interventionists.
This post will focus largely on trends in newly diagnosed COVID cases. I have been highly critical of our testing regime and COVID case counts because the most prominent diagnostic test (PCR) falsely identifies a large number of uninfected individuals as COVID-positive. However, case numbers are widely tracked and it’s fairly easy to find information across geographies for comparison. Deflate all the numbers by 30% if you want, or by any other factor, but please indulge me because I think the trends are meaningful, even if the absolute level of cases is inflated.
I’ll start with the good news and work my way down to states in which cases are still climbing (all of the following charts are from @Humble_Analysis (PLC)). The first chart is for the Great Plains, where cases peaked a little before Thanksgiving and have continued to fall since then. That peak came about six weeks after it began in earnest and cases have faded over the last four weeks.
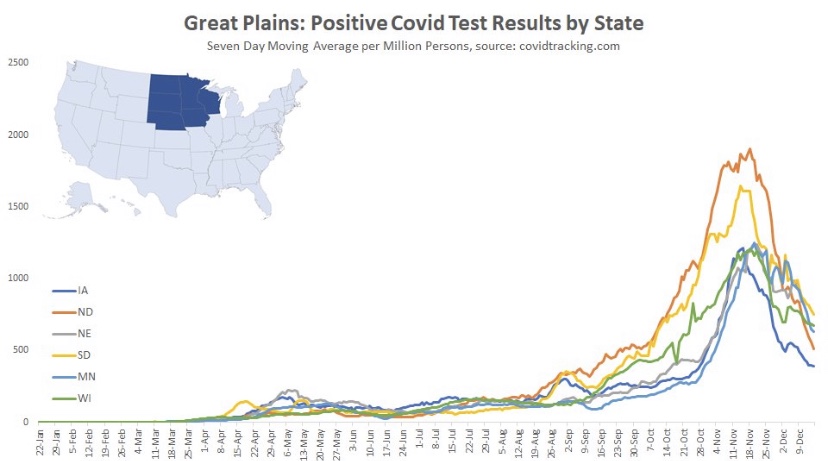
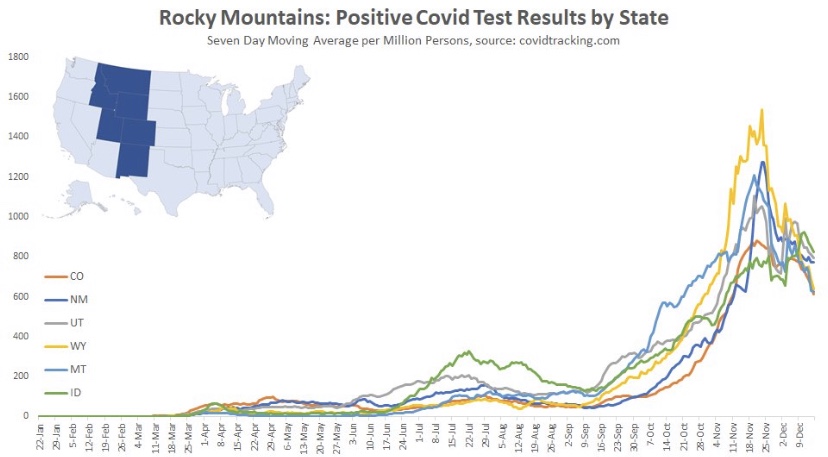
Next we have the Mountain states, where again, cases peaked around Thanksgiving, though Idaho saw a rebound after the holiday. You’ll see below that a number of states had a distinct drop in new cases during the week of Thanksgiving. There was somewhat of a pause in testing during that week, so the subsequent rebounds are largely due to a “catch-up” at testing sites, rather than some kind of Thanksgiving-induced spike in infections.
Back to the Mountain region, the peak came an average of about six or seven weeks into the wave, but the duration of the wave appears to have been longer in Montana and Wyoming.
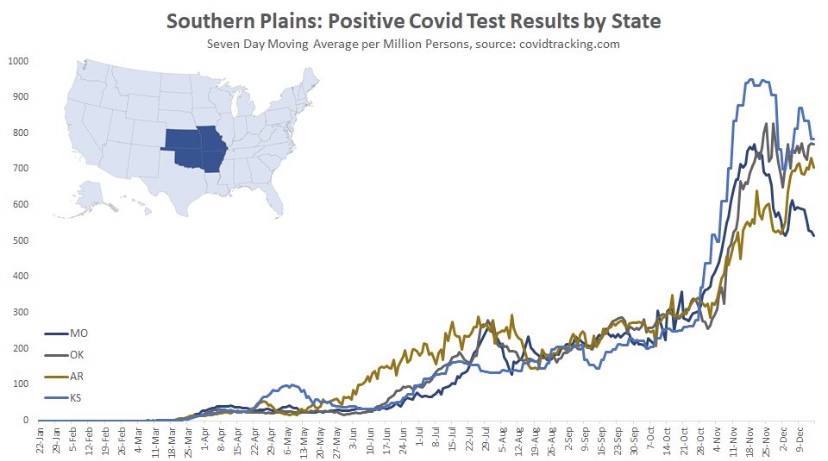
Here are the Southern Plain states, where cases plateaued around Thanksgiving (though cases in Missouri have clearly declined from their peak). In this region, case counts accelerated in October after a slow climb over the summer.
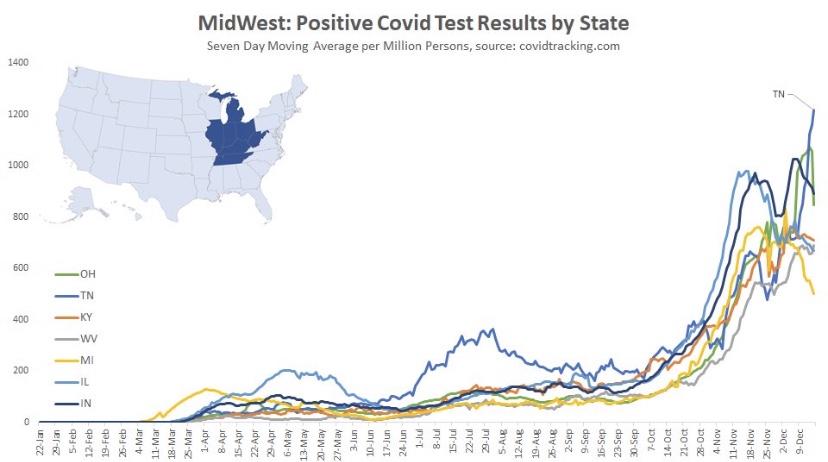
The situation is somewhat similar in the Midwest. where cases have generally plateaued. There were some post-Thanksgiving rebounds in several states, especially Tennessee. The wave began a little later in this region, in mid- to late October, and it is now seven to eight weeks into the wave, on average.
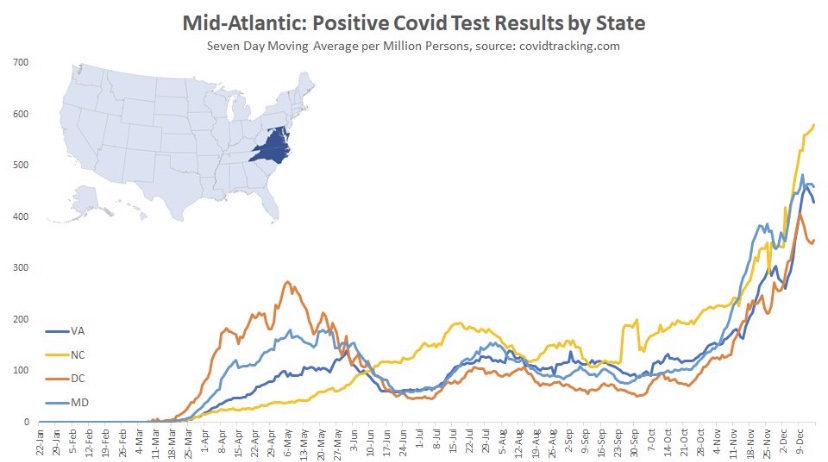
Here are the Mid-Atlantic states, which may be showing signs of a peak, though North Carolina has had the greatest caseload and is still climbing. These states are about seven weeks into the wave, on average.
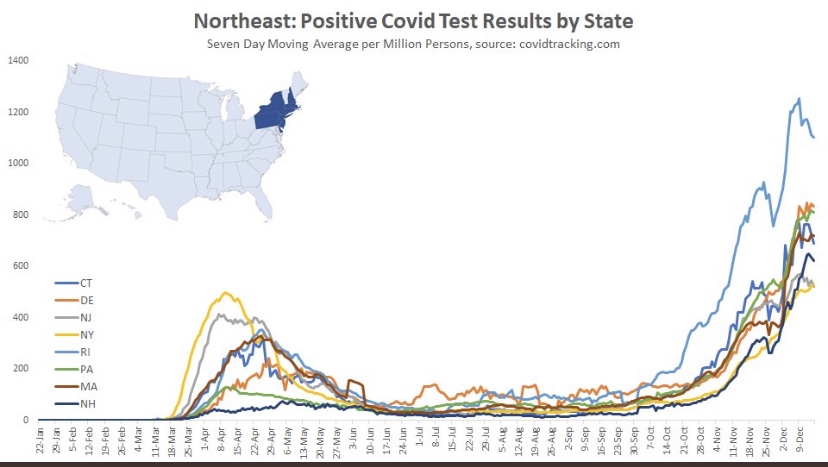
The Northeast also shows signs of a possible peak and is about seven weeks into the wave, except for Rhode Island, which saw an earlier onset and the most severe wave among these states.
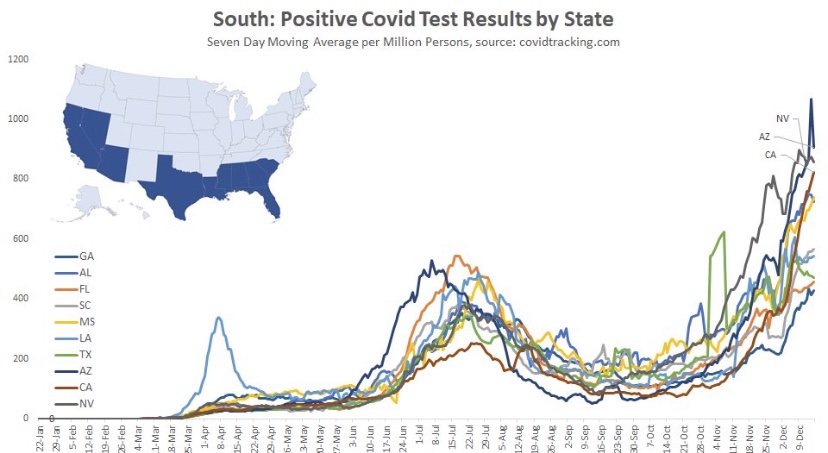
And finally we have the South, which is defined quite broadly in PLC’s construction. It’s a mixed bag, with a few states showing signs of a peak after about seven weeks. However, cases are still climbing in several states, notably California and Florida, among a few others.
Oregon and Washington were skipped, but they appear as the Pacific NW in the following chart, along with aggregations for all the other regions. Maine is Part of the “Rural NE”, which was also skipped. The fall wave can be grouped roughly into two sets of regions: those in which waves began in late September or early October, and those where waves began in early to mid-November. The first group has moved beyond a peak or at least has plateaued. The latter group may be reaching peaks now or one hopes very soon. It seems to take about seven weeks to reach the peak of these regional waves, so a late December peak for the latter group would be consistent.
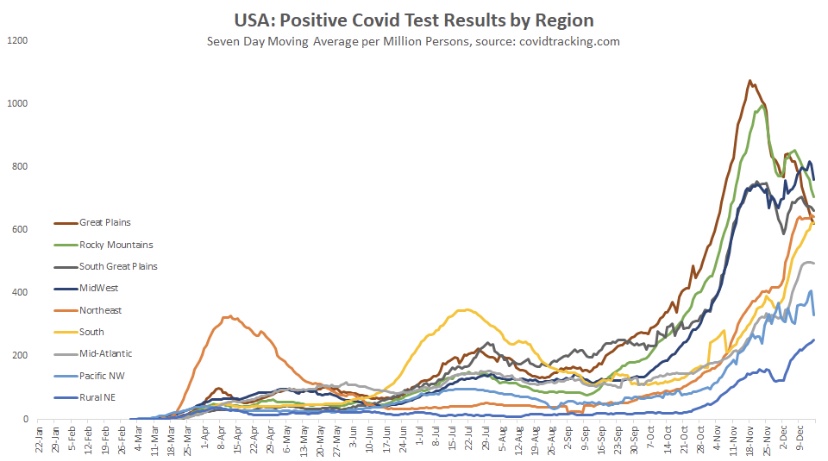
Justin Hart has a take on the duration of these waves, but he does so in terms of the share of emergency room (ER) visits in which symptoms of COVID-like illness (CLI) are presented. CLI tends to precede case counts slightly. Hart puts the duration of these waves at eight to ten weeks, but that’s a judgement call, and I might put it a bit longer using caseloads as a guide. Still, this color-coded chart from Hart is interesting.
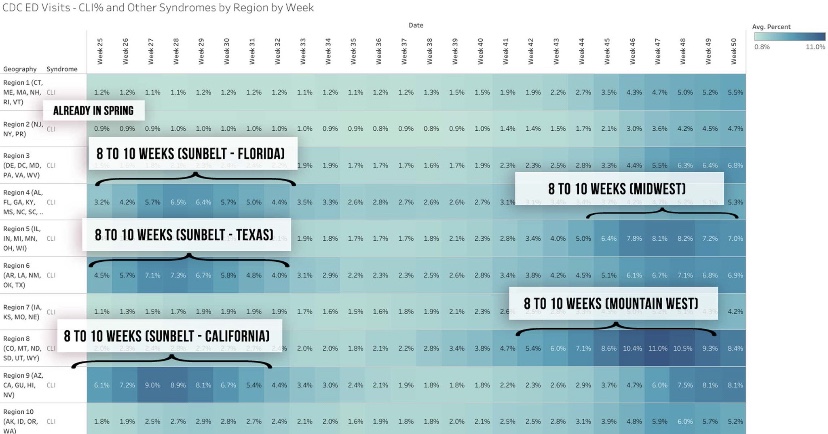
If this sort of cyclical duration holds up, it’s consistent with the view that cases in many of the still “hot” states should be peaking this month.
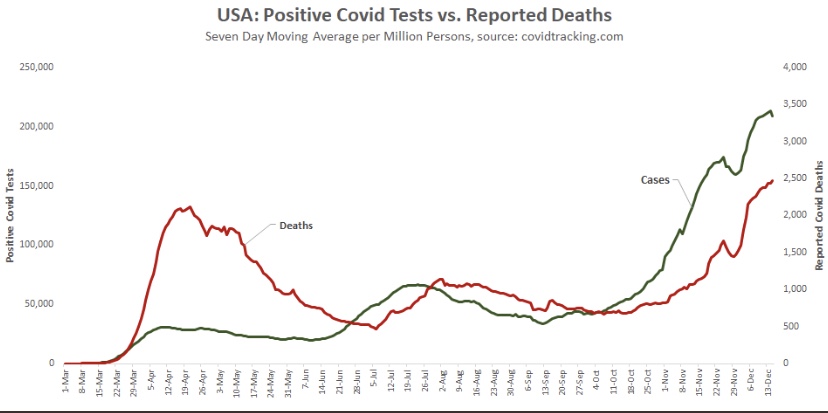
Aggregate cases for the U.S. appear below. The growth rate of new cases has slowed, and the peak is likely to occur soon. However, because it combines all of the regional waves, the duration of the wave nationwide will appear to be greater than for the individual regions. COVID-attributed deaths are also plotted, but they are reported deaths, not by date of death (DOD) or actual deaths, as I sometimes call them. Deaths by DOD are available only with a lag. As always, some of the reported deaths shown below occurred weeks before their reported date. Actual deaths were still rising as of late November, and are likely still rising. However, another indicator suggests they should be close to a peak.
A leading indicator of actual deaths I’ve discussed in the past now shows a more definitive improvement than it did just after Thanksgiving, as the next chart shows. This is the CLI share discussed above. An even better predictor of COVID deaths by actual DOD is the sum of CLI and the share of ER patients presenting symptoms of influenza-like illness (ILI), but ILI has been fairly low and stable, so it isn’t contributing much to changes in trend at the moment. There has been about a three-week lead between movements in CLI+ILI and COVID deaths by DOD.
(The reason the sum, CLI+ILI, has been a better predictor than CLI alone is because for some individuals, there are similarities in the symptoms of COVID and the flu.)
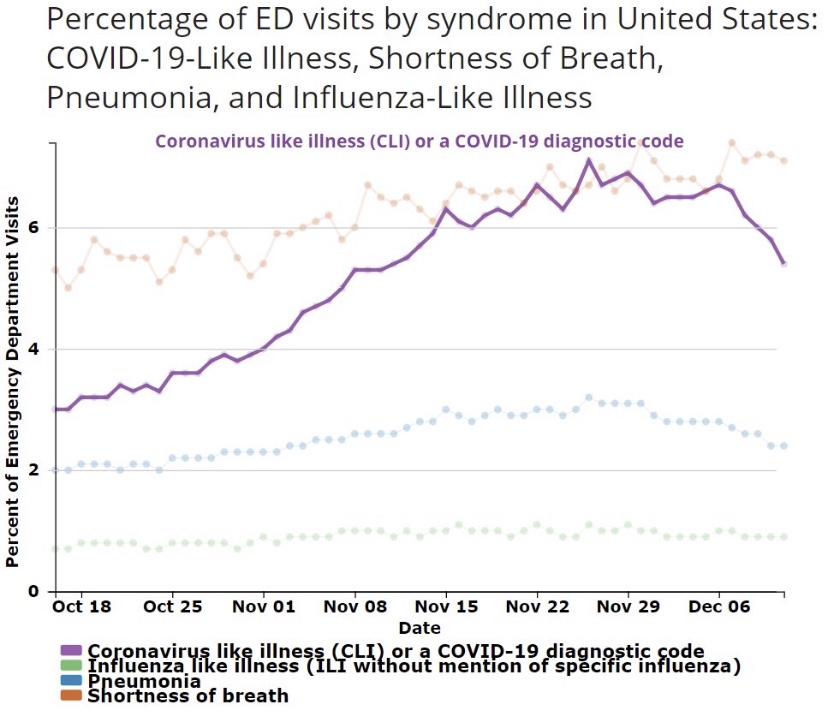
The chart shows that CLI peaked right around the Thanksgiving holiday (and so did CLI+ILI), but it remained on something of a plateau through the first week of December before declining. Some of the last few days on this chart are subject to revision, but the recent trend is encouraging. Allowing for a three-week lead, this indicates that peak deaths by DOD should occur around mid-December, but we won’t know exactly until early to mid-January. To be conservative, we might say the latter half of December will mark the peak in actual deaths.
The regional COVID waves this summer and fall seem to have run their course within 10 – 12 weeks. Several former hot spots have seen cases drop since Thanksgiving after surges of six to seven weeks. However, there are several other regions with populous states where the fall wave is still close to “mid-cycle”, as it were, showing signs of possible peaks after roughly seven weeks of rising cases. The national CLI share peaked around Thanksgiving, but it did not give up much ground until early December. That suggests that actual deaths (as opposed to reported deaths), at least in some regions, will peak around the time of the winter solstice. Let’s hope it’s sooner.
Successive waves within a region seem to reach particular subsets of the population with relatively few reinfections. The 10 – 12 week cycle discussed above is sufficient to achieve an effective herd immunity within these subsets. But once again, a large share of the vulnerable, and a large share of COVID deaths, are still concentrated in the elderly, high-risk population and in care homes. The vaccine(s) currently being administered to residents of those homes are likely to hasten the decline in COVID deaths beginning sometime in January, perhaps as early as mid-month. By then, however, we should already see a decline underway as this wave of the virus finally burns itself out. As vaccines reach a larger share of the population through the winter and spring, the likelihood of additional severe waves of the virus will diminish.
Lest there be any misunderstanding, the reasons for the contagion’s fade to come have mostly to do with reaching the effective herd immunity threshold within afflicted subsets of the population (sub-herds). Social distancing certainly plays a role as well. Nearly all of that is voluntary, though it has been encouraged by panicked pronouncement by certain public officials and the media. Direct interventions or lockdown measures are in general counter-productive, however, and they create a death toll of their own. Unfortunately, the fading pandemic might not rein-in the curtailment of basic liberties we’ve witnessed this year.
Post-Script: Let’s hope the side effects of the vaccines are not particularly severe in the elderly. That’s a little uncertain, because that sub-population was not tested in very high numbers.